Abstract
Testing provides essential information for managing infectious disease outbreaks, such as the COVID‐19 pandemic. When testing resources are scarce, an important managerial decision is who to test. This decision is compounded by the fact that potential testing subjects are heterogeneous in multiple dimensions that are important to consider, including their likelihood of being disease‐positive, and how much potential harm would be averted through testing and the subsequent interventions. To increase testing coverage, pooled testing can be utilized, but this comes at a cost of increased false‐negatives when the test is imperfect. Then, the decision problem is to partition the heterogeneous testing population into three mutually exclusive sets: those to be individually tested, those to be pool tested, and those not to be tested. Additionally, the subjects to be pool tested must be further partitioned into testing pools, potentially containing different numbers of subjects. The objectives include the minimization of harm (through detection and mitigation) or maximization of testing coverage. We develop data‐driven optimization models and algorithms to design pooled testing strategies, and show, via a COVID‐19 contact tracing case study, that the proposed testing strategies can substantially outperform the current practice used for COVID‐19 contact tracing (individually testing those contacts with symptoms). Our results demonstrate the substantial benefits of optimizing the testing design, while considering the multiple dimensions of population heterogeneity and the limited testing capacity.
Keywords: COVID‐19 testing, heterogeneous population, partition problem, pooled testing, resource allocation under limited resources
1. INTRODUCTION
Testing is a key element in managing disease outbreaks such as the COVID‐19 pandemic. As the WHO Director‐General states, “The most effective way to prevent infections and save lives is breaking the chains of transmission, and to do that you must test and isolate. We cannot stop this pandemic if we don't know who is infected” (World Health Organization, 2020). Unfortunately, inadequate testing capacity for COVID‐19 remains a serious problem in the United States, especially as more people go back to work, schools, and universities open, and stay‐at‐home restrictions are no longer in place. Furthermore, “most of the very limited testing capacity available today [for COVID‐19] is being used therapeutically (to ensure correct diagnosis for treatment) or in an unprioritized manner” (Allen et al., 2020). However, as we show in this paper, this is not necessarily the most effective utilization of the limited testing capacity for diseases such as COVID‐19, which are life‐threatening, highly contagious, have symptoms that are non‐specific (e.g., flu‐like), and can be spread by presymptomatic and/or asymptomatic individuals, which is thought to have played a major role in the COVID‐19 pandemic (Bai et al., 2020; Gandhi et al., 2020; Rothe et al., 2020; Zhang et al., 2020). Allocating the limited testing capacity among the potential testing population for the screening of such diseases, based on the heterogeneity of the testing population with respect to key dimensions important for testing, is the problem studied in this paper.
As a motivating example, consider contact tracing, where people having had contact with known infected individuals (i.e., with potential for disease transmission) are identified for appropriate follow‐up, which, in the case of COVID‐19, can involve isolation, quarantine, symptom monitoring, and/or testing. For example, Burke (2020) describes contact tracing for 10 COVID‐19‐infected subjects in the United States, finding 445 contacts. Korea Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (2020) describes the first 30 COVID‐19 cases in South Korea, and their 2370 contacts. These examples show the scope of the problem, and how the number of contacts, and thus potential transmission, grow quickly. In both of these cases, testing was reserved for symptomatic contacts; because transmission of COVID‐19 from presymptomatic and asymptomatic subjects is possible, this testing decision is not necessarily optimal for reducing the spread of the infection.
1.1. Screening under limited testing resources
We consider a testing facility and a population of subjects that would potentially benefit from screening for a certain disease. The facility has a limited testing capacity in each testing period, therefore, it needs to determine which subjects to test, and how to test them, so that it does not exceed the testing capacity. The subjects are heterogeneous in multiple dimensions that are important to consider for testing. The screening test is an in vitro laboratory test that is conducted on specimens (e.g., nasal swabs) collected from the subjects; the specimens allow for pooled testing schemes, wherein specimens from multiple subjects are combined into a pool and tested with a single test (with follow‐up testing performed as needed, see below).
In particular, we consider a PCR testing machine (i.e., the PCR test, the main technology used for COVID‐19 testing as well as for other infectious diseases), which has a tray with a number of reaction wells (trays with 96 wells are common), where a test is performed in each well, on either an individual specimen or a pool of specimens. Thus the tray capacity dictates the number of tests that can be performed per testing run (Carter et al., 2020; Lu et al., 2020; Yelin et al., 2020). Once the wells are loaded with specimens and testing reagents, the machine runs for 2–4 h, at the conclusion of which test results become available (Wiesbauer, 2020). (While the specific parameters are based on the testing platform used, our models can handle the different platforms.) Thus, this testing problem is characterized by batch testing, and the number of batches that can be run per day determines the daily testing capacity.
Potential testing subjects stochastically arrive over time, and subjects are removed from testing consideration if not tested within a given testing window. However, due to the logistical complexities of, and the time required for, collecting specimens for those subjects to be tested, this problem needs to be discretized, thus using daily snapshots is very practical. Therefore, given a set of potential testing subjects at the time of decision‐making and a daily testing capacity, we model the tester's problem as selecting those subjects to be tested on the next testing day, along with how they are to be tested (i.e., which specimens to pool and which specimens to test individually), setting in motion specimen collection and pool formation, after which testing is performed. Once pools are formed for the day, how these pools and the individual testing specimens are split among the multiple batches (e.g., trays) of the day will not alter the expected number of tests for the day, due to the additive nature of this function (Equation (3)). That is, the tester can randomly use any of those specimens (preformed pools or individual specimens) until the tray reaches its capacity, and repeat this process throughout the day. A practical rule of thumb, however, would be to test the pools earlier during the day, to ensure that the required follow‐up individual tests are performed on the same testing day.
We model two important dimensions of population heterogeneity, that is, attributes that vary across subjects: (i) positivity risk, that is, the probability of having the infection, and (ii) preintervention and postintervention harm, that is, the consequences of the infection when undetected versus detected (with subsequent intervention, e.g., isolation, quarantine, symptom monitoring, etc.), respectively. These two dimensions are not necessarily correlated, that is, a subject with low positivity risk may result in high levels of harm (from a societal or individual point of view) if infected and undetected. For example, in the context of COVID‐19, the positivity risk depends on the nature of exposure with an infected individual, for example, activity, duration, proximity, environment (Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, 2020b; Korea Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, 2020; Wang et al., 2020); on the other hand, subjects with larger social or professional networks (e.g., students, teachers, healthcare professionals, grocery store workers) may lead to a higher societal harm if undetected, due to a higher potential to spread the infection. We use the terms “intervention” and “harm” in a broad manner. For example, an alternative definition of harm could be the medical consequences if a subject is not treated in a timely manner (which can be measured via traditional health outcome metrics, e.g., fatality rate, QALY), while interventions would then include medical treatments.
To improve coverage (the number of subjects tested) under limited testing capacity, we incorporate pooled testing into the testing strategy. In particular, we consider Dorfman testing, which is used in public health screening (e.g., donated blood screening, sexually transmitted disease screening, e.g., Aprahamian et al., 2016; McMahan et al., 2012, and the references therein), and is viable for COVID‐19 testing (via the PCR test), as recent examples demonstrate, for example, Abdalhamid et al. (2020), Boyd (2020), Eberhardt et al. (2020), Joseph (2020), Kim et al. (2020), Pilcher et al. (2020), and Yelin et al. (2020).
Compared to the aforementioned works, as well as other relevant works in the general pooled testing literature (see Section 1.2), the main contributions of our work include designing pooled testing strategies that consider the multiple dimensions of population heterogeneity, and the key performance metrics of screening (harm mitigation and coverage maximization) under limited testing capacity (i.e., when not testing a subject is an option). While this analytical framework applies to many infectious diseases, it applies particularly well to COVID‐19, because the most common test used for COVID‐19 is the PCR test, which has scarce capacity compared to testing demand, and subjects have multi‐dimensional attributes that are important to consider in the testing decision.
