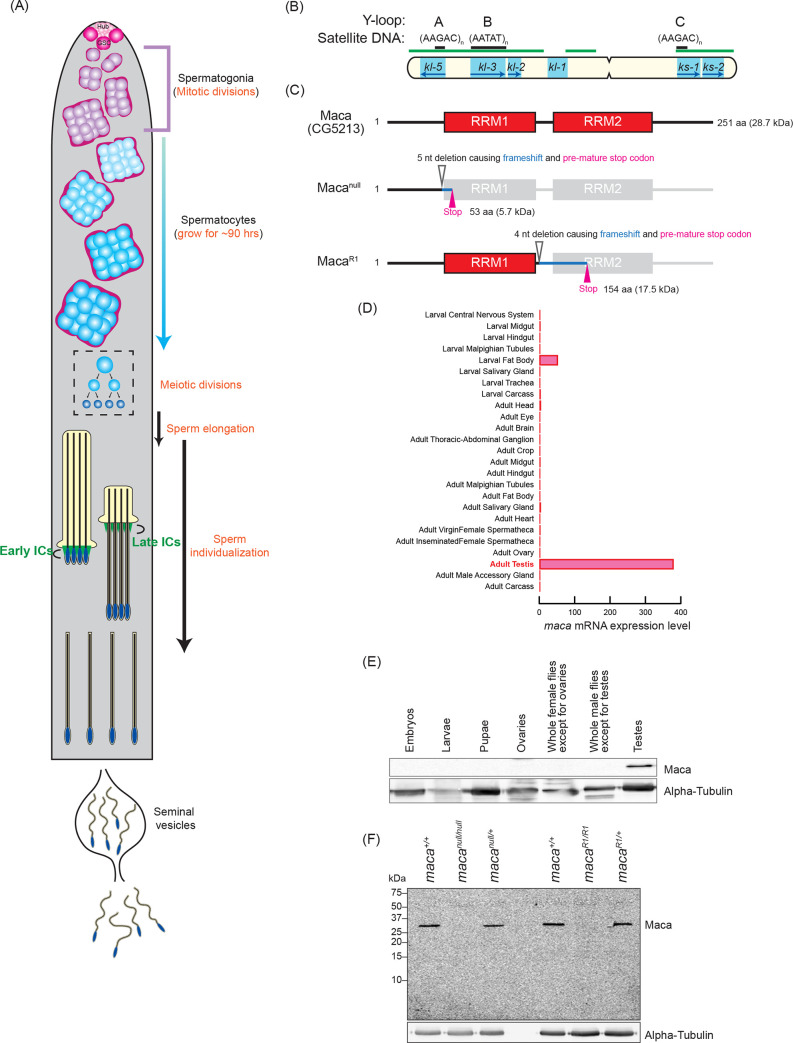
Fig 1. Maca domain structure, mutant alleles, and expression pattern.
(A) Diagram of spermatogenesis in Drosophila testis. At the apical tip of testis, germline stem cells (GSCs) are attached to the hub cells (Hub). GSCs produce daughter cell gonialblasts, which become mitotically-amplifying spermatogonia that then become spermatocytes. Spermatocytes grow in size for ~90 hours and then undergo the meiotic divisions to become 64 interconnected spermatids, which are then separated into individual spermatids by individualization complexes (ICs). Individualized mature motile sperm are stored in seminal vesicles. (B) Diagram of the Drosophila Y chromosome. Locations of the 6 male fertility factor genes (cyan. The transcription directions of the encoded genes are indicated by blue arrows), regions enriched for satellite DNA (green bars), and the Y-loop forming regions (black bars) with associated satellite DNA sequences are shown. (C) Domain structures of Drosophila Maca (Maca/CG5213), and its mutants, Macanull and MacaR1. (D) maca mRNA expression pattern. Data are obtained from http://flybase.org/reports/FBgn0038345. (E) Western blots of dissected fly tissues. (F) Western blots of testis lysates.