FIGURE 1.
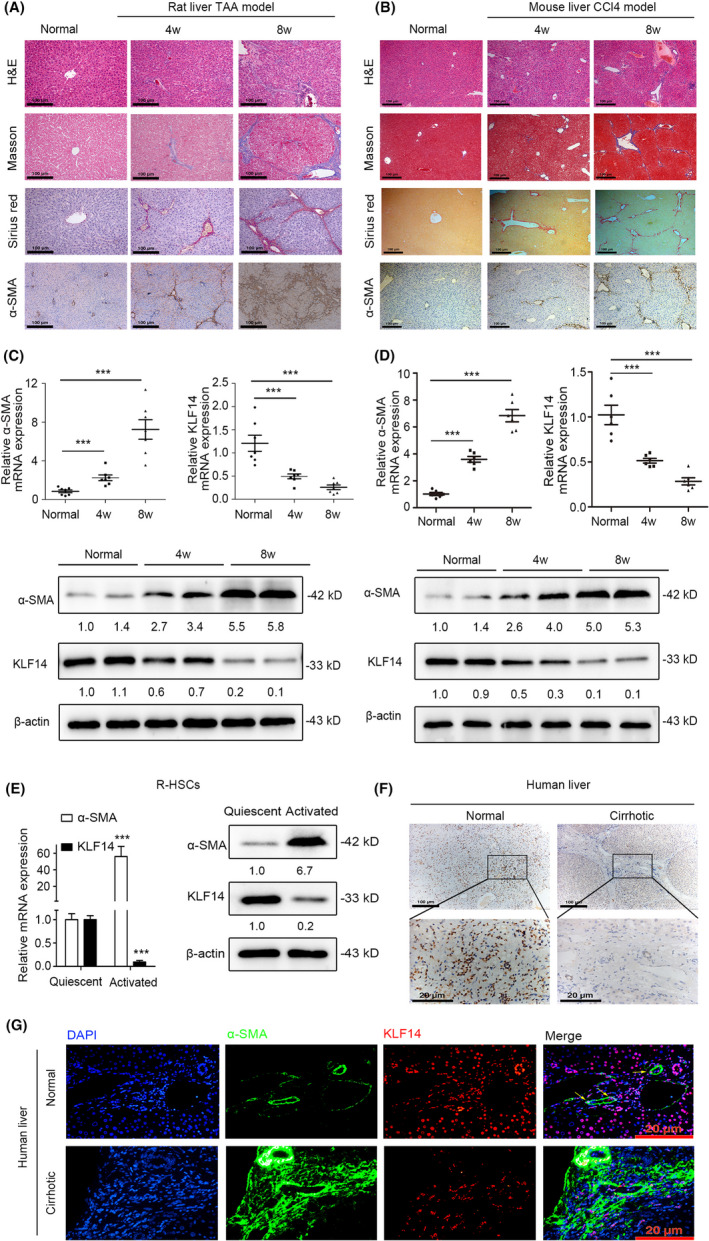
KLF14 is inversely correlated with liver fibrosis and HSCs activation. A, H&E, Masson's trichrome, Sirius red and α‐SMA staining of normal and TAA‐treated rat liver tissues (n = 7, Scale bars: 100 μm). B, H&E, Masson's trichrome, Sirius red and α‐SMA staining of normal and CCl4‐treated mouse liver tissues (n = 6, Scale bars: 100 μm). C, The normal and TAA‐treated rat liver tissues were subjected to RT‐qPCR (n = 7) and Western blotting (n = 2) analyses for detection of α‐SMA and KLF14 expression. D, The normal and CCl4‐treated mouse liver tissues were subjected to RT‐qPCR (n = 6) and Western blotting (n = 2) analyses for detection of α‐SMA and KLF14 expression. E, The quiescent and activated R‐HSCs were subjected to RT‐qPCR and Western blotting analyses for detection of α‐SMA and KLF14 expression (n = 3). F, Immunohistochemistry staining of KLF14 in human liver tissues (normal and cirrhotic, n = 3, Scale bars: 100 and 20 μm). G, Immunofluorescence staining of KLF14 and α‐SMA in human liver tissues (normal and cirrhotic, n = 3, Scale bars: 20 μm). Yellow arrows indicated HSCs. **P < .05, **P < .01, ***P < .001 versus the control group
