FIGURE 1.
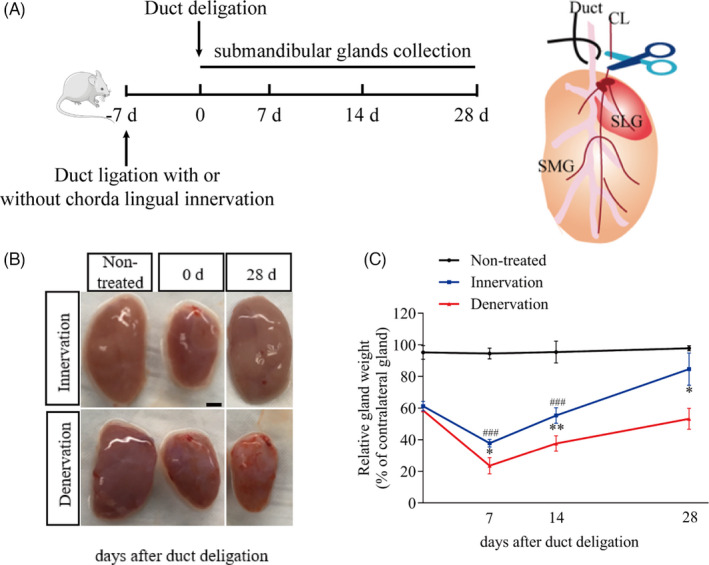
Complete parasympathetic innervation facilitates gland regeneration. (A) The specific process of this experiment. CL, chorda lingual. SMG, submandibular gland. SLG, sublingual gland. (B) The pictures of submandibular glands (SMG) in different groups after duct deligation. The non‐treated group were performed sham surgery and serves as a control (scale bar = 1mm). (C) The ratio of left gland weight to right gland in each group at different time points (0, 7, 14, 28 after duct deligation) during regeneration. The weight of innervated glands was significant recovered compared with the denervated (*indicates significance between the group innervation and denervation. # indicates significance between the non‐treated group and innervation group). *P < .05, ** and P < .01, ### P < .001). Data were shown as mean ± standard deviation
