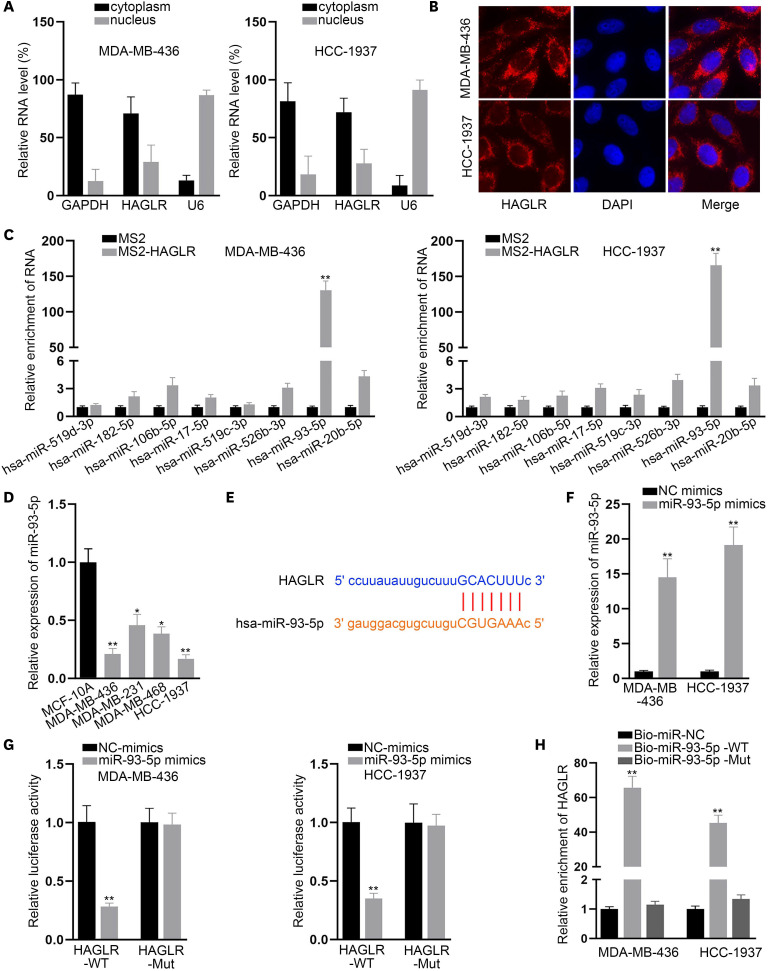
Figure 2. miR-93-5p could bind to HAGLR.
(A, B) Subcellular fraction and FISH assays were implemented to explore the location of HAGLR in MDA-MB-436 and HCC-1937 cells. (C). A MS2-RIP assay was conducted to detect the interaction of HAGLR with the indicated miRNAs. (D) miR-93-5p expression in TNBC cells was probed by qRT-PCR. (E). The binding site between miR-93-5p and HAGLR was presented according to ENCORI. (F) miR-93-5p overexpression was detected by qRT-PCR. (G, H) The binding relationship between miR-93-5p and HAGLR was tested by luciferase reporter assay and RNA pull-down assay.
HAGLR = HOXD antisense growth-associated lncRNA; FISH = fluorescence in situ hybridization; RIP = RNA immunoprecipitation; miR = microRNA; TNBC = triple-negative breast cancer; qRT-PCR = quantitative real-time polymerase chain reaction; GAPDH = glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate dehydrogenase; DAPI = 4′,6-diamidino-2-phenylindole; NC = negative control; WT = wild-type; Mut = mutant.
*p < 0.05, **p < 0.01.