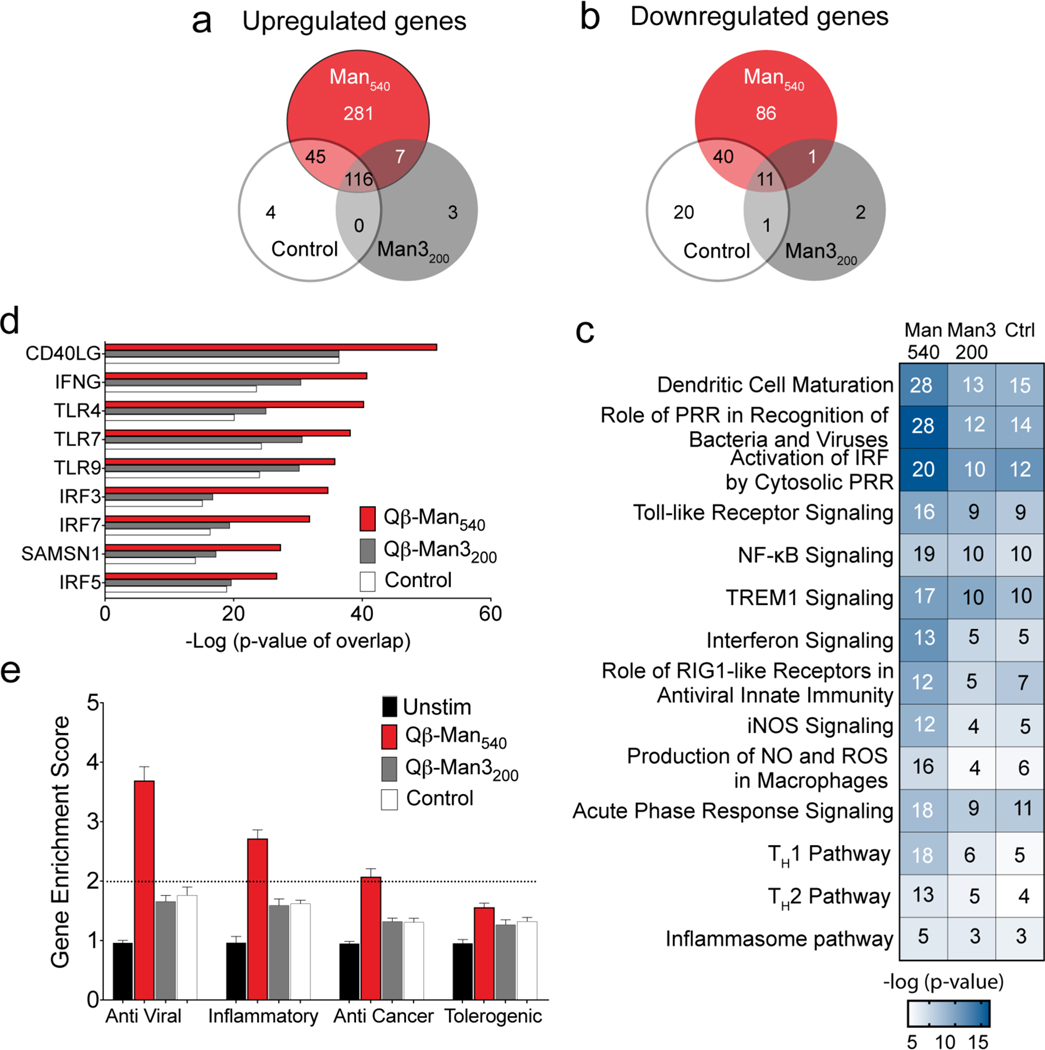
Figure 8. Transcriptional analysis of human monocyte-derived DCs treated with mannosylated particles.
The moDCs were treated with particles (4 nM) for 6 h before RNA sequencing (n=4). Qβ-PE540 was used as a control (Ctrl). (a-b) Venn diagram showing genes upregulated or downregulated at least two-fold compared to untreated cells. (c) Heat map of canonical pathways significantly upregulated (Fisher’s exact test, −log10 P values for each represented pathway is shown) in particle treated cells relative to untreated, as predicted by Ingenuity Pathway Analysis (IPA). In each pathway, the number of genes differentially regulated at least two-fold is indicated inside each box. (d) Significant putative upstream regulators with predicted activating influence on transcriptional signatures in moDCs treated with particles, as determined by IPA. (e) Gene enrichment score for 94 anti-viral, 41 inflammatory, 54 anti-cancer, and 30 tolerogenic genes. Abbreviations: PRR ≡ pattern recognition receptor, NF-κB ≡ nuclear factor kappa-light-chain-enhancer of activated B cells, TREM-1 ≡ triggering receptor expressed on myeloid cells-1, iNOS ≡ inducible nitric oxide synthase, NO ≡ nitric oxide, ROS ≡ reactive oxygen species.