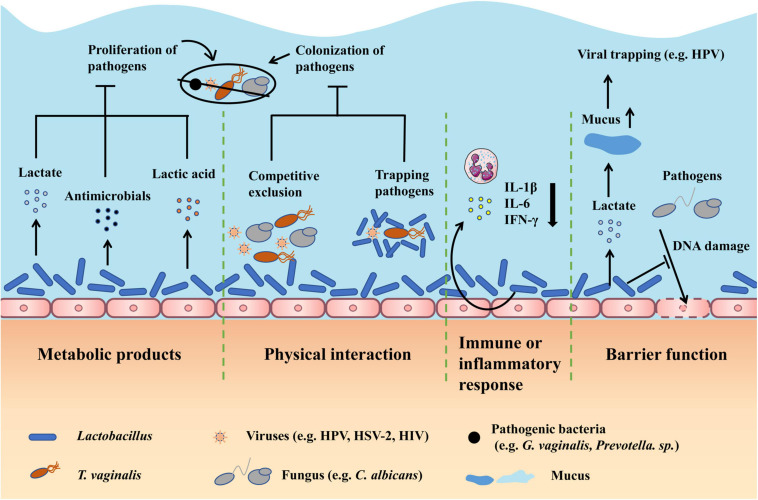
FIGURE 1.
Therapy effects of restoring Lactobacillus-dominated vaginal microbiota in infectious diseases. First, Lactobacillus can produce metabolites including lactate, antimicrobials, and lactic acid to inhibit the proliferation of pathogens. Second, Lactobacillus can competitively exclude pathogens from adhering to epithelium and trap pathogens by direct physical contact to prevent the colonization of pathogens. Third, Lactobacillus can regulate the immune or inflammatory response, particularly relieving the inflammation by decreasing cytokines like IL-1β. Fourth, Lactobacillus can improve the barrier function by producing lactate, which can increase the mucus viscosity to facilitate viral trapping, and inhibiting pathogens from damaging the DNA of epithelial cells. DNA, deoxyribonucleic acid.