FIGURE 2.
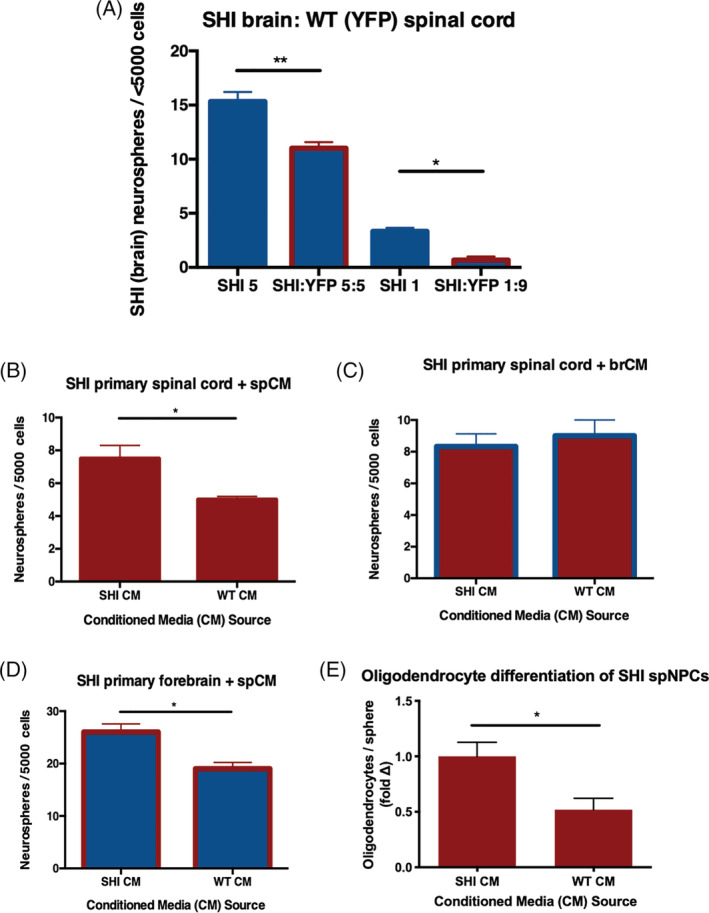
Myelin basic protein (MBP) interacts with the spinal cord niche to release an inhibitory factor that inhibits proliferation and oligodendrocyte differentiation of forebrain and spinal cord neural stem cells (NSCs). A, MBP in primary spinal cord cultures from YFP+ mice leads to reduced numbers of SHI forebrain (YFP‐negative) neurospheres in cocultures (n = 3 independent experiments per condition). B, SHI‐derived spinal cord NSCs cultures generate decreased numbers of neurospheres in the presence of littermate wild‐type (WT) spCM compared to SHI spCM (n = 3 independent experiments). C, SHI‐derived spNSCs form comparable numbers of neurospheres in both SHI brCM and WT brCM (n = 3 independent experiments); blue outline on bars indicates the presence of brCM. D, SHI‐derived brNSCs are similarly impaired in neurosphere formation when exposed to WT spCM compared to SHI spCM (n = 3 independent experiments); red outline on bars indicates the presence of spCM. E, SHI‐derived spinal cord neurospheres generate fewer oligodendrocytes in the presence of littermate WT spCM compared to SHI spCM (P = .0102).; n ≥ 7 neurospheres per group. Data are represented as means ± SEM. Statistics: A, One‐way ANOVA; B‐E, t tests. *P < .05, **P < .01
