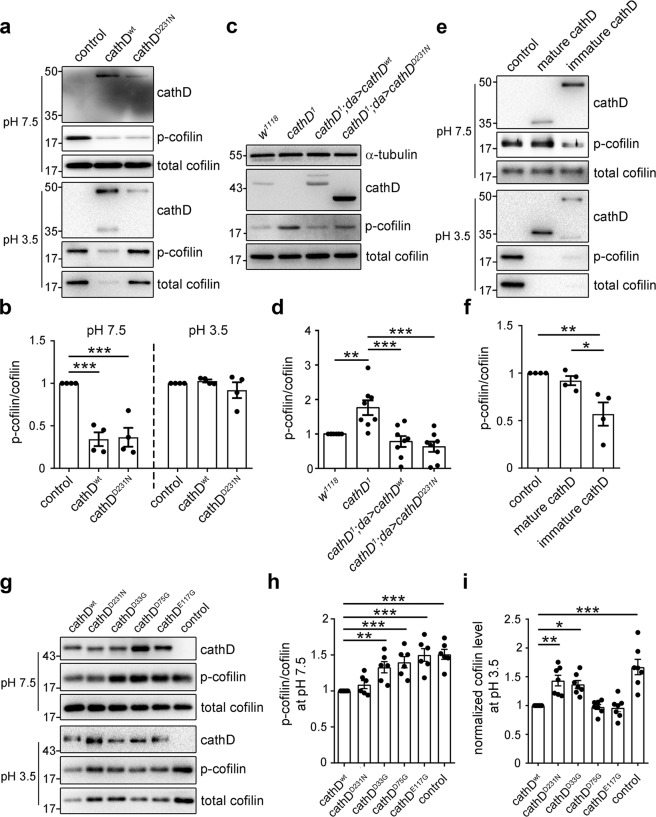
Fig. 4. Functional switch of cathD activities relies on pH and its maturation.
Representative immunoblot images (a) and quantification (b) of cathD-mediated cofilin phosphorylation in different pH conditions, showing both recombinant cathDwt and cathDD231N (10 nM) dephosphorylate cofilin in neutral pH (7.5), whereas cathDwt mainly degrades cofilin in acidic pH (3.5). Note that both cathDwt or cathDD231N significantly reduce p-cofilin/cofilin ratio in neutral but not acidic pH (c). Representative immunoblot images (c) and quantification (d) of cathD-mediated cofilin phosphorylation in flies. c Elevated p-cofilin levels in cathD1 mutants are restored upon expressing either wild-type (cathD1; da > cathDwt) or proteolytically inactive cathD (cathD1; da > cathDD231N). d Quantification of p-cofilin/total cofilin levels (normalized to w1118 controls). The ratio is reduced when cathDwt or cathDD231N is expressed in cathD1 mutant background. Representative immunoblot images (e) and quantification (f) of in vitro phosphatase assay showing that immature recombinant human cathD directly dephosphorylates cofilin at pH 7.5, whereas mature cathD degrades cofilin at pH 3.5 (e). f Quantifications of p-cofilin/cofilin ratio (normalized to control) show that immature cathD dephosphorylates cofilin, whereas mature cathD shows limited phosphatase activity in neutral pH (7.5). Representative immunoblot images (g), quantification of p-cofilin/cofilin ratio (normalized to cathDwt, h) and cofilin level (normalized to cathDwt, i) from in vitro phosphatase assays using recombinant cathDwt, cathDD231N, cathDD33G, cathDD75G, and cathDE117. Note that cathDD33G, cathDD75G and cathDE117G exhibit impaired activities in cofilin dephosphorylation at pH 7.5, whereas cathDD33G and cathDD231N present suppressed proteolytic activities for cofilin degradation at pH 3.5. Data are means ± SEM, *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001 by Mann–Whitney U test or One-way ANOVA with Tukey’s post hoc test.