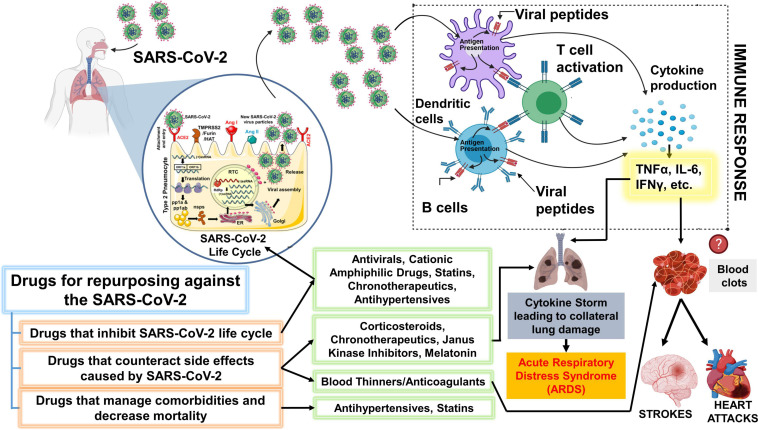
FIGURE 3.
Schematic showing key classes of drugs that are currently repurposed and suggested drugs that could be repurposed for SARS-CoV-2. The drugs proposed for repurposing have been classified under 3 categories: Drugs that inhibit SARS-CoV-2 lifecycle, counteract the side effects post-infection or can efficiently manage comorbidities and other risk factors. It is important to note that the representation above is purely hypothetical, and based solely on the limited literature that was available on SARS-CoV-2 or the beneficial effects that were observed with other viruses from both in vitro or in vivo studies. Antiviral drugs like remdesivir are effective against the SARS-CoV-2. Statins have also been shown to inhibit the SARS-CoV-2 life cycle. Cationic amphiphilic drugs (CADs), like amiodarone, chlorpromazine, and clomiphene have been shown to inhibit several virus families including the SARS-CoV-1 and MERS-CoV. Therefore, CAD’s potential against the SARS-CoV-2 should be further evaluated. Janus-associated kinase inhibitors, baricitinib, have been shown to decrease mortality among COVID-19 patients when used together with remdesivir. However, the beneficial effect of common corticosteroids like prednisone or methylprednisolone has not been determined but several clinical trials are evaluating the same. A higher incidence of blood clots is observed among COVID-19 patients. The massive inflammatory response during SARS-CoV-2 infection can trigger blood clots which can eventually cause strokes or heart attacks. Thus, blood thinners, which have been associated with decreased mortality among COVID-19 patients can be beneficial. We have additionally proposed a novel chronotherapeutic agent, SR9009, which has immense potential to inhibit several virus families, reduce lung inflammation and injury by interfering with the production of inflammatory cytokines. Additionally, REV-ERB agonists (e.g., SR9009 and GSK2667) can also be shown to boost endurance, reduce cholesterol, body weight and prevent heart disease. This schematic was prepared using SMART (Servier Medical Art), licensed under a Creative Common Attribution 3.0 Generic License. http://smart.servier.com/ and http://biorender.com.