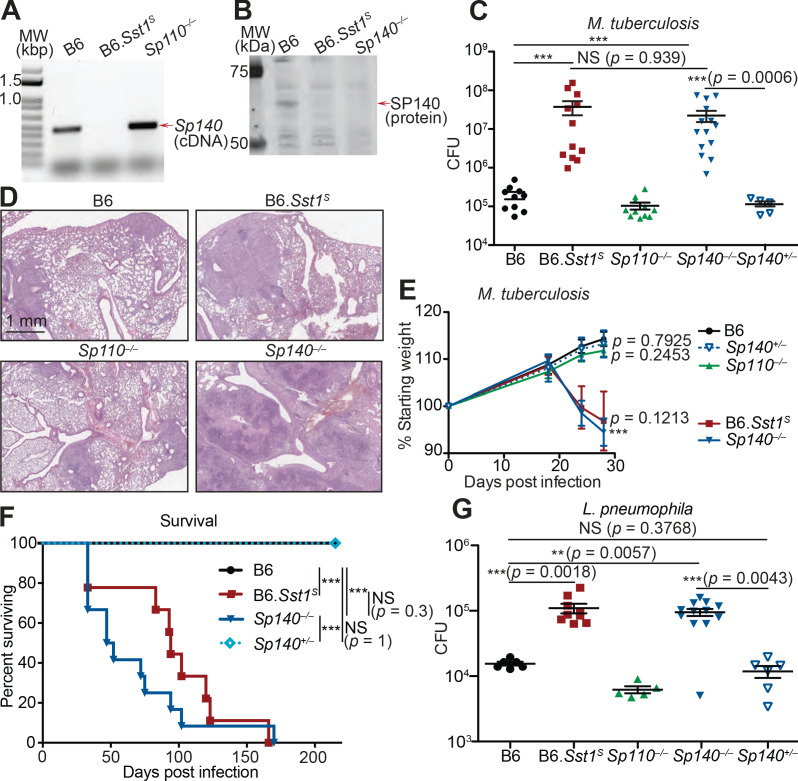
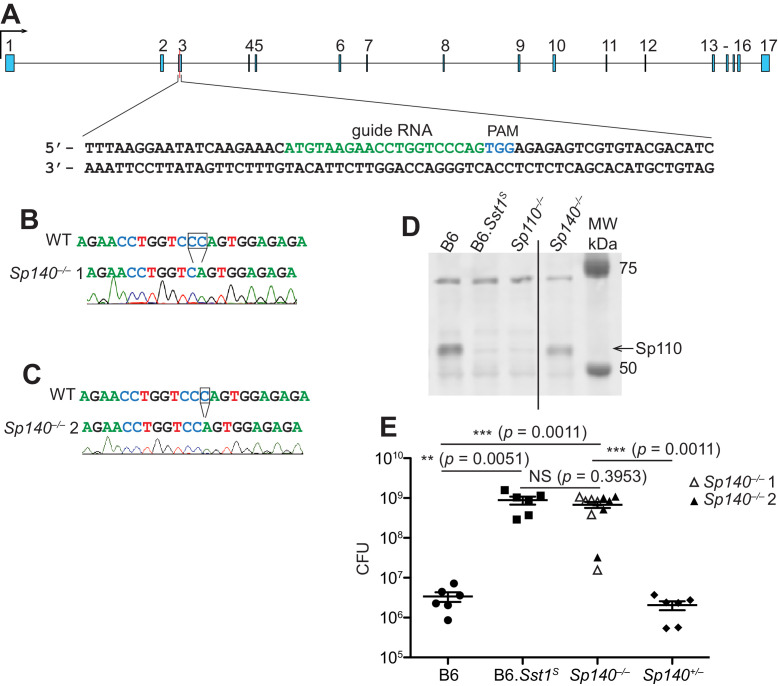
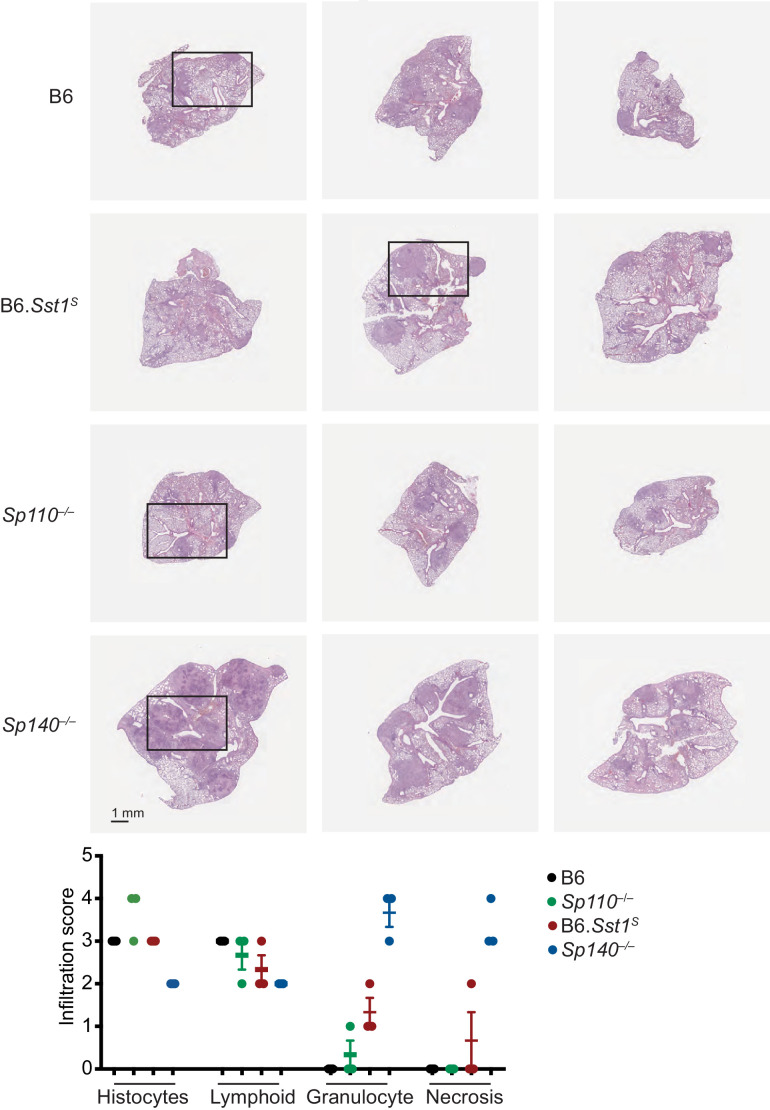
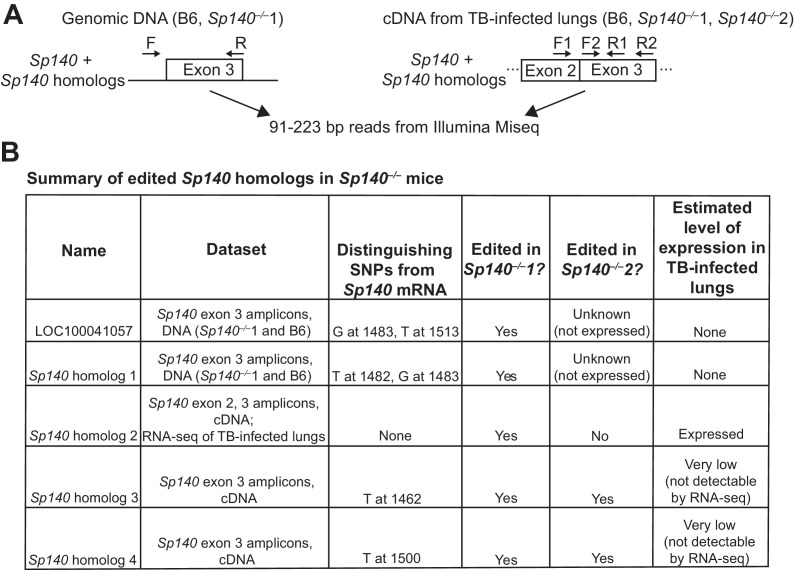
Figure 2. Sp140–/– mice are susceptible to bacterial pathogens.
(A) RT-PCR of cDNA from BMMs of the indicated genotypes. Red arrow indicates band corresponding to a portion of Sp140, verified by sequencing. (B) Immunoblot of lysates from Sp140–/– and B6 BMMs treated with 10 U/ml of recombinant mouse IFNγ for 24 hr. Equal amounts of protein were loaded for immunoblot with anti-SP140 antibody. (C–F) Mice were infected with Mycobacterium tuberculosis and measured for (C) lung CFU at 28 days post-infection, (E) body weight over time, and (F) survival. Statistics in (E) shows the comparison to B6 at day 28, and data are from 10 B6, 11 B6.Sst1S, 11 Sp110–/–, 14 Sp140–/–, and 6 Sp140+/–mice. (D) H&E staining of lungs at 25 days post-infection with M. tuberculosis. Full histology images are provided in Figure 2—figure supplement 2. (G) Mice were infected with Legionella pneumophila and lung CFUs were determined at 96 hr post-infection. All mice were bred in-house, Sp140–/– and Sp140+/– were littermates (C–F). (C), (E), and (G) are combined results of two independent infections. (A–D) show representative analysis of one Sp140–/– line (line 1), whereas (F, G) include a mixture of both lines 1 and 2. Results of infection of both lines with M. tuberculosis are shown in Figure 2—figure supplement 1E. (C, E, F, G) Mann-Whitney test. *p≤0.05; **p≤0.01; ***p≤0.005. BMM, bone marrow-derived macrophage; CFU, colony-forming unit; H&E, hematoxylin and eosin; RT-qPCR, real-time quantitative-polymerase chain reaction; WT, wild-type.