A specimen (e.g., swab) collected from a subject contains enough material for multiple tests. Under Dorfman testing, material from multiple subjects is combined into a single testing pool, and tested with a single test; if the pool tests negative, then all subjects in the pool are classified as test‐negative; and if the pool tests positive, then all subjects in the pool are individually re‐tested (via additional material from the specimens) and classified based on this outcome (Dorfman, 1943). Dorfman testing can increase efficiency, but if the test has imperfect sensitivity (true positive probability), then it will also have a higher false‐negative rate than individual testing, simply because a positive subject must be tested twice to be classified as positive. Mathematically speaking, the decision problem is to partition subjects into three mutually exclusive sets under limited testing resources: those individually tested, pool tested, and not tested. Additionally, those subjects tested in pools must be further partitioned into separate testing pools, potentially containing different numbers of subjects. If any of the pools is too big or too small, or has a combined positivity risk that is too large, the efficiency of pooled testing will be reduced. Testing subjects with multi‐dimensional heterogeneity complicates the pooling problem, because the subjects that are most beneficial to test can also have a higher positivity risk, leading to a higher number of tests. Thus, there can be a tradeoff between harm mitigation and testing efficiency.
Our objectives are to provide a data‐driven, optimization‐based framework for pooled testing design, which applies to many infectious diseases; and to demonstrate the potential benefits of this framework and derive specific insight in the context of COVID‐19 screening. To this end, our case study utilizes realistic data to study contact tracing schemes for COVID‐19. We demonstrate the potential benefits of the proposed testing strategies, with the hope that this will encourage practitioners to utilize similar models to overcome the aforementioned challenges in infectious disease screening. For this purpose, we also discuss the practical aspects of using our optimization‐based approaches for decision‐making, especially in the context of COVID‐19.
1.2. Contributions
From a methodological perspective, to the best of our knowledge, this paper is the first to analyze, and establish a theoretical framework for, the design of pooled testing strategies while considering multiple dimensions of population heterogeneity and the limited testing capacity. Integrating the multi‐dimensional heterogeneity of the testing population and the limited testing capacity with the pooled testing aspect is the key feature of our models: in our setting, the tester may not be able to test all the subjects in the testing population, and needs to select which subjects to test, and how. As a result, our performance metrics shifts from the traditional efficiency maximization paradigm commonly used in the pooled testing literature, which minimizes the expected number of tests needed for pooled testing so as to cover all the subjects in the testing population, to coverage maximization and harm mitigation under limited testing capacity. This is a major departure from the pooled testing literature, and gives rise to the new decision problems studied in this paper. In the following, we first discuss the general pooled testing literature, followed by the more recent, COVID‐19‐specific pooled testing literature.
The vast majority of the pooled testing literature assumes a homogeneous population, for example, Aprahamian et al. (2020), Eberhardt et al. (2020), Gollier and Gossner (2020), Gupta and Malina (1999), Kim et al. (2007), and Zenios and Wein (1998). Of particular relevance is the work in Aprahamian et al. ( 2020), which considers a homogeneous testing population and unlimited testing capacity, with the objective of minimizing the expected number of tests. In particular, Aprahamian et al. (2020) derive closed‐form expressions for the optimal Dorfman pool size that minimizes the expected number of tests in this setting under a deterministic prevalence rate of the population, but, needless to say, these expressions do not extend to our setting, with population heterogeneity, limited testing capacity, and different objective functions. Such one‐size‐fits‐all strategies, which stem from the homogeneous population assumption, are often suboptimal. A number of papers incorporate subject‐specific information into the modeling framework, but only through a single attribute (i.e., subject positivity risk), for example, Aprahamian et al. (2018, 2019), Hwang (1975), and McMahan et al. (2012). In contrast, this paper considers multiple dimensions of population heterogeneity, and constructs customized pooled testing strategies that are shown to substantially outperform existing approaches. The resulting formulations belong to a class of difficult combinatorial optimization problems, namely the constrained multivariate set partitioning problem, which, even in their simplified univariate unconstrained form are known to be NP‐complete (Chakravarty et al., 1982). As a result, the existing literature generally restricts the study to problem instances having a particular form, for example, specific objective functional forms or simple constraints (e.g., limit on the number of subsets in the partition) (Aviran & Onn, 2002; Chakravarty et al., 1985; Gal & Klots, 1995; Hwang et al., 1999, 2000; Onn & Schulman, 2001).
We exploit the structure of our problem to extract key insights on optimal testing designs, and take advantage of a reformulation technique in which the underlying set partitioning problem is cast as a more tractable network flow problem (Aprahamian et al., 2019). As a result, for coverage maximization, we are able to develop an exact polynomial‐time algorithm; and for harm mitigation, we provide a heuristic, identify a set of conditions under which the heuristic solution converges to the optimal harm solution, and bound its deviation from the optimal solution.
Because limited testing capacity continues to constrain COVID‐19 testing, there has been a recent interest in exploring pooled testing for COVID‐19, for example, Abdalhamid et al. (2020), Boyd (2020), Eberhardt et al. (2020), EurekAlert (2020), Gollier and Gossner (2020), Joseph (2020), Lohse et al. (2020), Mallapaty (2020), News Medical (2020), Park (2020), Wacharapluesadee et al. (2020) and Yelin et al. (2020). However, most COVID‐19 testing is still performed via individual testing, and, at least initially, testing mainly focused on symptomatic subjects, which made it difficult to detect those presymptomatic or asymptomatic subjects who could spread the disease. Furthermore, to the best of our knowledge, the pooled testing strategies used for COVID‐19 use pool sizes that are determined in an ad hoc manner, and testing pools, for the most part, are formed without considering the heterogeneity of the testing population.
There is a recent stream of COVID‐19‐specific pooled testing papers, but all these papers consider a homogeneous population, for example, Abdalhamid et al. (2020), Eberhardt et al. (2020), Gollier and Gossner (2020), Mallapaty (2020), and Wacharapluesadee et al. (2020). In particular, Eberhardt et al. (2020) use Monte Carlo simulation to compare the efficiency of various pooled testing strategies, whereas Gollier and Gossner (2020) determine an optimal pool size that maximizes the proportion of pools that test negative, and Mallapaty (2020) considers various pooled testing strategies, including Dorfman testing, three‐stage pooling schemes, and a one‐stage pooling scheme with overlapping pools. On the other hand, Abdalhamid et al. (2020) and Wacharapluesadee et al. (2020) study the efficiency of pooled testing for COVID‐19 using fixed pool sizes, of 5 and 10, respectively.
Our case study on contact tracing, an important tool in managing disease outbreaks, illustrates the benefits of the proposed testing strategies. Under realistic parameters, a common strategy, of individually testing only the symptomatic contacts, increases harm (measured, in the case study, in terms of future infections) by 261% over our harm mitigation strategy. On the other hand, a strategy of individually testing contacts with the highest expected harm (thus taking into account both measures of heterogeneity considered in this paper) increases harm by 99% over our harm mitigation strategy, underscoring the value of allowing for pooled testing for a heterogeneous population (the harm mitigation strategy often uses a combination of individual and pooled testing in the case study). We also show that the objective of maximizing coverage under limited tests (which is closely related to a common pooled testing objective of minimizing the number of tests used, e.g., Abdalhamid et al., 2020; Aprahamian et al., 2016, 2019; McMahan et al., 2012) substantially underperforms in terms of harm mitigation, especially if complete coverage is not attainable. We further study the effect of estimation error in subject‐specific parameters, and find that when risk and preintervention harm values of each subject randomly deviate by ±20% from their estimated values, the expected harm resulting from our harm mitigation strategy only deviates by, on average, 4.1%, from its estimated value, while significantly outperforming the other strategies tested. Our numerical study also indicates that a point estimation of subject‐specific risk and harm values is not necessary, rather, a practical approach of simply categorizing each subject with respect to their risk and harm (e.g., high, moderate, low) works well for the proposed strategies. This research is timely and important, and while it is motivated by COVID‐19, it is applicable to other infectious diseases.
The remainder of this paper is organized as follows. Section 2 discusses the notation and models; Section 3 provides key structural properties and algorithms; Section 4 discusses some limitations of, and practical considerations for, our models; Section 5 presents a case study on contact tracing; and Section 6 discusses the conclusions. All mathematical proofs are relegated to the Appendix.
