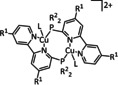
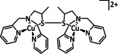
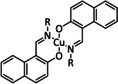
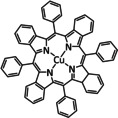
Table 11.
Catalytic systems, major products, maximum FEs, and mechanisms of Cu and Zn complexes in electrochemical CO2 reduction (n.a.=not available, prop.=proposal, comp.=computational investigation, exp.=experimental evidence).
|
Entry |
Cat. system |
Substitution |
Major product |
Max. FE (%) |
Mechanism |
Basis |
Method |
Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
1 |
CuCl2 + PPh3 (in situ) |
– |
CO HCO2H H2C2O4 |
73 (combined) |
n.a. |
n.a. |
n.a. |
|
|
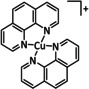
2 |
|
L=MeCN, py R1=H, Me, tBu R2=iPr, Ph |
CO/CO3 2− |
n.a. |
ETM |
exp. [332] |
IL, IR‐SEC |
|
|
3 |
|
– |
C2O4 2− |
96 |
ETM |
exp. |
MS, XRD |
|
|
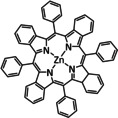
4 |
|
R=octyl, dodecyl |
n.a. |
n.a. |
n.a. |
n.a. |
n.a. |
|
|
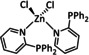
5 |
|
– |
CO [335] CH4 [336] H2 [336] |
48 7 90 |
n.a. |
n.a. |
n.a. |
|
|
6 |
|
– |
CO HCO2H |
78 31 |
ETM |
exp. comp. |
IR‐SEC DFT |
|
|
7 |
|
– |
CO |
33 |
n.a. |
n.a. |
n.a. |
|
|
8 |
|
– |
CO |
n.a. |
ETM |
prop. |
n.a. |