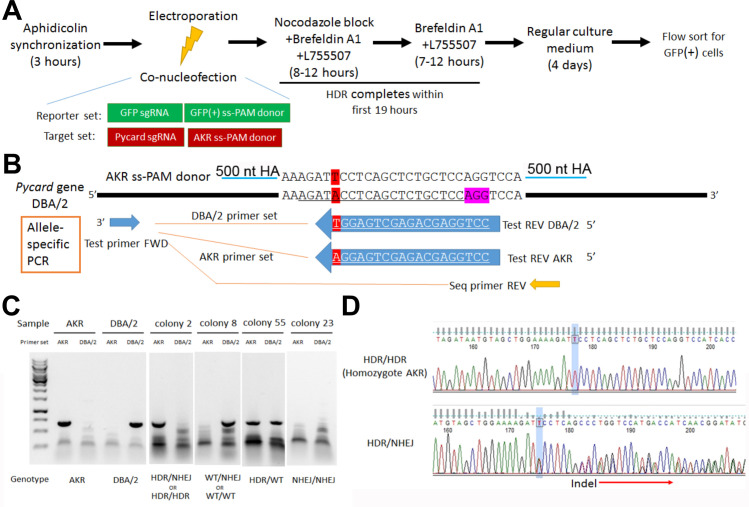
Figure 4. Pycard gene editing of ES cells to convert the DBA/2 allele to the AKR allele.
(A) Strategy used to decrease NHEJ by use of HDR reporter and small molecules to modulate cell cycle and inhibit NHEJ. (B) Sequence of the AKR allele ss donor (3’UTR SNP highlighted in red) with 500 nt homology arm (HA), which will change the SNP from DBA/2 to AKR and eliminate Cas9 re-cutting, since the SNP is within the sgRNA sequence (underlined in the DBA/2 gene sequence). The sequence of the AKR and DBA/2 allele-specific PCR reverse primers are also shown with the SNP at the 3’ end, along with the positions of the common forward primer and the reverse PCR primer used for sequencing the edited clonally derived genomic DNA. (C) Example of allele-specific PCR using AKR and DBA/2 genomic controls, and DNA from expanded colonies after gene editing. Genotypes cannot all be distinguished, as one of both alleles may be edited by NHEJ precluding DNA amplification. (D) Sanger sequencing of DNA after gene editing showing a homozygous HDR conversion to the AKR allele (top) and a compound heterozygous with editing to one AKR allele and one indel allele due to NHEJ (bottom).