Figure 2.
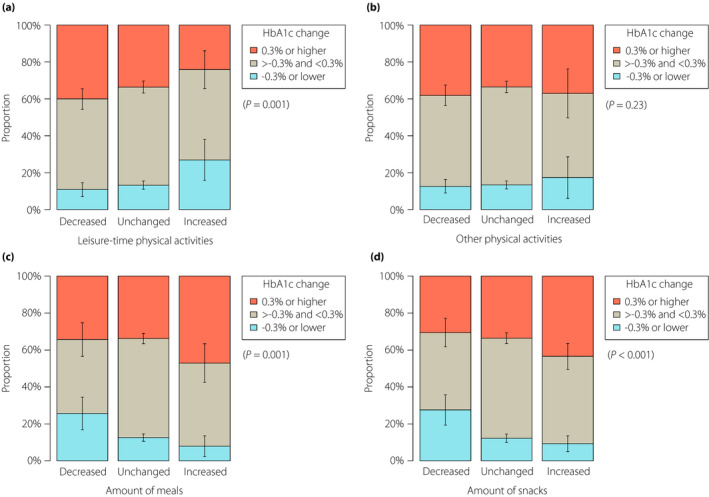
Clinically important hemoglobin A1c (HbA1c) change by lifestyle change during the coronavirus disease 2019 pandemic. Data are proportions and 95% confidence intervals of clinically important change of HbA1c levels (i.e., HbA1c increase or decrease by ≥0.3% between February and May 2020) in subgroups classified according to the change of (a) leisure‐time physical activities, (b) other outside physical activities, (c) the amount of meals and (d) the amount of snacks. P‐values were derived from the cumulative link models.
