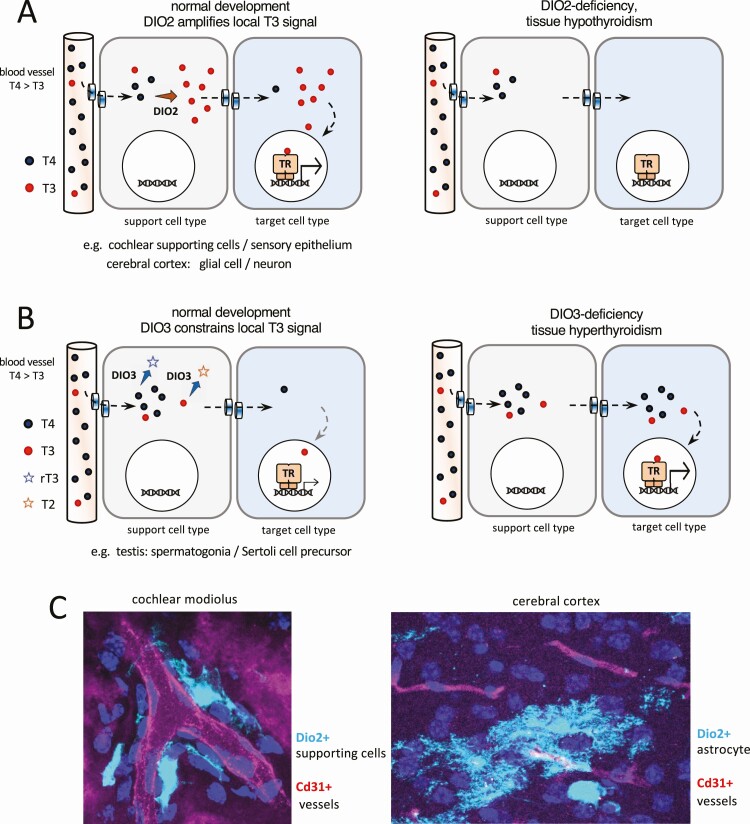
Figure 3.
Conceptual diagrams of paracrine-like control of 3,5,3′-triiodothyronine (T3) action by type 2 deiodinase (DIO2) and type 3 deiodinase (DIO3) within a tissue. A, DIO2+ cell types close to capillaries take up thyroxine (T4) from the circulation, convert T4 to T3, then transfer T3 to neighboring, T3-responsive cell types. Examples are found in the cochlea and cerebrum. B, DIO3+ support cell types deplete T4 and T3, thereby constraining the T3 signal available for other response cell types. An example is found in the testis. Transplasma membrane transport of T4 and T3 by specific transporter proteins is an integral part of the models shown in panels A and B. C, Images of DIO2+ support cells (pale blue) in proximity to blood vessels (red): specifically DIO2+ supporting cells in the cochlea and DIO2+ astrocytes in the cerebral cortex (images are the authors’ own work using a Dio2cre knockin; manuscript in preparation). TR, thyroid hormone receptor in the nucleus of target cells.