Figure 7.
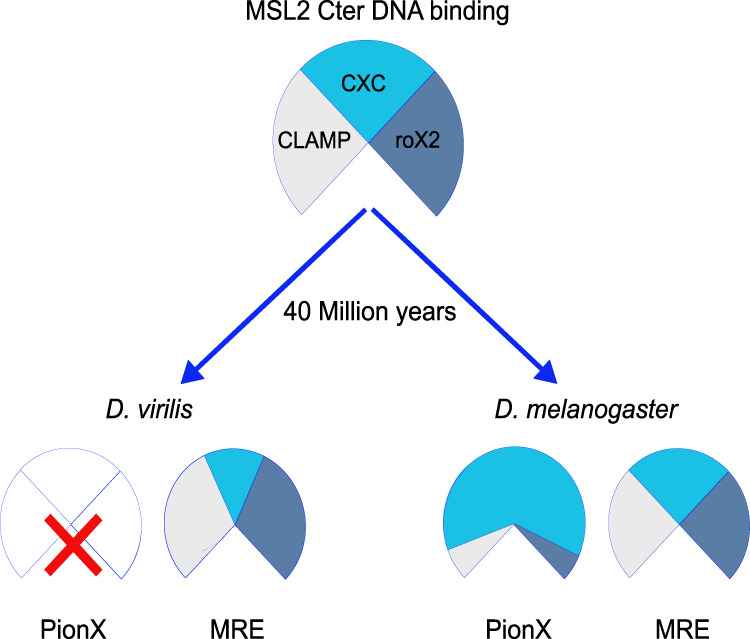
Model. Species-specific ways to achieve X-chromosome specificity in dosage compensation. The CXC domain of MSL2, the CLAMP protein, and the roX2 lnc RNA are conserved factors involved in the targeting of the DCC to the X chromosome both in D. virilis and in D. melanogaster, two species that diverged 40 million years ago. The X chromosome of D. virilis is not marked by PionX motifs, and the binding of the CXC domain of MSL2 to DNA (MREs) relies on CLAMP cooperativity and on roX2 modulation to achieve X specificity. In D. melanogaster, the coevolution of PionX sites enriched on the X chromosome, together with the ability of the CXC domain of MSL2 to specifically recognize them, endows MSL2 with direct X-chromosome selectivity. The cooperative interaction with CLAMP and roX2 RNA contributes to recognition of non-PionX MREs.
