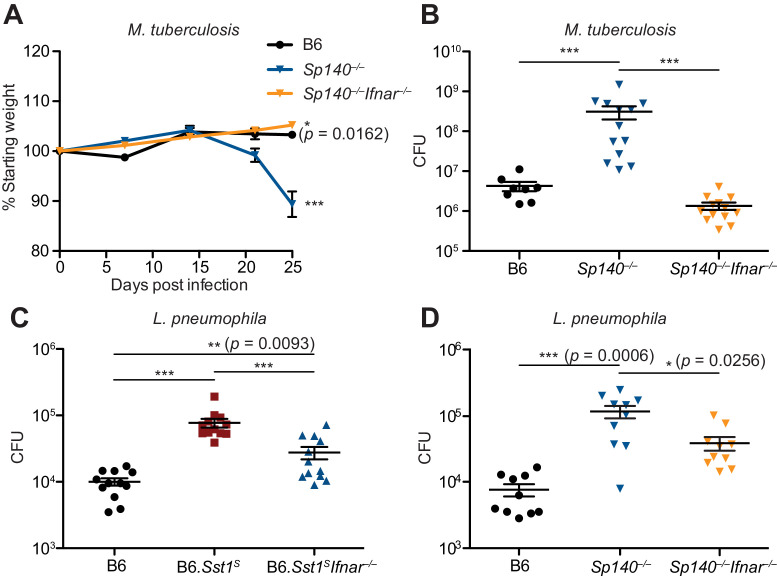
Figure 5. Susceptibility of Sp140–/– to Mycobacterium tuberculosis and Legionella pneumophila is dependent on type I IFN signaling.
(A, B) Mice were infected with M. tuberculosis and measured for (A) body weight, and (B) bacterial burdens at day 25. Statistics in (A) show comparison to B6; data are from 9 B6, 13 Sp140–/–, and 13 Sp140–/– Ifnar–/– mice. Combined results of two experiments. (C, D) Bacteria burden in L. pneumophila-infected mice at 96 hr. Combined results of two experiments. All mice were bred in-house (A, B, D); all but B6 were bred in-house (C). Mann-Whitney test (A–D). *p≤0.05; **p≤0.01; ***p≤0.005.
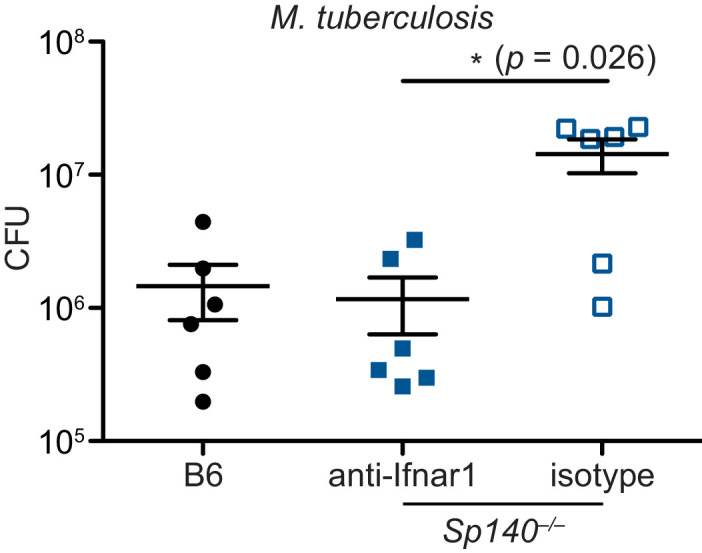
Figure 5—figure supplement 1. Antibody blockade of IFNAR1 reduces bacterial burden in Sp140–/– mice during Mycobacterium tuberculosis infection.