2. NOTATION, PRELIMINARIES, AND MODELS
Testing serves to identify the subjects that are positive for an infection. A test produces either a positive or a negative outcome, and all test‐positive subjects undergo some intervention to mitigate harm. In each testing period (e.g., a day), the tester (a certain testing facility) has a daily testing capacity of tests, and faces a testing population of S = {1, …, N}, where (otherwise the trivial solution is to test each subject individually, i.e., with one test per subject). Thus, N and are both known at the time the tester makes the testing decision for the next testing period. Note that the tester will need to solve the testing problem repeatedly, once for each testing period, and will face a potentially different testing population (with new arrivals and leftover subjects) in each testing period, hence, the value of parameter N (and perhaps ) may vary over time. However, for our purposes, the testing problem is solved for one period at a time, based on a static testing population that is present at the current time, as discussed in Section 1.1.
The tester can use Dorfman pooled testing to expand the testing coverage (i.e., the number of subjects tested); and wishes to design a testing strategy to either achieve the largest harm reduction possible, or to maximize the coverage. The test is not perfect, with sensitivity (true positive probability, denoted by se), or specificity (true negative probability, denoted by sp), that may be less than 1; and the test's sensitivity remains the same under pooled testing.
Throughout, we use the superscript index m to refer to a subject, subscript index i to refer to a pool, and omit the index to refer to all subjects in set S, that is, X m for subject m and X i for pool i. We use |S| to denote the cardinality of set S.
Subjects are heterogeneous: subject m ∈ S has positivity risk, p m ∈ [0, 1], and if infected, then preintervention and postintervention harm, and , respectively, with intervention benefit, (i.e., intervention reduces the harm). For analytical tractability, we assume that each subject m ∈ S is infected according to an independent Bernoulli distribution with probability p m ; if a positive subject is not detected (i.e., either not tested, or tested but not detected), then the preintervention harm will be realized, and if detected, then the postintervention harm will be realized; and the harm faced by the society is additive.
Then, for each subject in S, the tester must decide if the subject is to be tested or not, and if tested, whether individually or in a pool, and if in a pool, then the size and composition of the pool. The decision problem is to find the best feasible partition of set S for a certain objective (i.e., minimize harm or maximize coverage), under a limit on the number of tests (). We represent a partition by a combination of mutually exclusive sets, Ω = (Ω0, Ω I , Ω P ), such that ∪ i ∈ {0, I, P}Ω i = S, and Ω i ∩ Ω j = ∅, for all i, j ∈ {0, I, P} : i ≠ j; where the subjects in Ω0 are not tested, those in Ω I are individually tested, and those in Ω P are pool tested. We further partition the pooled testing set, Ω P , into mutually exclusive subgroups (testing pools), Ω P = (ω i ) i = 1, …, g , for some g ∈ Z +, such that |ω i | > 1 and the subjects in each subgroup ω i are tested together via Dorfman testing with pool size |ω i |. For any partition Ω of set S, we define random variables H(Ω) and T(Ω) to respectively denote the harm and number of tests, and the counting variable C(Ω) to denote the coverage, for all subjects in set S; and attach superscript index m and subscript index i when referring to their counter‐parts per subject and per pool.
Specifically, our measure of harm represents a weighted sum of false‐negatives and true‐positives, that is, an infected subject will incur a preintervention harm if undetected, and a (reduced) postintervention harm if detected. Because an infected subject will be detected with probability se if tested individually, and with probability se × se if tested within a pool (i.e., the pooled test outcome is positive and the individual test outcome is positive), and not detected in the absence of testing, the expected harm for any subject m ∈ S follows:
| (1) |
The coverage indicator for any subject m ∈ S follows:
| (2) |
Regarding the expected number of tests, following Aprahamian et al. (2019), for each pool Ω i , i = {0, I, P}:
| (3) |
Thus, for any partition Ω, both the expected harm and coverage of a subject depend only on whether the subject is in set Ω I , Ω P , or Ω0, that is, for a subject that is pool tested, it does not depend on the pool size or the other subjects in the pool. On the other hand, the expected number of tests does depend on both pool composition and size, because the probability that the pool tests positive is a nonlinear function of the positivity risk of all the subjects in the pool.
The decision problem is to determine a partition Ω of set S, under a limit on the number of tests (), so as to: (i) minimize the expected harm, E[H(Ω)], that is, harm minimization problem (HP); or (ii) maximize the coverage, C(Ω), that is, coverage maximization problem (CP).
| (4) |
| (5) |
| (6) |
where E[H(Ω)], C(Ω), and E[T(Ω)] are as given in Equations (1), (2), and (3), respectively. We use the superscript *k, k ∈ {H, C}, to denote an optimal partition to HP and CP, respectively, that is, Ω *k denotes an optimal partition, which is comprised of sets , , and , with an optimal objective function value of C * ≡ C(Ω *C ) for CP, and E[H *] ≡ E[H(Ω *H )] for HP.
Next, we establish important structural properties of optimal partitions, which allow us to develop an exact algorithm for CP and an effective heuristic for HP.
3. STRUCTURAL PROPERTIES AND ALGORITHMS
The ordering of the subjects in the potential testing population (set S) with respect to a certain attribute will play a key role in the proposed solution algorithms. To represent different specific orderings of the subjects, we use the notation S(p) and S(p × δ) to respectively denote a nondecreasing ordering of the subjects in set S with respect to parameter p, and with respect to parameter p × δ, with ties broken arbitrarily unless specified otherwise. In particular, sets S(p) and S(p × δ) are constructed to respectively focus on improvements in the number of tests (Equation (5)) and the harm (Equation (4)).
Lemma 1
Among all partitions with cardinalities |Ω I |, |Ω P |, and |Ω0|, the partition in which subjects {1, …, |Ω0|} in set S(p × δ) are not tested (i.e., in set Ω0), subjects {|Ω0| + 1, …, |Ω0| + |Ω P |} in set S(p × δ) are tested in pools (i.e., in set Ω P ), and subjects {N − |Ω I |, …, N} in set S(p × δ) are tested individually (i.e., in set Ω I ) minimizes the expected harm, E[H(Ω)], but this partition is not necessarily feasible for HP.
Corollary 1
Consider that there is no pooled testing (Ω P = ∅). Then, the partition in which subjects in set S(p × δ) are not tested, and subjects in set S(p × δ) are individually tested is optimal for HP.
Lemma 1 and Corollary 1 consider partitions that follow the ordered set S(p × δ) (i.e., based on a nondecreasing order of the subjects with respect to the parameter p × δ), that is, each group (individual testing, pooled testing, and no testing) contains a number of subjects that are ordered consecutively in set S(p × δ). However, in general an optimal HP partition does not necessarily follow an ordered set, and HP remains ‐hard (Chakravarty et al., 1982).
As we shall see subsequently, a relevant problem is to minimize the expected number of tests when the only constraint is that all subjects are tested. In this case, there exists an optimal partition that follows the ordered set S(p) (i.e., based on a nondecreasing order of the subjects with respect to the parameter p), leading to an equivalent representation of the underlying set partitioning problem as a network flow problem (Aprahamian et al., 2019), as summarized in Property 1.
Property 1
(From Aprahamian et al., 2019) The problem of determining a partition of set S that minimizes the expected number of tests, E[T(Ω(S))], under the constraint that all subjects in set S are tested (Ω0 = ∅), can be formulated as a Shortest Path Problem (SP(S)) on graph G = (V, E). Specifically, graph G is comprised of vertex set, V = S(p) ∪ {N + 1}, that is, each subject in the ordered set S(p) represents a vertex (indexed based on the subject's order in set S(p)), with vertex N + 1 representing a dummy vertex; and edge set, E = {(i, j) : i > j}, with edge (i, j) corresponding to a pool comprised of subjects {i, i + 1, …, j − 1}, with weight corresponding to the expected number of tests for the pool. In this graph representation, each path from vertex 1 to vertex N + 1 corresponds to an ordered partition of set S(p), which we define as a partition in which every pool is comprised of subjects with consecutive indices in set S(p). Furthermore, the set of all paths from vertex 1 to vertex N + 1 in G is equivalent to the set of all ordered partitions of set S(p).
Aprahamian et al. (2019) show that there exists an optimal partition (i.e., which minimizes the expected number of tests, under the constraint that all subjects are tested) that is an ordered partition of set S(p), and that this optimal partition corresponds to the Shortest Path from vertex 1 to vertex N + 1, which we denote by Ω *SP (S). Because G is a directed acyclic graph with nonnegative weights, the Shortest Path Problem can be solved via a topological sorting algorithm in .
