Fig. 6. RNA binding triggers a conformational change in Aub, exposing its N terminus to the methyltransferase Csul/Vls complex.
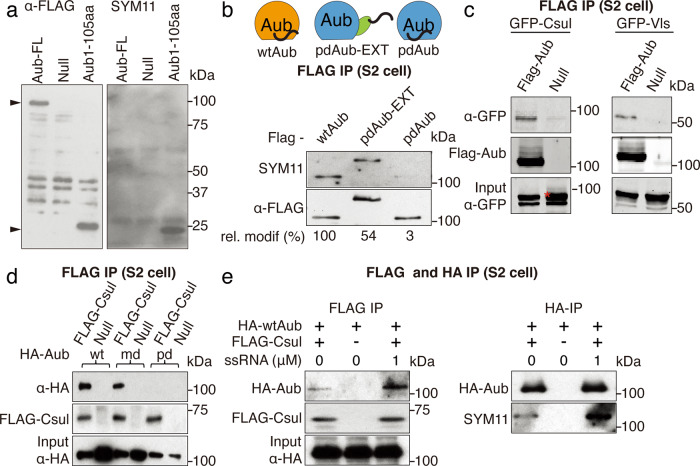
a N-terminal region within Aub protein is not easily accessible to methylation. FLAG-tagged full length and N-terminal truncated (1-105aa) Aub were expressed in S2 cells and immunoprecipitated. Total protein and methylation level were assessed by Western blot. Arrowheads indicate correct size for full-length and N-terminal fragment, respectively. Experiment reproduced twice with similar results. b Top: scheme showing architectures of different Aub constructs expressed and IP-ed from S2 cells. EGFP inserted between the N-terminal and PAZ domain (pdAub-EXT) artificially exposes N-terminus in absence of piRNA binding. Bottom: western blot analysis of methylation states. Relative methylation level as estimated by the ratio of SYM11/FLAG band intensities normalized to wildtype is listed. Experiment reproduced twice with similar results. c Aub interacts with Csul and Vls in S2 cells. Co-IP Western blot of tagged transgenes. Asterisk indicates band corresponding to GFP-Csul in the INPUT. d Aub binding to Csul depends on RNA binding but not on Arg methylation. FLAG-Csul and HA-Aub transgenes were expressed in S2 cells and coIP followed by Western detection. Experiment reproduced twice with similar results. e RNA loading of Aub leads to increased binding to Csul and increased methylation of Aub. FLAG-Csul and HA-Aub were expressed in S2 cells, lysates were incubated in the presence or absence of ssRNA oligo prior to coIP followed by Western detection. Experiment reproduced twice with similar results.