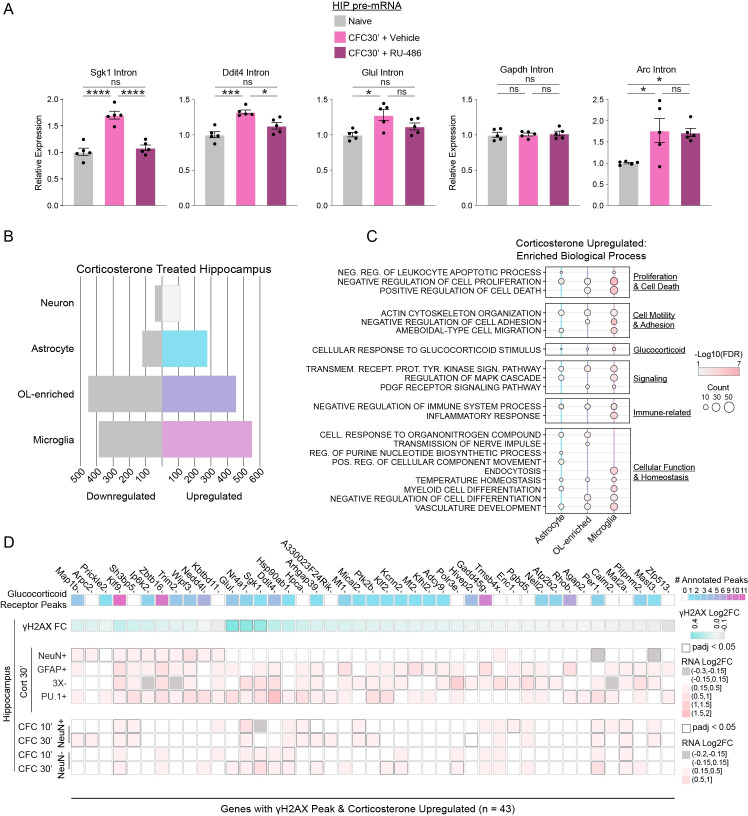
Fig 5. Glia, not neurons, have a robust transcriptional response to corticosterone.
(A) Pretreatment with glucocorticoid receptor antagonist RU-486 (Mifepristone) blocks CFC-induced gene expression in hippocampus. Pretreatment with vehicle (1% v/v Tween 80 in saline) or 50 mg/kg RU-486 IP occurred 30 minutes prior to CFC. qRT-PCR analysis of pre-mRNA with intronic primer and normalized to Hprt. cDNA was primed with random hexamers. N = 5 mice per group; one-way ANOVA with Tukey’s multiple comparisons test. (B) Number of corticosterone upregulated and downregulated genes from RNA-Seq of FACS-isolated nuclei from hippocampal cell types 30 minutes after saline or corticosterone:HBC complex (2mg/Kg) treatment. Cutoff padj < 0.05. (C) Twenty-one representative top enriched biological processes for the upregulated genes in purified hippocampal nuclei from astrocytes, microglia, and oligodendrocyte-enriched after corticosterone treatment (276, 453, and 551 genes respectively; padj < 0.05). Summary categories representing each grouped list of GOs is listed on the right. No enrichment of processes at threshold padj < 0.05 with the 112 upregulated genes in neuronal nuclei. Over-representation analysis with gene ontology (GO) category “Biological Process.” (D) Heatmap of 43 γH2AX peaks at genes upregulated in FACS-isolated neurons and glia following corticosterone treatment. From top: number of glucocorticoid receptor (GC) binding sites annotated per gene (rat cortical ChIP-Seq) [55, 56], γH2AX Log2FC in HIP after CFC, corticosterone-induced genes in NeuN+, GFAP+, PU.1+, and oligodendrocyte-enriched (3X-; NeuN-GFAP-PU.1-) hippocampal nuclear RNA-Seq 30 minutes after corticosterone treatment, and HIP RNA-Seq after CFC.