To illustrate the paths implied by graph G in Property 1, consider a testing population with 10 subjects (N = 10). Then, path 1 → 5 → 11 in graph G corresponds to the ordered partition, {{1,2,3,4}, {5,6,7,8,9,10}}, that is, the four lowest risk subjects are placed in one pool, while the remaining subjects are placed in another pool. Observe that this grouping follows because the graph is constructed based on the ordered set S(p).
Turning our attention to CP, the following algorithm takes advantage of the fact that the coverage objective depends only on whether a subject is tested (individually or in a pool) or not, while for any given set of subjects to be tested, there exists an expected number of test minimizing partition that follows the ordered set S(p) (Property 1).
Algorithm 1. CP (ALGM‐CP).
1.

Theorem 1
ALGM‐CP Part 1 solves CP to optimality; and the optional Part 2 reduces the expected harm (E[H]) without altering the coverage. The computational complexity is .
ALGM‐CP works as follows: Part 1 of the algorithm maximizes coverage by finding a feasible set S 0 (i.e., the set of subjects that are not tested) with minimum cardinality. Initially starting with a set S 0 that is empty (i.e., all subjects are tested), at each iteration the algorithm fixes set S 0, and determines the minimum expected number of tests required to test the remaining subjects, that is, in set S 2 = S\S 0, which contains those subjects that can be either tested individually or in a pool, based on partition Ω *(S 2): if a feasible solution exists (i.e., the number of tests required for set S 2 does not exceed ), then maximum coverage is attained, and Part 1 is completed; otherwise, the highest risk subject (i.e., the subject that contributes most to the number of tests) in set S 2 is moved to the no testing set S 0, and the process is repeated until a feasible solution is found, that is, maximum coverage is attained.
Given an optimal coverage partition from Part 1, Steps 3–6 then obtain an alternative optimal coverage partition (if one exists) in which the value of the optimal coverage is attained, while a number of the highest risk subjects in the pooled testing set are moved to the individual testing set S 1 (this improves harm without altering coverage, see Equation (1)). This is done by moving the subject with the highest p × δ value (i.e., the subject that contributes the most to the expected harm function) in set S 2 to set S 1: if this solution is feasible (i.e., the number of tests required for sets S 1 and S 2 does not exceed ), then the incumbent partition is updated and the process is repeated, otherwise the algorithm moves to Step 7. Then, Step 7 swaps the subjects in sets S 0 (no testing set) and S 1 (individual‐testing set), if feasible, to reduce harm, again without altering the coverage. This follows because the subjects in sets S 0 and S 1 can be interchanged without altering the number of tests (Equation (3)), but the composition of sets S 0 and S 1 does affect harm (Equation (1)).
While ALGM‐CP produces a partition Ω *C that is optimal for CP, that is, with maximum coverage (with subjects not tested), this partition is also optimal for HP for some special cases. Further, this CP‐optimal partition allows us to derive a lower bound for HP, via constructing an alternative partition having the same coverage as Ω *C , but one that is not necessarily feasible with respect to constraint (5).
Lemma 2
Consider that se = 1. If the partition produced by ALGM‐CP is such that , then this partition must be optimal for HP.
If the partition produced by ALGM‐CP is such that , then this partition must be optimal for HP.
Lemma 3
Construct a partition in which subjects in set S(p × δ) are not tested, subjects in set S(p × δ) are pool tested, and subjects in set S(p × δ) are individually tested, where denotes the size of the no testing group in the CP‐optimal partition. The harm corresponding to this partition provides a lower bound for HP:
Next we provide a heuristic for HP that utilizes the ordered set S(p × δ) (breaking ties arbitrarily), and has computational complexity .
Algorithm 2. HP (ALGM‐HP).
1.

ALGM‐HP works as follows: the algorithm initially starts by including the subjects with the highest p × δ values in set S 1, which contains those subjects that are tested individually, and does not assign any subject to set S 0, which contains those subjects that are not tested. In Steps 1 and 2, the algorithm fixes sets S 0 and S 1 in an iterative manner, and determines a partition of set S 2 = S\(S 0 ∪ S 1) that minimizes the number of tests needed to test all the subjects in set S 2, given by Ω *(S 2): if this partition is not feasible with respect to the testing capacity constraint (i.e., the number of tests required for sets S 1 and S 2 exceeds ), then the algorithm moves to Step 3, where the subject with the lowest p × δ value (i.e., the subject that contributes the least to the expected harm function) in set S 2 is moved to the no testing set S 0, and the process is repeated until a feasible solution is found, that is, set S 0 has the smallest feasible cardinality. If the partition in Steps 1–3 is better than the current incumbent partition, then the incumbent partition is updated; otherwise the current incumbent partition remains unchanged (Steps 4 and 5). Then in Step 6 the algorithm reduces the number of subjects that are individually tested (i.e., the cardinality of set S 1) by one, and the process, that is, Steps 1–6, is repeated until the individual testing set S 1 is empty, which corresponds to the last evaluated solution before the algorithm terminates in Step 7, at which point all possible cardinalities of set S 1, , are considered.
The following lemma characterizes the special cases for which ALGM‐HP produces an optimal solution for HP.
Lemma 4
Consider that se = 1. If the partition produced by ALGM‐HP is such that either , or , then this partition must be optimal for HP.
If p m = p, ∀m ∈ S, the partition produced by ALGM‐HP is optimal for HP.
4. MODEL LIMITATIONS AND PRACTICAL CONSIDERATIONS
For analytical tractability, our models rely on certain assumptions that may not necessarily hold in reality. In order to reduce the gap between the mathematical models developed in this paper and their practical application for designing COVID‐19 testing strategies, we discuss some limitations of our models, and how they could be addressed in practice.
Dilution effect: We assume that test sensitivity remains unchanged with pool size. In reality, test sensitivity may reduce as pool size increases because of the dilution of the viral load of the disease‐positive specimen(s) in the pool by the disease‐negative specimens; this phenomenon is referred to as the dilution effect in the literature, for example, Nguyen et al. (2019). To model test sensitivity as an explicit function of pool size, extensive testing data are needed, and in the absence of such data, the tester can simply impose an upper bound on the allowable pool sizes (i.e., a pool size limit) so that the dilution effect is negligible for pool sizes that do not exceed the upper bound. This is a common approach in the pooled testing literature, and is the direction we pursue in the case study (Section 5). This is also in alignment with current studies that investigate the sensitivity of the PCR test for COVID‐19, and indicate that the dilution effect is negligible up to certain pool sizes, for example, Lohse et al. (2020), Mallapaty (2020), and Yelin et al. (2020).
Risk and harm estimation: Our models are constructed for the general setting where the risk and harm of each subject have continuous values. As a result, the number of possible subject categories (i.e., unique risk and harm combinations) is infinite. While this allows for modeling flexibility, the computational times for ALGM‐HP do not scale well for realistic problem instances (e.g., over a thousand subjects in the testing population). On the other hand, we also assume that each subject's risk and harm are known with certainty. In practice, risk and harm values are unobservable, and need to be estimated, and it is realistic to consider that one can estimate these variables in the form of categorical variables (e.g., high, moderate, low), as we do in the case study. In addition to being practical, this setting, with a discrete number of subject categories, allows us to improve the efficiency of ALGM‐HP substantially, by taking into consideration that subjects in each category are identical (hence interchangeable).
Risk independence: We assume that each subject becomes disease‐positive independently of the other subjects. While this assumption is reasonable in general, there may be cases where the disease status of certain subjects is positively correlated, for example, subjects belonging to the same household. However, the proportion of correlated subjects should be fairly small within the large testing population, and hence this assumption should not significantly impact the performance of the resulting testing strategies.
The need for a second swab: In general, a nasal swab, commonly used for COVID‐19 testing via a PCR test, has sufficient genetic material for multiple tests: Once the RNA is extracted, the lab dilutes the RNA sample for testing (under both pooled testing and individual testing protocols), and there is sufficient leftover RNA for multiple tests, which can be used for individual follow‐up testing as needed. Indeed, the current literature on COVID‐19 pooling and the literature on pooled testing in other contexts state that one specimen per subject is typically sufficient for pooled testing, for example, Ben‐Ami et al. (2020); and the Centers for Disease Control now provides discussion and guidance on pooling for COVID‐19 (Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, 2020a), which includes issues like dilution, but does not discuss the need to obtain another swab. Therefore, while there may be occasional cases where a second swab may be necessary, which may cause logistical challenges, we do not anticipate these cases to be in the majority.
