Figure 1.
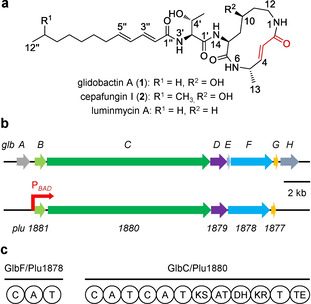
Select GLNP structures, BGC, and domain organization. a) Structures of glidobactin A and related natural products. The functional α,β‐unsaturated carbonyl group is marked red. b) BGC of glidobactins from Burkholderia K481‐B101 (glbA−H) and P. laumondii (plu1881–1877). Homologous genes are shown in identical colors. The putative functions of glbA−H in encoding proteins are as follows: GlbA: regulator, GlbB: lysine 4‐hydroxylase, GlbC: hybrid NRPS‐PKS, GlbD: transporter, GlbE: MbtH‐like protein, GlbF: NRPS, GlbG and GlbH: unknown. The position where the natural promoter in plu1881–1877 is exchanged with the arabinose‐inducible promoter PBAD is shown by a red arrow. c) Domain organization of the NRPS and hybrid NRPS‐PKS encoded by code biosynthetic genes glbF/plu1878 and glbC/plu1880, respectively. Domains: C: condensation, A: adenylation, T: thiolation, KS: ketosynthase, AT: acyltransferase, DH: dehydratase, KR: ketoreductase, TE: thioesterase.
