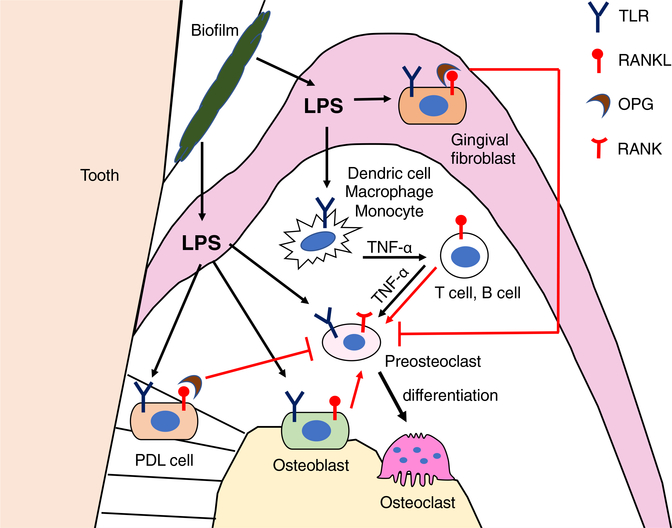
FIGURE 6.
Regulation of bone resorption in periodontal disease. Lipopolysaccharide (LPS) originates from bacteria in the oral biofilm. LPS initiates osteoclastogenesis upon binding toll-like receptor (TLR) that is expressed on dendritic cells, macrophages, monocytes, osteoblasts, PDL cells, and gingival fibroblasts. Osteoblasts produce RANKL in response to LPS stimulation. RANKL and TNF-α secretion by B cells and T cells are induced by TNF-α produced by dendritic cells, macrophages and monocytes. Osteoclast differentiation is enhanced either by continuous exposure to RANKL, TNF-α, or both, while OPG secreted form gingival fibroblasts and PDL cells inhibit osteoclast differentiation. The direct interaction of LPS with preosteoclasts through TLR also promotes osteoclast differentiation