FIGURE 8.
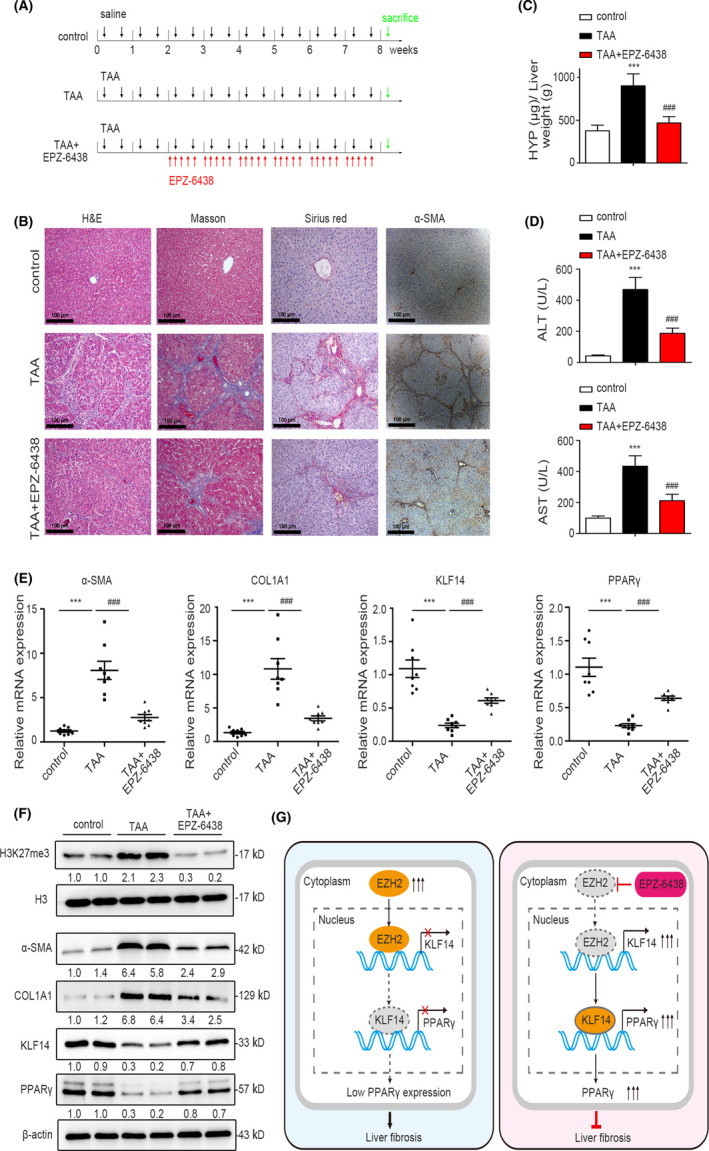
In vivo administration of EPZ‐6438 alleviates TAA‐induced rat liver fibrosis. A, Schematic diagram of the in vivo experiment, saline or TAA and EPZ‐6438 were administered accordingly (n = 8). B, H&E, Masson's trichrome, Sirius red and α‐SMA staining of rat liver sections for histological and collagen examinations (n = 8, Scale bars: 100 μm). (C,D) Liver hydroxyproline content, serum ALT and AST levels were assessed by relevant kit (n = 8). (E,F) The mRNA expression of KLF14, α‐SMA, COL1A1 and PPARγ was assessed by RT‐qPCR (n = 8). The protein expression of H3K27me3, α‐SMA, COL1A1, KLF14 and PPARγ was assessed by Western blotting analysis (n = 2). β‐actin and total H3 were used as loading control. G, A schematic diagram of the role EZH2‐KLF14‐PPARγ signalling in liver fibrosis. Upon HSCs activation, the elevated EZH2 mediates suppression of KLF14 expression, which promotes HSCs activation and liver fibrosis by downregulating PPARγ. The EZH2 inhibitor EPZ‐6438 rescues EZH2‐mediated KLF14 downregulation, which transactivates PPARγ expression, converts the activated HSCs to the quiescent phenotype and induces apoptosis, and therefore alleviating liver fibrosis. ***P < .001 versus the control group. ### P < .001 versus the TAA group
