Figure 1.
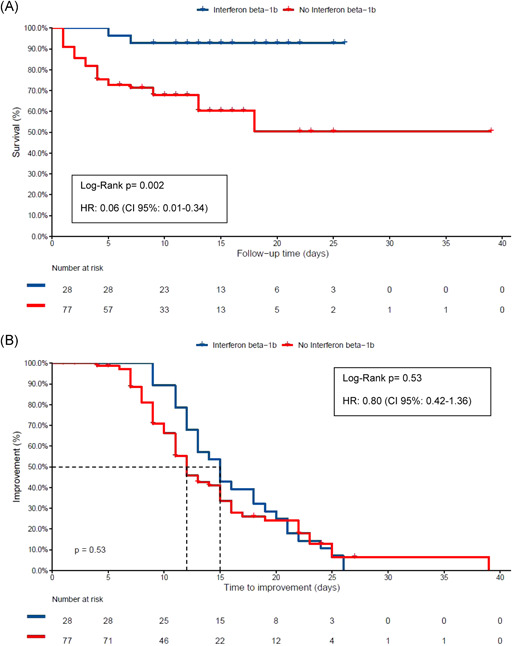
(A) Cumulative survival and hazard ratio (HR) in the control group and interferon β‐1b (INFβ‐1b) treated group. Patients not discharged were exitus letalis or hospitalized in the intensive care unit. Kaplan‐Meier and Cox hazards analyses were used. (b) Kaplan‐Maier plot for time to clinical improvement. Clinical improvement was defined as two points decrease in the WHO's Eight‐category scale or live discharge from the hospital, whichever occurs first. Not discharged patients (censored patients) died. Cox regression was adjusted for propensity score index for interferon use, oxygen requirements (patients requiring noninvasive mechanical ventilation [NIMV], high flow nasal cannula or FiO2 > 0.40, or patients requiring supplemental oxygen with FiO2 < 0.40) and corticosteroids. To calculate the propensity score index, sex, age, diabetes, hypertension, obesity, CURB‐65 at admission, and C‐reactive protein were included