5. CASE STUDY
To demonstrate the proposed harm mitigation and coverage maximization approaches to testing design, we consider a case study of COVID‐19 contact tracing via a PCR test. Throughout, we refer to the testing designs generated by ALGM‐CP and ALGM‐HP, which respectively maximize coverage and mitigate harm, as the CP and HP strategies.
Our objectives in the case study are two‐fold: (1) To compare the performance of CP and HP strategies with a testing strategy used in practice for contact tracing (Burke, 2020; Korea Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, 2020). To this end, we conduct a Monte Carlo simulation of a 12‐week testing period, where subject risk and harm estimates are assumed to be accurate. (2) To analyze the sensitivity of the results to uncertainty in harm and risk estimates, and to variations in test sensitivity; and to quantify the benefits of considering the two dimensions (risk and harm) of population heterogeneity in testing design. To this end, we conduct a second Monte Carlo simulation that randomly perturbs subject risk and harm values from their estimated values.
Next we describe the data and sources (Section 5.1), followed by discussion of the two simulation studies (Section 5.2).
5.1. Data and data sources
We construct a realistic scenario of a testing population comprised of potentially infected subjects (e.g., identified via contact tracing), to which new subjects are added stochastically over time. The testing population is generated based on data in two contact tracing studies (Burke, 2020; Korea Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, 2020), which respectively describe contact tracing for 10 COVID‐19‐infected subjects in the United States (with their 445 contacts), and the first 30 COVID‐19 cases in South Korea (with their 2370 contacts), as well as some other data from the literature. Each subject has an estimated positivity risk (p), and preintervention and postintervention harm (γ pre , γ post ), where the latter represents an infected subject's potential for spreading the disease (i.e., estimated number of new infections caused by the subject) if the disease is undetected (not tested, or tested but not detected) versus detected via testing (resulting in some intervention), respectively. We divide the subjects into eight categories based on their positivity risk and preintervention and postintervention harm, as we detail below.
With respect to the positivity risk, the subjects are divided into household (5% of all subjects) and other categories (in line with Burke, 2020; Korea Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, 2020), which report the proportion of household subjects as 4.3% and 5%, respectively), with household subjects having a higher risk. Each category is further divided into symptomatic (12.2% of subjects) and asymptomatic subjects (in line with Burke, 2020), which reports 12.2% of all subjects to be symptomatic; (Burke, 2020) does not break down the symptomatic subjects among household and other subjects, and we use 12.2% for both categories). The harm measure, as defined here, was not a concept discussed in either contact tracing paper (Burke, 2020; Korea Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, 2020), hence, we assume that around 10% of the subjects in each risk category is in the high‐harm (high‐spreader) category, and the remaining in the low‐harm (low‐spreader) category. The resulting proportion of subjects in each category is depicted in Table 1.
TABLE 1.
Proportion of subjects in each subject category based on positivity risk and harm
| Harm (preinterventionand postintervention) (γ pre , γ post ) | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| High (6.49, 0) | Low (3.08, 0) | ||
| Positivity risk (p) | Symptomatic household (0.10) | 0.061% | 0.549% |
| Asymptomatic household (0.05) | 0.439% | 3.951% | |
| Symptomatic other (0.005) | 1.159% | 10.431% | |
| Asymptomatic other (0.0025) | 8.341% | 75.069% | |
Next we discuss how one can estimate the positivity risk and harm of each subject category in general, and detail how we estimate the values used in Table 1.
Positivity risk: The probability that disease transmission from an infected subject to a contact occurs (p) can be estimated based on the nature of their interaction, for example, activity, duration, proximity, environment (Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, 2020b; Korea Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, 2020; Wang et al., 2020). Furthermore, both Burke (2020) and Korea Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (2020) report the transmission rates from infected to uninfected subjects for both household members and all subjects.
In particular, from Burke (2020), the estimated positivity risk is 0.45% for all subjects, and 10.5% for household members; and from Korea Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (2020), the estimated positivity risk is 0.55% for all subjects, and 7.56% for household members. We set the positivity risk of symptomatic subjects to 10% for household subjects (similar to the rate reported in Burke, 2020), and 0.5% for other subjects (similar to the rates reported in Burke, 2020; Korea Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, 2020). Burke (2020) and Korea Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (2020) do not provide this information for asymptomatic subjects, hence we assume their positivity risk to be 50% of their symptomatic counterparts (i.e., for asymptomatic subjects, 5% for household subjects and 0.25% for other subjects); see Table 1.
Harm: We measure the preintervention and postintervention harm (γ pre , γ post ) in terms of the expected number of new infections from a disease‐positive subject if the subject is undiagnosed versus diagnosed, respectively. This concept of harm is similar to the reproduction number R 0, but individualized, considering the value of a diagnosis in limiting the disease spread. While one strategy is to isolate all subjects without testing, this is not always practical, especially as the number of contacts increases, for example, in Korea Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (2020), the number of contacts per infected subject ranged from 15 to 649. Furthermore, not all contacts can be identified, and it may be more difficult to isolate, without testing, some essential workers, such as medical workers, due to labor shortages. Thus, in the absence of a diagnosis, the preintervention harm of a contact can be estimated based on their social/professional networks, living arrangement (institutional, roommate, large family), and profession.
In particular, to estimate the preintervention harm, γ pre , we use estimates of R 0 for COVID‐19. The meta‐analysis in Alimohamadi et al. (2020) leads to a mean R 0 value for COVID‐19 of 3.38 ± 1.40, with a range of 1.90–6.49. We set γ pre to 6.49 for high‐spreaders (the upper bound of the range in Alimohamadi et al., 2020), and 3.08 for low‐spreaders, which, when weighted by the proportions of high‐ and low‐spreaders in Table 1, yields the mean in Alimohamadi et al. (2020). For both categories, we set the postintervention estimated number of transmissions, γ post , to 0 (Table 1).
Daily testing capacity: Daily testing is limited by the capacity of the PCR testing machine. A common limit on the number of tests that can be performed by a PCR machine is 96 per testing run (i.e., the number of wells in a tray, see Section 1) (Carter et al., 2020; Lu et al., 2020; Yelin et al., 2020). Each testing run requires 2–4 h, including the preparation time (extracting and reverse transcribing the RNA) (Wiesbauer, 2020). Hence, we assume a testing run of 3 h and a total of three runs per day, leading to a maximum daily number of tests of .
Pool size limit: Recent studies indicate that screening for COVID‐19 using a pooled PCR test does not lead to a noticeable deterioration in classification accuracy for pools of up to 30 subjects, that is, the dilution effect is negligible for pools of 30 or less, for example, Lohse et al. (2020), Mallapaty (2020), and Yelin et al. (2020). As a result, we consider a pool size limit of 30.
Test sensitivity and specificity: The sensitivity of the PCR test is shown to be in the range 71%–98% for COVID‐19 (Arevalo‐Rodriguez et al., 2020). Therefore, we consider a test sensitivity of se = 0.90 as our base value, and complement this with one‐way sensitivity analysis on the se parameter. For test specificity, we consider sp = 0.95 based on Surkova et al. (2020) and Watson et al. (2020).
5.2. Simulation analysis
We present the results of two simulation studies, which respectively consider that the estimated subject risk and harm values are accurate (Section 5.2.1), and not accurate (Section 5.2.2).
5.2.1. Simulation study under accurate risk and harm estimates
We first compare CP and HP strategies with a contact tracing strategy used in practice (Burke, 2020; Korea Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, 2020), namely the Symptomatic Individual Testing Strategy (SI), which individually tests only the symptomatic subjects in the potential testing set, up to the daily testing capacity.
