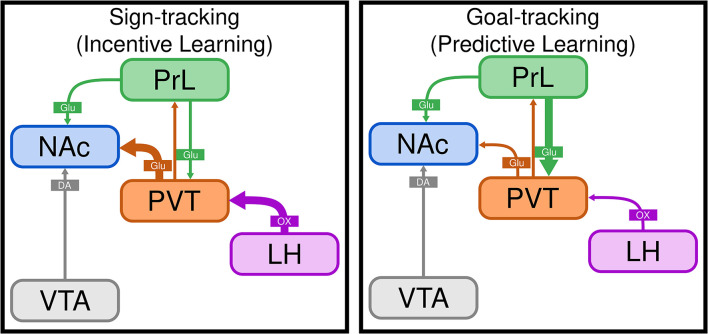
Figure 2.
The PVT differentially mediates sign- and goal-tracking behavior. Schematic illustrating the paraventricular nucleus of the thalamus (PVT) as a central locus that acts to differentially regulate sign-tracking and goal-tracking behavior. Sign-tracking is a result of incentive cue-reward learning, whereas goal-tracking is the result of predictive cue-reward learning. We hypothesize that the incentive value of reward cues is encoded in the LH-PVT-NAc circuit (as indicated by thick purple and orange arrows), which is engaged to a greater degree in sign-trackers. In contrast, goal-trackers rely on top-down cortical control mechanisms (as indicated by thick green arrow) to encode the predictive value of reward cues and inhibit incentive motivational processes. LH, lateral hypothalamus; NAc, nucleus accumbens; PrL, prelimbic cortex; PVT, paraventricular thalamic nucleus; VTA, ventral tegmental area; DA, dopamine; Glu, glutamate; OX, orexin.