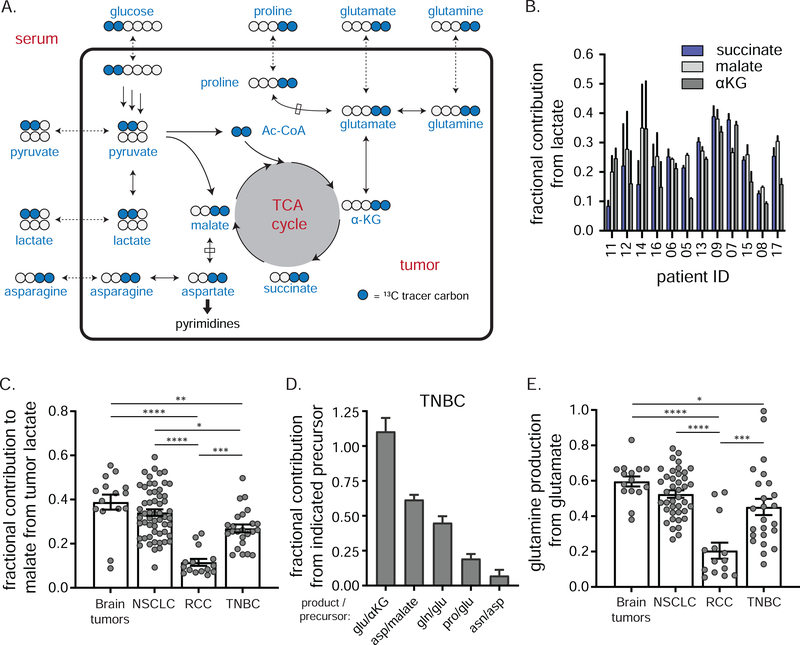
Figure 6. Glucose carbon makes TCA intermediates and associated amino acids in TNBC.
a) Pathways from circulating [1,2-13C]glucose to M+2 TCA intermediates and associated amino acids. Blue circles represent 13C. Glucose, pyruvate, lactate, glutamine, glutamate, proline and asparagine can exchange between the systemic circulation and tumor. b) Fractional carbon labeling of tumor succinate, malate, and α-ketoglutarate (αKG) to that of tumor lactate (mean ± SEM, n = 2 biopsies per patient). c) Fractional carbon labeling of tumor malate to that of tumor lactate in the indicated cancers (mean ± SEM, each point represents a single tumor sample of several collected from each of 5 (brain), 30 (NSCLC), 5 (RCC) or 12 (TNBC) patients, one-way ANOVA w/ Tukey’s correction). d) Fractional carbon labeling of indicated tumor amino acid relative to that of respective metabolic precursor in TNBC (mean ± SEM, n = 12 patients, 2 technical replicates per patient). e) Fractional carbon labeling of tumor glutamine relative to that of tumor glutamate in indicated cancers (mean ± SEM, each point represents a single tumor sample of several collected from each of 5 (brain), 30 (NSCLC), 5 (RCC) or 12 (TNBC) patients, one-way ANOVA w/ Tukey’s correction). Three fragments (two from NSCLC, one from RCC) where ratios exceeded 1 were removed as outliers. * = p < 0.05, ** = p < 0.01, *** = p < 0.001, **** = p < 0.0001. See also Figure S6.