The Monte Carlo simulation spans a 12‐week period, with each week consisting of five testing days (Monday through Friday). For each testing day, we randomly generate a set of potential testing subjects, the size of which is uniformly distributed between 1500 and 2500 subjects. Each new subject is randomly assigned to one of the eight categories based on the proportions in Table 1; this categorization also provides the subject's risk and harm. Subjects not tested on the day they arrive roll over to the next testing day (with the exception discussed below); if they are still not tested on the second day after their arrival, then they are removed from testing consideration. Because the subjects in each category are interchangeable, as a policy, within each of the eight categories, we give testing priority to those subjects that were rolled over. On each Friday, all subjects that are not tested are removed from testing consideration. This policy reflects the importance of timely testing. Thus, the set of potential testing subjects on each testing day consists of the newly arriving subjects plus any subject that has rolled over from the previous testing day. We repeat this process for each of the 12 weeks independently. Figure 1A,B depict the weekly coverage and harm from HP, CP, and SI strategies, along with the size of the potential testing set and the lower bound on the optimal harm (from Lemma 3). We discuss our findings below.
Coverage: Not surprisingly, of the three strategies, CP leads to the highest coverage, testing, on average, 95.6% of the total testing population per week, and achieving full coverage on 7 out of the 60 testing days in the study period. HP tests, on average, 83.5% of the total testing population per week, and never reaches full coverage. This happens because, from a harm mitigation perspective, it becomes more advantageous to individually test some high‐risk, high‐harm subjects rather than expand coverage to low‐risk, low‐harm subjects. SI, which does not use pooled testing, has much lower coverage, with an average coverage of only 12.4%. Detailed weekly coverage results are displayed in Figure 1A.
Expected harm: The baseline expected weekly harm without any testing (i.e., the preintervention harm) is 197.8 on average, which HP reduces to 43.7 (a reduction of 78%). Of the three strategies considered, HP incurs the lowest expected weekly harm, and its harm closely tracks the lower bound on the optimal harm, LB(H *), from Lemma 3. CP and SI increase the expected weekly harm respectively by 118.3% and 261.0%, on average, over HP. The poor harm performance of SI stems from its low coverage, coupled with the fact that SI uses the presence of symptoms as the sole testing criterion, which does not perfectly coincide with risk and harm values, for example, for COVID‐19, there is considerable spread (and thus harm) from asymptomatic subjects (Burke, 2020; Korea Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, 2020). Detailed weekly harm results are displayed in Figure 1B.
FIGURE 1.
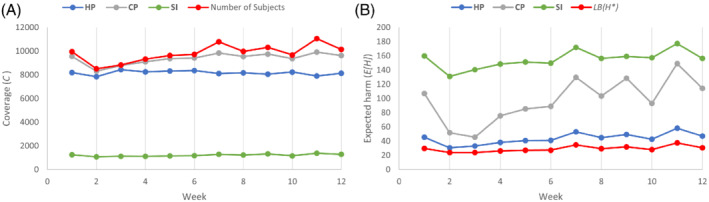
(A) The coverage (C) and (B) expected harm (E[H]) for CP, HP, and SI strategies over a 12‐week testing period
Furthermore, HP and CP use pool sizes between 5 and 23, well below the pool size limit of 30. While the pool sizes used for household members range between 5 and 7, those used for other categories range between 15 and 23.
5.2.2. Simulation study under inaccurate risk and harm estimates
Next, we expand our analysis to the setting where subject harm and risk estimates are not perfectly reliable. We do this through a second Monte Carlo simulation that simulates 1 week of testing under randomly perturbed subject risk and harm values. In addition to CP and HP, we consider two hypothetical strategies in the simulation, so as to illustrate the benefits of using two dimensions of heterogeneity and how this interacts with pooled testing. The new strategies are:
The Highest Harm Individual Testing Strategy (HI), which individually tests the subjects with the highest expected harm, that is, p × δ.
The Risk‐based HP Strategy (HP(risk)), which allows for pooled testing, but considering only one dimension of population heterogeneity, namely the risk. (This is equivalent to the current HP strategy, with the difference that all subjects are assumed to have identical harm, i.e., , , ∀m ∈ S).
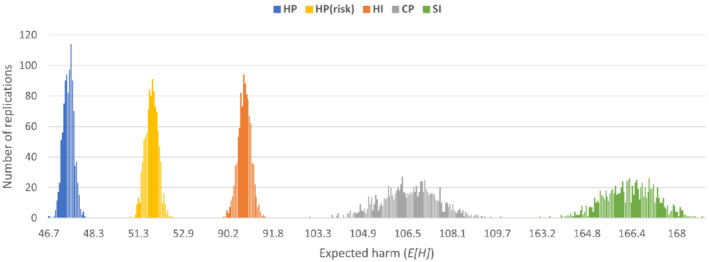
In the second simulation, we use the potential testing population generated for the first week of the simulation in Section 5.2.1, comprised of 9965 potential testing subjects. Then, in each of the 1000 replications, we randomly perturb each subject's risk and preintervention harm by ±20% from their estimates given in Table 1. The results are displayed in Figures 2 and 3B; and we discuss our findings below.
Expected harm: We depict the distribution (over 1000 replications) of the expected weekly harm incurred by each strategy (Figure 2). The harm incurred by HP is the lowest, and has the narrowest range (with an average of 47.4, and a range of 46.7 to 48.0). This is followed by the one‐dimensional HP variation, namely HP(risk) (with an average of 51.7), and then by HI, CP, and SI, with average values of 90.0, 106.5, and 166.3, respectively. Observe that the weekly harm values for HP, CP, and SI are higher than those reported for the first week of the first simulation (Section 5.2.1), because the uncertainty in risk and harm is more likely to increase the expected harm than decrease it (that is, p × δ deviates within the range of −36% to 44%).
Testing composition: Table 2 shows the distribution of the week's potential testing population among individual testing, pooled testing, and no testing sets under the different strategies, and Figure 3A,B depict how the various subject categories are placed into the different sets. CP maximizes coverage (at 95.9% for this first week) by solely using pooled testing, and, as a result, by neglecting those high‐risk subjects (i.e., symptomatic household contacts) who are less efficient to test in pools due to their high positivity risk. As opposed to this, HP individually tests symptomatic high‐ and low‐harm household contacts, as well as asymptomatic high‐harm household contacts: this is because these high‐risk subjects are not only less efficient to test in pools, but also lead to a higher number of false‐negatives when pool tested, making individual testing a better option for them.
FIGURE 2.
The distribution of expected harm (E[H]) for CP, HI, HP, HP(risk), and SI strategies over a 1‐week testing period
FIGURE 3.
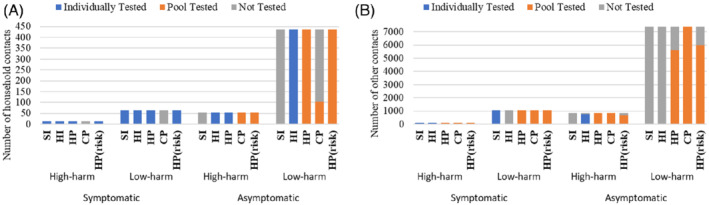
The number of subjects in the individual testing, pooled testing, and no testing sets (|Ω I | , | Ω P | , | Ω0|), for each subject category in Table 1, for CP, HI, HP, HP(risk), and SI strategies over a 1‐week testing period. (A) Household contacts. (B) Other contacts
TABLE 2.
The number of subjects in the individual testing, pooled testing, and no testing sets (|Ω I | , | Ω P | , | Ω0|) for CP, HI, HP, HP(risk), and SI strategies over a one‐week testing period (with 9965 potential testing subjects)
| Individually tested (|Ω I |) | Pool tested (|Ω G |) | Not tested (|Ω0|) | |
|---|---|---|---|
| CP | 0 | 9555 | 410 |
| HP | 130 | 8056 | 1779 |
| HP(risk) | 76 | 8325 | 1564 |
| HI | 1440 | 0 | 8525 |
| SI | 1248 | 0 | 8717 |
While HP(risk) individually tests symptomatic high‐ and low‐harm household contacts (similar to HP), it pool tests asymptomatic high‐risk household contacts (unlike HP); and the composition of other contacts that are pool tested under this strategy is skewed more towards those with a higher positivity risk. This leads to not being able to test some of the high‐harm subjects in the asymptomatic other category, who may have a relatively high contribution to the expected harm (Table 1 and Equation (1)). On the other hand, both HI and SI solely use individual testing, but HI outperforms SI in terms of harm. This is because HI prioritizes the testing of subjects with the highest expected harm (p × δ), while SI only tests symptomatic subjects, which is an imperfect measure of risk and harm.
