FIGURE 5.
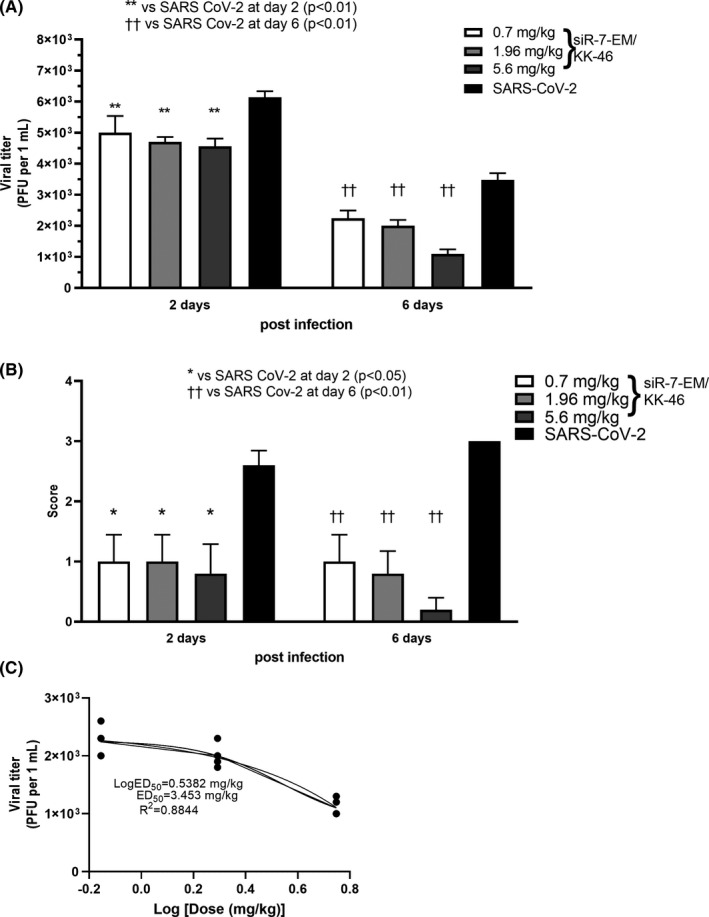
Dose‐dependent inhibition of SARS‐CoV‐2 reproduction with modified siR‐7‐EM‐peptide dendrimer KK‐46 complexes in Syrian hamsters after repeated inhalation exposure. Syrian hamsters were infected with SARS‐CoV‐2 with a dose of 105 PFU/animal and treated with three doses of the modified siR‐7‐EM‐peptide dendrimer KK‐46 complexes (35, 98 and 289 μg siR‐7‐EM/animal, 0.7, 1.96 and 5.6 mg KK‐46/kg, respectively). Inhalations with complexes were repeated daily for six days. Two and six days after infection animals were sacrificed and determination of viral titer (A) and macroscopic evaluation plus scoring of histopathology (B) in the lung were performed. The results are expressed as plaque forming units (PFU) per mL (A) or scores (B) obtained for histological analysis of pathologic alterations in hamsters’ lung. (C) Dose‐response curve of SARS‐CoV‐2 levels in the lungs at day six after infection, where the ED50 estimation is ∼ 3.453 mg/kg. Differences between multiple groups were estimated using a Kruskal–Wallis test followed by post‐hoc testing (if the Kruskal–Wallis was significant) using un‐paired Mann‐Whitney U tests. Bars show medians of one experiment (five animals per group) + SDs. Data are provided for one experiment representative of two independent experiments with five hamsters /group. Footnotes: */† represent differences with hamsters infected with SARS‐CoV‐2 and assessed at day two/six after infection, respectively. **††p < 0.01, *p < 0.05
