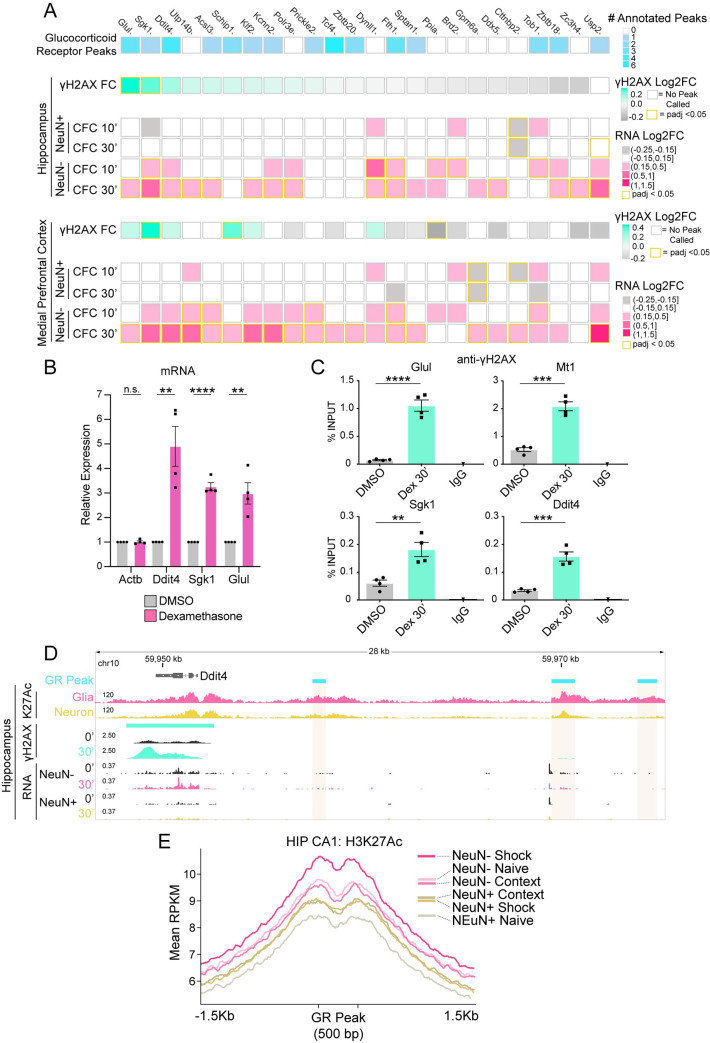
Fig 4. Glucocorticoid-regulated genes are sites of DNA double-strand breaks.
(A) Heatmap of γH2AX peaks occurring at genes upregulated specifically in non-neuronal nuclei. Top, number of glucocorticoid receptor binding sites annotated per gene (rat cortical ChIP-Seq) [55, 56]. γH2AX Log2FC and upregulated genes for HIP and mPFC after CFC. (B) RT-qPCR analysis of mRNA induction in mouse glial primary cultures 2 hours after treatment with glucocorticoid receptor agonist dexamethasone (100nM). N = 4 independent cultures; two-tailed unpaired student’s t-test; **P ≤ 0.01; *** P ≤ 0.001; **** P <0.0001; Mean ± SEM. (C) ChIP-qPCR analysis of γH2AX induction at select gene bodies in mouse glial primary cultures 30 minutes after treatment with dexamethasone (Dex) (100nM). N = 4 independent cultures; two-tailed unpaired student’s t-test; **P ≤ 0.01; *** P ≤ 0.001; **** P <0.0001; Mean ± SEM. (D) Genome browser snapshot of the gene Ddit4. Top, glucocorticoid receptor binding sites (‘GR Peak’; rat cortical ChIP-Seq) [55, 56], hippocampal region CA1 H3K27ac ChIP-Seq from NeuN+ or NeuN- isolated nuclei 1 Hour after CFC (‘K27Ac’) [57], γH2AX LogLR signal tracks, and nuclear RNA-Seq. (E) Average H3K27ac signal at glucocorticoid receptor binding sites (rat cortical ChIP-Seq) [55, 56] containing the GR motif in mouse (n = 5591 peaks). H3K27ac ChIP-Seq of mouse hippocampal CA1 region from NeuN+ or NeuN- isolated nuclei 1 hour after exposure to context, or CFC (‘shock’) [57]. Colored bars represent the apex of each condition.