Two dimensions of heterogeneity: HP and HP(risk) are similar, except that the former considers both risk and harm, while the latter considers only risk. As a result of ignoring the harm dimension, HP(risk) increases the expected weekly harm by 9.1% over HP. HP(risk) does not individually test any subject, as discussed above, and this is what causes most of the difference. (Overall, HP(risk) coverage is slightly higher than HP, due to not using individual testing, but lower than CP, as it selects subjects to be tested based on high risk, and not efficiency.) HI also uses both dimensions of heterogeneity, but it only performs individual testing; this leads to an increase in expected weekly harm of 89.8% over HP, demonstrating, once again, the value of pooled testing in this context.
Test sensitivity: We next discuss findings from a one‐way sensitivity analysis on the test sensitivity parameter, se. For illustrative purposes, we discuss our results for HP for a base case (se = 0.9). In particular, at each sensitivity value, we derive the true HP strategy, evaluate both the base case and the true HP strategies, and compare them. The efficiency (the expected number of tests) in the base case HP decreases (increases) as test sensitivity decreases (increases), because the pooled test detects the true‐positives in the pool less (more) frequently, decreasing (increasing) the number of individual follow‐up tests, but this effect is small, for example, when se changes from 0.90 to 0.85, the base case has only a 1.9% reduction in the expected number of tests. On the other hand, the expected harm increases (decreases) as test sensitivity decreases (increases), because the test's ability to detect the true‐positives reduces, for example, when se changes from 0.90 to 0.85, the base case has a 33% increase in harm, while HP specifically derived for se = 0.85 has a 30% increase over the base case. Thus, most of the increase in harm comes from having a less sensitive test, and not due to a change in testing design.
As this case study demonstrates, using multiple dimensions of heterogeneity, in conjunction with the option to select subjects for individual or pooled testing, or no testing at all, can significantly reduce harm.
6. CONCLUSIONS AND FUTURE RESEARCH DIRECTIONS
The models in this paper can be used to design testing strategies for infectious diseases under scarce testing resources, and should be informed by data‐driven estimates of key parameters, as well as an intervention strategy (a portfolio of interventions). The choice of interventions provides the structure needed for estimating the preintervention and postintervention harm, which could be extended to represent a multi‐dimensional harm vector (i.e., intervention‐specific). We consider harm and intervention in a broad manner. For example, in the case study we measure harm in terms of the number of future infections, but as we move towards effective treatments for COVID‐19, harm can be considered from the perspective of testing to detect people in need of treatment. This is especially important if there are limits on treatment capacity and/or advantages to early treatment, for example, before symptoms manifest. Our case study on COVID‐19 screening demonstrates the substantial benefits of a data‐driven, optimization‐based framework that incorporates multiple key subject‐specific characteristics and the limited testing capacity into the testing design. The key takeaway of this paper is that both aspects of the problem (i.e., key dimensions of population heterogeneity and test scarcity) are essential to consider by testing facilities for designing screening strategies for harm mitigation. This paper provides decision‐makers with the necessary analytical tools to achieve this objective.
This paper can be extended in a number of ways. The models studied in the paper can be generalized to consider stochastic risk and harm, which are unobservable in reality; or to consider that the disease status of some subjects may be correlated. In addition, test sensitivity is generally dependent on disease dynamics, testing too “early,” when the subject's viral load is low, can miss an infected subject, while testing too “late” can result in increased harm. Therefore, as a future direction, integrating the models presented in this paper with a disease progression model (e.g., Nguyen et al., 2019) could be beneficial. One could utilize such an integrated model to design strategies that might test a subject multiple times, based on an optimal schedule. Integrating the models presented in this paper with an epidemiology model could provide valuable insights, because part of the larger goal of testing is to reduce the effective reproduction number to below 1, so that the outbreak disappears. Another important dimension is to study the testing design when the tester can utilize a combination of screening tests (e.g., antibody test and a PCR test) such that, when combined, these tests can reduce the misclassification probability.
ACKNOWLEDGMENTS
We are grateful to Professors Ming Hu and Sanjay Mehrotra, the Associate Editor, and two anonymous reviewers for excellent suggestions that greatly improved the analysis and presentation of the paper. This material is based upon work supported in part by the National Science Foundation under Grant No. #1761842. Any opinion, findings, and conclusions or recommendations expressed in this material are those of the authors and do not necessarily reflect the views of the National Science Foundation.
APPENDIX A.
A.1. Mathematical proofs
We define:
| (7) |
respectively denoting the reduction in expected harm when testing a subject in a pool versus individually, and when not testing versus testing in a pool.
We first provide a supporting lemma that will be used in the subsequent proofs.
Lemma A.1
E[T P (Ω P )] is strictly increasing in p m , ∀m ∈ Ω P .
ΔH P − I (p, δ) is nondecreasing in p × δ, and ΔH 0 − P (p, δ) is strictly increasing in p × δ.
Proof of Lemma A.1
For any subgroup ω i ∈ Ω P , i = 1, …, g, and any subject m ∈ ω i , we have that E[T P (Ω P )] is linear in p m , and the coefficient of p m , , is strictly positive, and the result follows.
We have that ΔH P − I (p, δ) and ΔH 0 − P (p, δ) are linear in p and the coefficients of p, (se − se 2) and se 2 respectively, are nonnegative, and the result follows.
Proof of Lemma 1
We show that among all partitions with fixed cardinalities |Ω0|, |Ω I |, and |Ω P |, there exists a partition in which the no testing set, Ω0, includes |Ω0| subjects with the lowest p × δ values, that is, subjects {1, …, |Ω0|} in set S(p × δ), and the individual testing set, Ω I , includes |Ω I | subjects with the highest p × δ values, that is, subjects {N − |Ω I | + 1, …, N} in set S(p × δ) (hence the pooled testing set, Ω P , includes subjects {|Ω0|, …, N − |Ω I |}), such that this partition attains the minimum expected harm, E[H(Ω)], in the absence of constraint (5).
We start by showing that the no testing set, Ω0 includes subjects {1, …, |Ω0|} in set S(p × δ). To this end, assume that there is a partition in which the no testing set, Ω0, does not include the |Ω0| subjects having the lowest values of p × δ, and this partition yields the minimum expected harm E[H(Ω)]. Then, there must exist two subjects, i and j, such that i ∈ Ω0 : i ∈ S(p × δ), i > |Ω0| and j ∈ Ω I ∪ Ω P : j ∈ S(p × δ), j ≤ |Ω0|: If j ∈ Ω I , then swapping subjects i and j alters the harm by ΔH 0 − P (p i , δ i ) + ΔH P − I (p i , δ i ) − ΔH 0 − P (p j , δ j ) − ΔH P − I (p j , δ j ) > 0; and if j ∈ Ω P , then swapping subjects i and j alters the harm by ΔH 0 − P (p i , δ i ) − ΔH 0 − P (p j , δ j ) > 0, where both inequalities follow by definition of set S(p × δ), and because ΔH 0 − P (p, δ) is strictly increasing in p × δ and ΔH P − I (p, δ) is nondecreasing in p × δ (Lemma A.1). In either case, we have identified a partition that leads to a harm that is reduced over the original partition, without affecting the cardinalities of sets |Ω0|, |Ω I |, and |Ω P |.
Similarly, we show that the individual testing set, |Ω I |, contains subjects {N − |Ω I | + 1, …, N} in set S(p × δ). To this end, assume that there is a partition in which the individual testing set, Ω I , does not include the |Ω I | subjects having the highest values of p × δ, and this partition yields the minimum expected harm E[H(Ω)]. Then, there must exist two subjects, i and j, such that i ∈ Ω I : i ∈ S(p × δ), i < N − | Ω I | + 1 and j ∈ Ω0 ∪ Ω P : j ∈ S(p × δ), j ≥ N − | Ω I | + 1: if j ∈ Ω0, then swapping subjects i and j alters the harm by ΔH 0 − P (p j , δ j ) + ΔH P − I (p j , δ j ) − ΔH 0 − P (p i , δ i ) − ΔH P − I (p i , δ i ) > 0; and if j ∈ Ω P , then swapping subjects i and j alters the harm by ΔH P − I (p j , δ j ) − ΔH P − I (p i , δ i ) ≥ 0, where both inequalities follow by definition of set S(p × δ), and because ΔH 0 − P (p, δ) is strictly increasing in p × δ and ΔH P − I (p, δ) is nondecreasing in p × δ (Lemma A.1). In either case, we have identified a partition that leads to a harm that is either reduced or unchanged over the original partition, without affecting the cardinalities of sets |Ω0 | , | Ω I |, and |Ω P |. Thus, the partition in which the no testing set, Ω0, includes the lowest p × δ subjects, the individual testing set, Ω I , includes the highest p × δ subjects, and Ω P contains all other subjects, yields the lowest expected harm, among all partitions having cardinalities |Ω0 | , | Ω I |, and |Ω P |.
