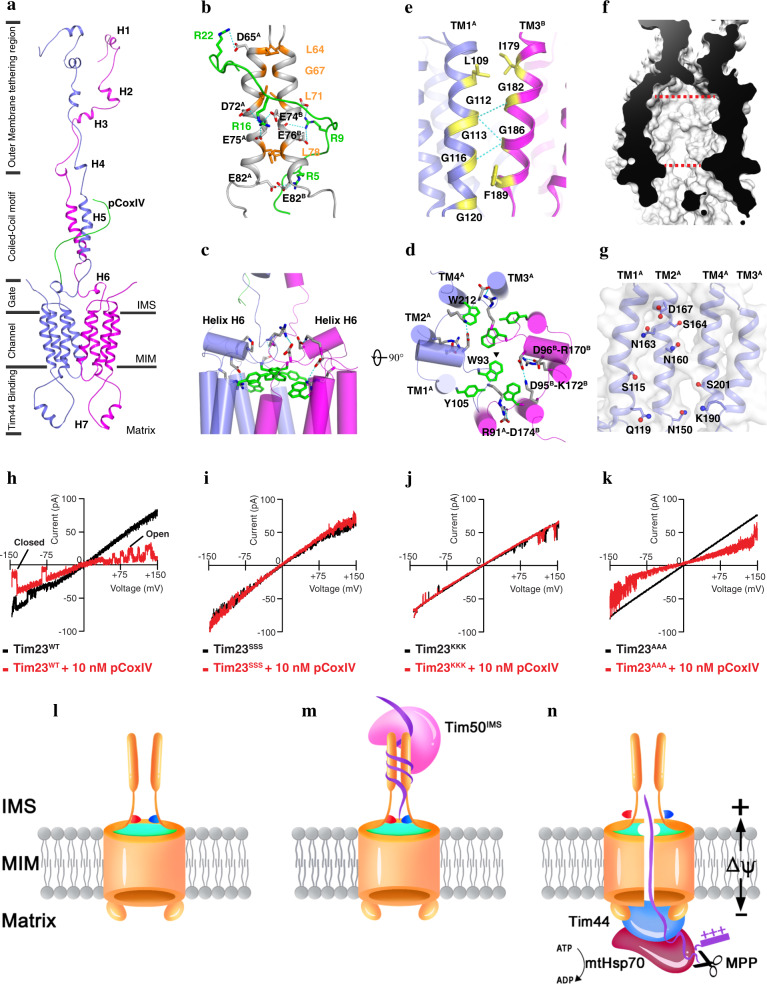
Fig. 1. Solution structure of the Tim23-pCoxIV complex.
a Cartoon representation of the Tim23–pCoxIV structure. The seven soluble helices (H1–H7) of the monomers are indicated. The presequence peptide of CoxIV (green) is labeled as pCoxIV. The complex structure is divided into regions of the channel in the mitochondrial inner membrane (MIM); the gate, coiled-coil motif and outer membrane tethering region in the intermembrane space (IMS); and Tim44-binding helix H7 in the matrix. b Stick representation of the positively-charged arginine residues (R22, R16, R9, and R5) in pCoxIV (green) and the negatively-charged aspartate (D65, D72) and glutamate (E74, E75, E76, and E82) residues in the coiled-coil motif (gray) of the Tim23 channel. The superscripts A and B indicate monomer A and B, respectively. Potential interactions via an electrostatic effect are shown by dashed cyan lines. The residues forming the coiled-coil motif are shown and labeled in orange. c, d Side and top views of cylindrical representations of the gating zone of the Tim23 channel. Salt bridges are shown by dashed cyan lines. The large side chain residues W93, Y105, and W212 are shown in green. Half of the salt bridges and side chains are labeled at their positions. The triangle represents the center position of the Tim23 channel. e The residues in the Tim23 dimer interface are shown in yellow and labeled in TM1A (light blue) and TM3B (magenta) for each monomer. The H-bonds are indicated by dashed cyan lines. f Sliced-surface view of the Tim23 channel in membrane. The red dashed lines indicate the widest and narrowest diameters. g The hydrophilic and charged residues inside of the channel are shown on the TM helices of monomer A with side chains and labeled. h–k Representative traces of channel currents showing Tim23WT (h), and the Tim23 sequence variants Tim23SSS (i), Tim23KKK (j), and Tim23AAA (k) in the absence (black) or presence (red) of 10 nM pCoxIV. l A closed Tim23 channel in the idle state. The coiled-coil region interaction is relatively loose, and the channel is sealed by salt bridges (red and blue) and the aromatic rings of tryptophan and tyrosine (green). m Tim50IMS, the soluble domain of Tim50 located in the IMS, and the precursor protein bind to the coiled-coil region, changing it into a tight conformation. n In the presence of an appropriate change in the membrane potential (ΔΨ), the channel is opened when the salt bridges are broken and the aromatic rings are dispersed. The presequence is pulled through the channel by an electrophoresis effect and digested by protease MPP. The mature polypeptide is transported into the matrix by scaffold protein Tim44 and chaperone mtHsp70 using ATP.