Coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID‐19) and subsequent containment measures affected consumer behaviour in Australia, including the stockpiling of essential items. Increased demand for prescription medications caused concern about potential medication shortages, and a range of policies were implemented in March 2020 to protect supplies. 1
We used interrupted time series modelling to quantify the impact of the COVID‐19 pandemic on medication dispensing. The Pharmaceutical Benefits Scheme (PBS) subsidises public medication costs in Australia. We analysed Section 85 date of supply data 2 to model dispensing during January 2016 – December 2019, by month, separately for all PBS prescriptions, the ten medications most frequently dispensed during the 2018–19 financial year, hydroxychloroquine, and dexamethasone. These models, which accounted for long term trends and seasonal changes, were used to predict expected dispensing during January – June 2020 (with 95% confidence intervals [CIs]), which we compared with actual dispensing rates during this period (online Supporting Information). Ethics approval was not required for our analysis of publicly available data.
The number of prescriptions dispensed during March 2020 was significantly higher than predicted (4.80 million more prescriptions, +18.5%; 95% CI, +14.0% to +23.3%), but significantly lower in April (2.28 million fewer prescriptions, –9.2%; 95% CI, –5.3% to –12.8%) and May (2.08 million fewer prescriptions; –8.1%; 95% CI, –4.3% to –11.5%); there was no significant difference in June 2020 (988 778 fewer prescriptions, –3.8%; 95% CI, –7.5% to +0.1%) (Box). A similar pattern applied to the ten most dispensed medications; the increase in the number of hydroxychloroquine prescriptions dispensed in March was particularly large (24 286 more prescriptions, +95.5%; 95% CI, +89.1 to +102%) (Supporting Information).
Box 1. Total number of prescriptions dispensed in Australia, January 2016 – June 2020, and numbers of COVID‐19 diagnoses in Australia, January 2020 – June 2020.
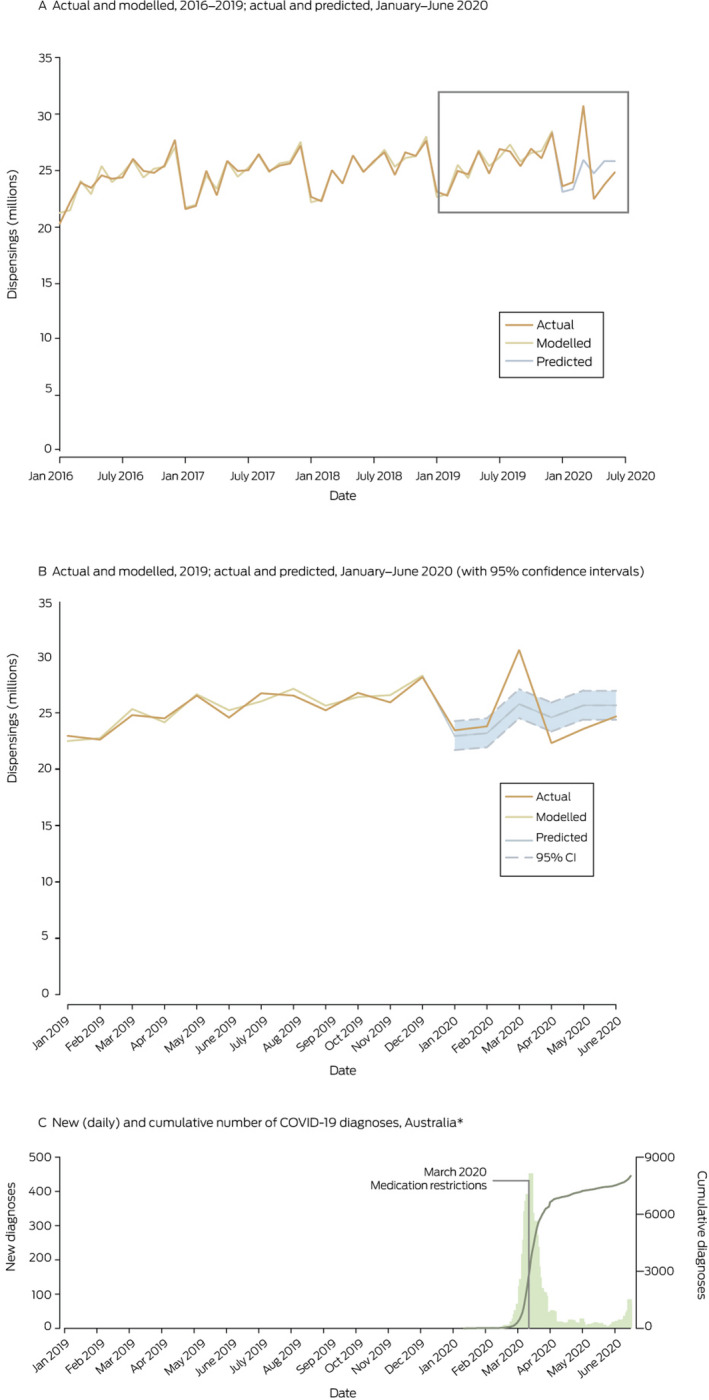
CI = confidence interval. * Source: Australian Department of Health. 2
Increased dispensing of prescription medications in March 2020 was consistent with the general panic buying reported early in the COVID‐19 pandemic. 3 Pharmacies also received increased requests for prescription and over‐the‐counter medications at this time, in some cases causing local shortfalls 1 and concern that continued high dispensing might interrupt medication supply at the national level. This applied in particular to drugs considered early in the pandemic as potential treatments for COVID‐19, such as hydroxychloroquine.
