Figure 1.
mRNA-1273 potently elicits S-2P binding and neutralizing antibodies compared to inactivated SARS-CoV virus or denatured SARS-CoV-2 spike protein delivered in alum
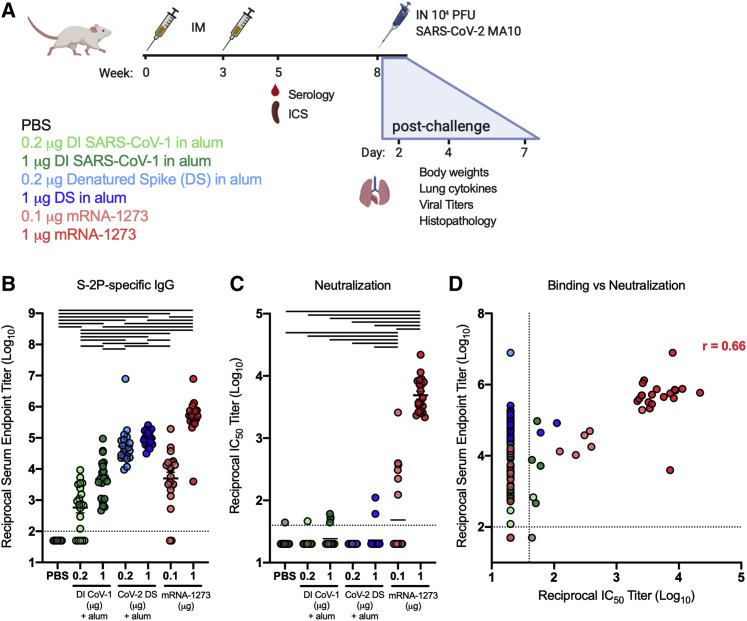
(A) Experimental design aimed at eliciting immune responses that have historically been associated with vaccine-enhanced respiratory disease in BALB/c and to compare immunogenicity and efficacy with that of mRNA-1273. Type-2-skewing regimens (double-inactivated SARS-CoV virus, DI CoV-1, and denatured SARS-CoV-2 spike protein [CoV-2 DS]) were dosed at 0.2 or 1 μg. mRNA-1273 was given at 0.1 or 1 μg, established subprotective and protective doses, respectively. All mice were immunized intramuscularly (IM) at weeks 0 and 3. T cell (ICS) and serological readouts were obtained 2 weeks post-boost. 20 animals per group were challenged with 104 PFUs of SARS-CoV-2 MA10 (mouse-adapted, passage 10, lethal challenge virus), weight loss (10 animals per group through day 7), and viral titers (5 animals per group at days 2 and 4) in the lungs, and nasal turbinates were obtained after challenge. Data from study 1 are presented in Figures 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, and S1–S3 and Tables S1 and S2.
(B and C) S-2P-binding antibodies (B) neutralizing activity (C) against SARS-CoV-2 614G pseudovirus was assessed in sera obtained 2 weeks post-boost.
(D) Correlation between S-2P binding and SARS-CoV-2 614G pseudovirus neutralization. Correlation coefficient r = 0.66 for mRNA-1273 samples with measurable binding and neutralization. Statistics were performed using one-way ANOVA with Tukey’s multiple comparisons test between all experimental groups, with a black line between groups indicating adjusted p < 0.05. N = 20 animals per group; means of log-transformed data are shown. The limit of detection is indicated by a dotted line, and values below the limit of detection were assigned a value of half the limit of detection.
See also Table S1.