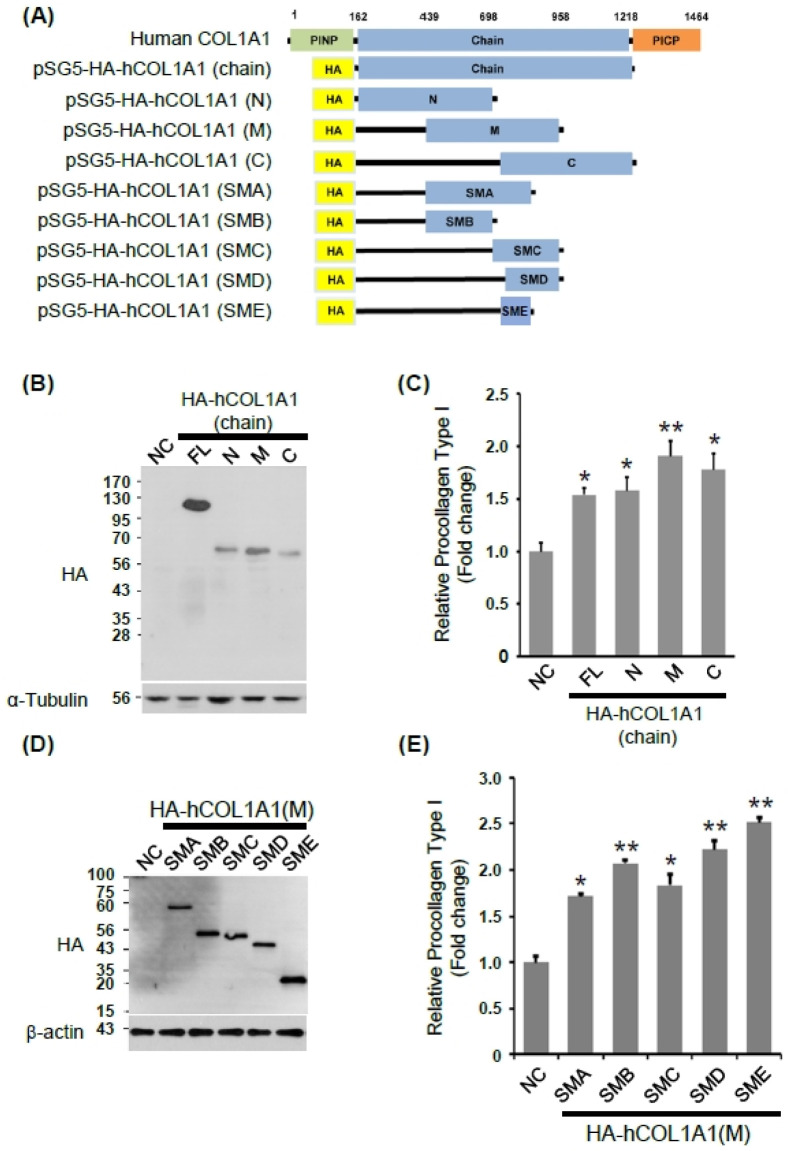
Fig. 1.
Identification of hCOL1A1 domain for the synthesis of collagen type I. (A) Schematic representing full-length hCOL1A1 and its various deletion mutants. (B and C) Human dermal fibroblasts (HDFs) were transfected with plasmids encoding hemagglutinin (HA), as the negative control (NC), HA-tagged full length hCOL1A2 (FL), and each of the deletion mutants (N-terminal chain [N], middle chain [M], or C-terminal chain [C]). Forty-eight hours after transfection, cells were collected and cell lysates were analyzed by immunoblotting with anti-HA and anti-tubulin antibodies (B). The amount of collagen type I in transfected HDF culture media was measured with an enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) kit (C). (D and E) HDF cells were transfected with plasmids encoding HA (NC) and each of the indicated mutants (small middle A [SMA], small middle B [SMB], small middle C [SMC], small middle D [SMD], or small middle E [SME]). Forty-eight hours after transfection, cells were collected and cell lysates were analyzed by immunoblotting with anti-HA and anti-tubulin antibodies (D). The amount of collagen type I was measured with an ELISA kit in a transfected HDF-cultured media (E). Results are presented as mean ± SD of three independent experiments. Student’s t-test was used for statistical analyses (*P < 0.05, **P < 0.005).