Figure 2.
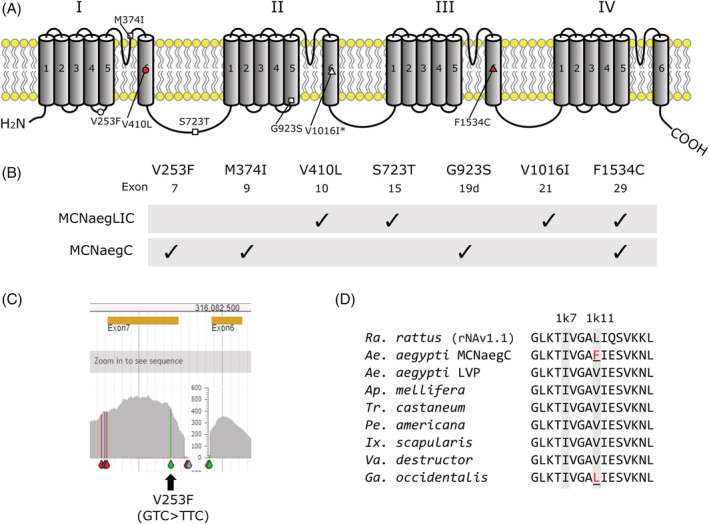
(A) Mapping of the amino‐acid substitutions discovered in haplotypes of the MCNaeg‐LIC and MCNaeg‐C sub‐colonies to the VGSC protein. Triangle and circles points indicate residues consisting of pyrethroid receptors 1 and 2, respectively, according to the dual‐receptor model by Du et al. 4 , 5 Rectangle points indicate residues with no known association with insecticide resistance. Filled points indicate known resistance substitutions with evidence from electrophysiological studies. V1016I annotated by an asterisk has been shown to enhance pyrethroid insensitivity mediated by F1534C. 11 (B) Amino‐acid substitutions in each VGSC haplotype. The exon in which each substituting mutation resides is indicated. (C) NGS read mapping view for a MCNaeg‐C individual in exon 7 of VGSC (chromosome III), including the V253F substation. (D) An alignment of the IL45 linker region of the sodium channel in the rat Rattus rattus rNAv1.1 (NP_110502), and Ae. aegypti Liverpool (LVP) and MCNaeg‐C (LC557527) strains, the bee Apis mellifera (XP_006561583.1), the beetle Tribolium castaneum (XP_015837360.1), the cockroach Periplaneta americana (ACX44801.1), the tick Ixodes scapuraris (EEC03677.1), the mite Varroa destructor (XP_022662766.1), and the mite Galendromus (Metaseiulus) occidentalis (XP_028966827.1). Two pyrethroid‐sensing residues, 1 k7 and 1 k11 (according to Du et al. 4 ), are highlighted.
