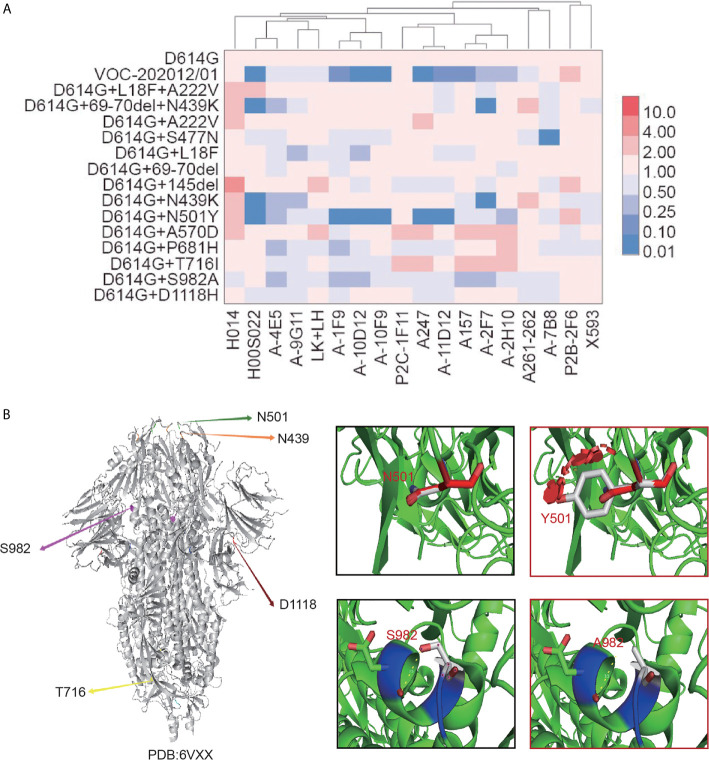
Figure 2.
The neutralization activity of mAbs against 16 SARS-CoV-2 variants and mutations. (A) Monoclonal antibodies were serially diluted and mixed with equal amounts of the five different SARS-CoV-2 variants and those containing a single mutation. After pre-incubation at 37°C for 1 h, trypsinized Huh 7 cells were added. After cultivation for 24 h, the luminescence of the target cells was measured. The neutralization inhibition rate of the antibody and ID50 was calculated using the Reed–Muench method. The data represent the ID50 ratio of each variant to that of D614G. The neutralization ability of 19 different monoclonal antibodies (x axis) against 16 SARS-CoV-2 variants and mutations (y axis) are shown as heatmap. Red represents an increase in neutralization capacity, while blue represents a decrease in neutralization capacity. Four-fold changes were considered statistically significant. (B) Structure modeling of the mutation N501Y in S1 and S982A in S2 based on “6VXX”.