Fig 2.
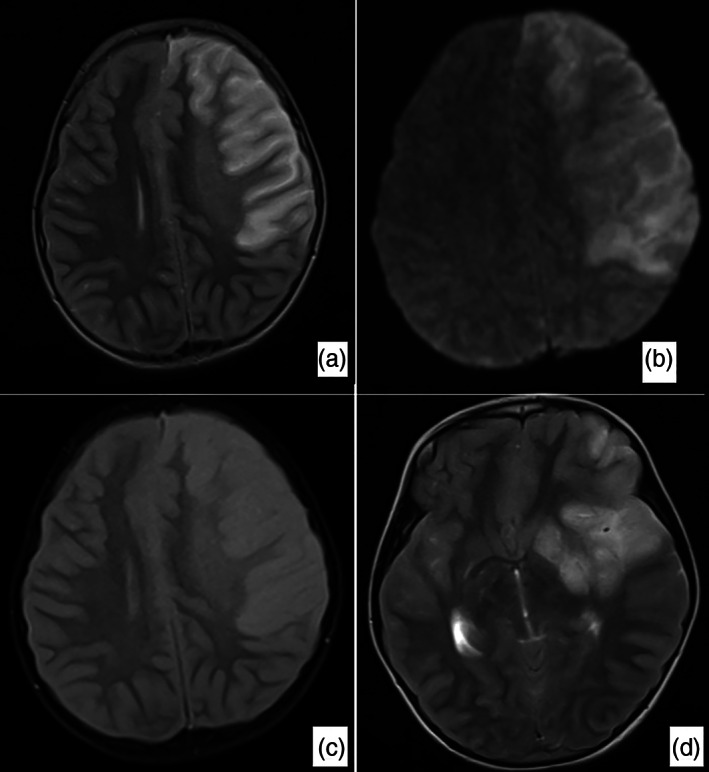
Brain magnetic resonance imaging, a large infarct area affecting the majority of the left frontal lobe and the anterior part of the parietal lobe and creating a compression effect on the left lateral ventricle was detected. Widespread signal increase was present in T2‐weighted, Fluid‐Attenuated Inversion Recovery (FLAIR) and Diffusion‐Weighted Imaging (DWI) sequences (a–c). In the T2‐weighted sequence, the signal void in the right middle and anterior cerebral artery was observed in the cross section passing through the Willis polygon level, while the signal void in the middle cerebral.