In response to increased dispensing in March, the Australian government rapidly implemented a range of policies for protecting medication supplies. Dispensing limits of one month’s supply were applied to medications if shortages would have serious health consequences. 1 These policies reduced the total number of medications dispensed in April and May 2020, followed by the return to normal levels of prescription dispensing in June. Other factors likely to have been important were stockpiles amassed by people during March, public adjustment to the pandemic, and the early suppression of COVID‐19 in Australia.
Restrictions on prescription dispensing were balanced by services to assist susceptible patients to isolate themselves; for example, the COVID‐19 home medicines service funded home delivery of prescription medications by community pharmacies and Australia Post, 4 and funding for telehealth was increased to facilitate remote prescribing. 5
Our findings indicate that medication supply can be safeguarded from panic dispensing by a range of regulatory policies combined with medication services for vulnerable people. This may be particularly important for ensuring equitable access to medications for treating COVID‐19. The risk of further COVID‐19 outbreaks underscores the importance of maintaining these policies and services.
Competing interests
No relevant disclosures.
Supporting information
Supplementary Material Supplementary methods and results
References
- 1. Therapeutic Goods Administration . Limits on dispensing and sales of prescription and over‐the-counter medicines [media release]. 19 Mar 2020. https://www.tga.gov.au/media-release/limits-dispensing-and-sales-prescription-and-over-counter-medicines (viewed Sept 2020).
- 2. Australian Department of Health . PBS and RPBS section 85 date of supply data. https://www.pbs.gov.au/info/statistics/dos-and-dop/dos-and-dop (viewed Sept 2020).
- 3. Australian Bureau of Statistics . Retail trade, Australia. https://www.abs.gov.au/statistics/industry/retail-and-wholesale-trade/retail-trade-australia/latest-release (viewed Sept 2020).
- 4. Pharmacy Programs Administrator . COVID‐19 home medicines service. www.ppaonline.com.au/programs/covid-19-home-medicine-service (viewed Sept 2020).
- 5. Australian Department of Health . COVID‐19 temporary MBS telehealth services. Updated 23 Sept 2020. http://www.mbsonline.gov.au/internet/mbsonline/publishing.nsf/Content/Factsheet-TempBB (viewed Sept 2020).
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Supplementary Materials
Supplementary Material Supplementary methods and results


