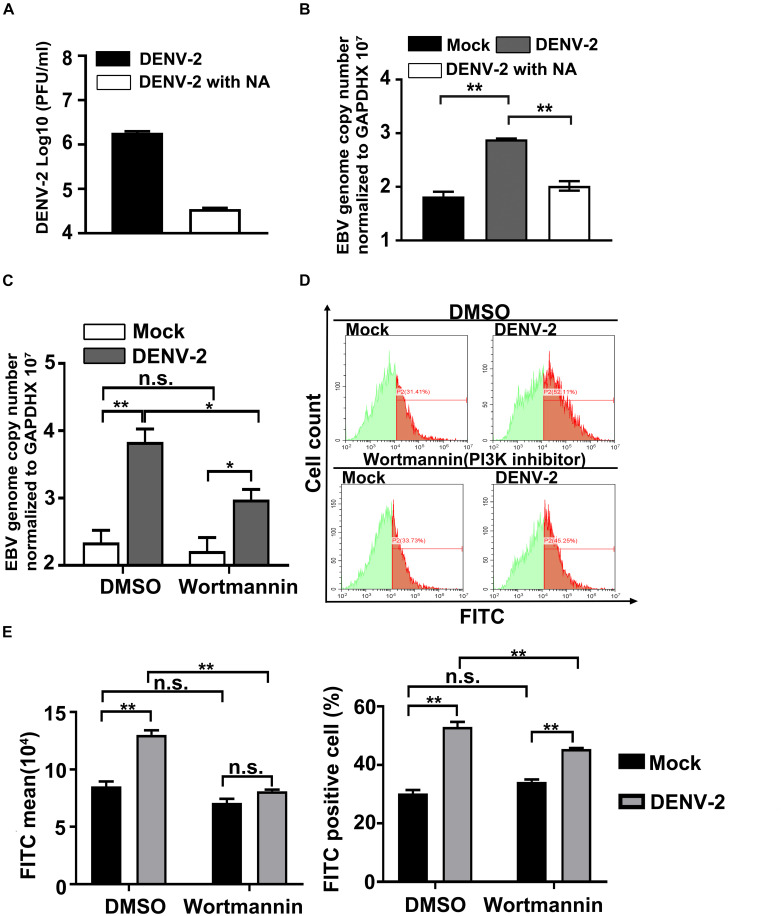
FIGURE 2.
Wortmannin treatment blocks DENV-2 infection-induced Epstein–Barr virus (EBV) reactivation. (A) A neutralizing antibody (NA) was mixed with the DENV-2 virus to neutralize infectious viral particles (DENV-2 with NA). The neutralization effect was confirmed by plaque assay. (B) EBV + Akata cells were mock-infected or infected with non-neutralized (DENV-2) or neutralized DENV-2 (DENV-2 with NA). At 72 hpi, relative EBV genome load was quantified. (C,D) Mock- or DENV-2-infected EBV + Akata cells were treated with DMSO or 0.2 μM wortmannin. At 72 hpi, relative EBV genome load was determined (C). Green fluorescent protein (GFP) intensity of the four experimental groups was quantified by flow cytometry. The representative result of three independent experiments was shown in panel D, and quantification and statistical analysis of mean GFP value and percentage of GFP-positive cells were shown in panel E. p < 0.01 was marked as ** and p < 0.05 was marked as *.