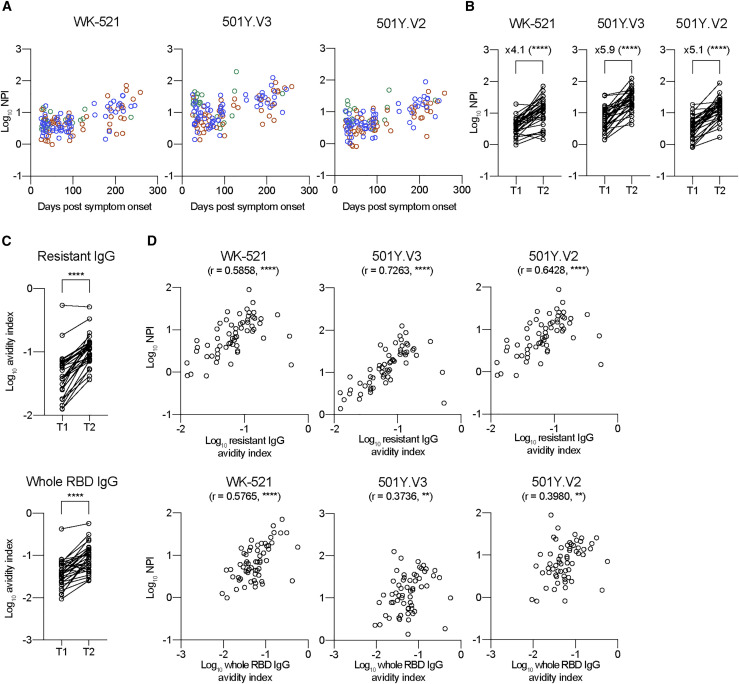
Figure 6.
Temporal increase of NPIs to VOCs in correlation with affinity maturation of mutation-resistant IgG antibodies
(A) NPIs against WK-521, 501Y.V3, and 501Y.V2 strains were quantitated from mild (green, n = 20), moderate (blue, n = 59), and severe (red, n = 46) groups and plotted as log10.
(B) NPIs against the indicated strains are plotted as log10 in T1 and T2 periods (longitudinal samples; n = 31). Data from the same individual are connected with lines. Statistical significance and fold increase are indicated; ∗∗∗∗p < 0.0001 (Wilcoxon test).
(C) Avidity indexes of IgG to triple mutant (top; resistant IgG) and whole RBD (bottom; whole RBD-binding IgG) are plotted. Data from the same individual are connected with lines. ∗∗∗∗p < 0.0001 (Wilcoxon test).
(D) Correlations between avidity indexes of resistant IgG/whole RBD IgG and NPI against WK-521 (left), 501Y. V3 (middle), and 501Y.V2 (right) strains are plotted. Spearman r and p values are indicated; ∗∗p < 0.01 and and ∗∗∗∗p < 0.0001.