Proof of Corollary 1
The result follows from Lemma 1, because the partition described in the corollary arises as a special case of that in Lemma 1, with , |Ω P | = 0, and . Further, this partition uses tests, and hence is feasible with respect to constraint (5).
Property A.1
Consider that there is no individual testing (Ω I = ∅). Then, in light of Part 1 of Lemma A.1 among all partitions in which |Ω P | subjects are pool tested, the partition in which |Ω P | subjects with the highest p values, that is, subjects {1, …, |Ω P |} in set S(p), are pool tested yields the minimum expected number of tests, E[T(Ω)].
Proof of Theorem 1
We start by showing that Part 1 of ALGM‐CP solves CP to optimality. In Part 1 of the algorithm, the value of |Ω0| is iteratively increased from a starting value of zero. In each of the aforementioned iterations, the algorithm fixes the value |Ω0| and identifies the partition that minimizes the expected number of tests. Solving this optimization problem can be achieved by noting that (for fixed cardinality |Ω0|) the partition that minimizes the expected number of tests, E[T(Ω)], places the highest |Ω0| risk subjects in set Ω0 (Part 1 of Lemma A.1) and tests the remaining subjects according to the optimal scheme provided by Aprahamian et al. (2019) (Property 1). Part 1 of the algorithm terminates as soon as it identifies the first value of |Ω0| (denoted by ) that leads to a feasible partition, because further increasing |Ω0| does not improve the coverage. Because the partition obtained at each iteration minimizes the expected number of tests (for the corresponding value), represents the smallest possible number of subjects that are not tested. Consequently, Part 1 provides a solution with the maximum possible coverage, . Associated with this optimal solution are the sets and , which respectively correspond to the set of individually and pool tested subjects. Note that , as .
Next, we show that Part 2 of ALGM‐CP reduces the expected harm without altering the coverage of the Part 1 solution. In Part 2 of the algorithm, Steps 3–6 maximize the number of individually tested subjects in set while conserving the coverage C * that was identified in Part 1. This is achieved by an iterative procedure in which the number of individually tested subjects, |Ω I |, is fixed and the expected number of tests is minimized on the remaining subjects. This is done by noting that (for fixed cardinality |Ω I |) the partition that minimizes the expected number of tests, E[T(Ω)], places the highest |Ω I | risk subjects in set Ω I (Part 1 of Lemma A.1) and tests the remaining subjects according to the optimal scheme provided by Aprahamian et al. (2019) (Property 1). This procedure is repeated until feasibility is no longer satisfied. Note that the aforementioned procedure tests every subject in set , which is why the optimal coverage identified in Part 1 is maintained. Finally, Step 7 rearranges the subjects in sets and while conserving the cardinalities of these sets. Since the cardinalities are not impacted, then the total number of subjects getting tested is fixed and hence the optimal coverage, C *, will not be impacted. Moreover, since the expected number of tests for subjects that are either individually tested or not tested is independent of their risk, Step 7 will not impact the feasibility of the solution. Given this, and in light of Part 2 of Lemma A.1, assigning the subjects with the highest p × δ values in set to set and the remaining subjects to set provides the best possible harm. As such, Step 7 maintains the optimal coverage and feasibility while reducing the harm.
Regarding the computational complexity of ALGM‐CP, there exists an algorithm with complexity that solves SP(S) (Property 1); and Part 1 of the algorithm solves Problem SP(S) N − C * + 1 times (at most N times since C * ≥ 1) and Part 2 of the algorithm solves SP(S) C * times (at most N times since C * ≤ N). Thus, ALGM‐CP solves Problem SP(S) N + 1 times, and the result follows.
Proof of Lemma 2
If se = 1, we have that ΔH P − I (p m , δ m ) = 0, ∀m ∈ S, and E[H(Ω)] becomes independent of which subjects are tested individually or pool tested, as long as those subjects are tested (Equation (1)). We also have that ΔH 0 − P (p m , δ m ) > 0, ∀m ∈ S, that is, testing any subject (either individually or in a pool) will reduce the harm, compared to not testing the subject. Therefore, any feasible partition with Ω0 = ∅ must be optimal for HP.
If , then by Theorem 1, it is feasible to test at most subjects; and in case of no pooled testing, i.e., Ω P = ∅, it is feasible to test subjects individually. Then, Part 2 of ALGM‐CP results in individually testing the subjects with the highest p × δ values. Since ΔH P − I (p m , δ m ) ≥ 0, ∀m ∈ S, we have that, for any set of subjects, individually testing them will either reduce, or not affect, the harm over pool testing these subjects. Therefore, individually testing the subjects with the highest p × δ values must be optimal for HP, and the result follows.
Proof of Lemma 3
By definition, C * is the maximum number of subjects that can be tested; and is the maximum number of subjects that can be tested individually. Therefore, in an optimal solution to HP we must have that, and . Furthermore, because ΔH 0 − P (p m , δ m ) > 0, ∀m ∈ S, testing reduces the harm over not testing, and because ΔH P − I (p m , δ m ) ≥ 0, ∀m ∈ S, individual testing does not increase the harm over pooled testing (Equation (7)). In addition, for any fixed cardinalities, |Ω0|, |Ω I |, and |Ω P |, individually testing subjects with the highest p × δ values, and not testing subjects with the lowest p × δ values, leads to the lowest expected harm (Lemma 1). Therefore, the partition in which the subjects with the highest p × δ values are individually tested, the N − C * subjects with the lowest p × δ values are not tested, and the remaining subjects are pool tested, provides a lower bound on the optimal harm, E[H *].
Proof of Lemma 4
We start by proving the result under the condition that . If se = 1, we have that ΔH P − I (p m , δ m ) = 0, ∀m ∈ S, and the expected harm, E[H(Ω)], becomes independent of which subjects are tested individually and which subjects are tested in pools, as long as those subjects are tested (Equation (1)). We also have that ΔH 0 − P (p m , δ m ) > 0, ∀m ∈ S, that is, testing reduces the harm over not testing (Equation (7)). Therefore, any feasible partition with Ω0 = ∅ must be optimal for HP.
Next we prove the result under the condition that . By definition of C *, it is feasible to test at most C * subjects. By Lemma 1, and since ΔH 0 − P (p m , δ m ) > 0, ∀m ∈ S, we have that testing the C * subjects with the highest p × δ values must be optimal for HP, if such a partition is feasible. By the condition provided in the lemma, we have that , and by definition of ALGM‐HP, this partition tests the subjects with the highest p × δ values. Therefore, the partition suggested by Lemma 1, that is, not testing subjects in set S(p × δ), individually testing subjects {N−| Ω I | , ⋯, N} in set S(p × δ), and pool testing the remaining subjects, is feasible, and hence, must be optimal for HP.
First, we prove that there exists an optimal partition Ω*H in which the subjects with the highest p × δ values are individually tested, the subjects with the lowest p × δ values are not tested, and the remaining subjects are pool tested. By Lemma 1, if this partition is feasible, then it must be optimal for HP. Since p m = p, ∀m ∈ S, then the expected number of tests is independent of the partition of the subjects as long as , , and remain unchanged. Then, this partition is feasible, and hence, must be optimal for HP.
Next, we prove that ALGM‐HP generates this specific partition. The algorithm enumerates over the number of individually tested subjects, , and for each case, maximizes the number of subjects that are pool tested, . In particular, one of the iterations of ALGM‐HP considers the case where , and since p m = p, ∀m ∈ S, we must have that . Therefore, the result follows because the partition provided by ALGM‐HP individually tests the subjects with the highest p × δ values, and does not test the subjects with the lowest p × δ values.
El Hajj H, Bish DR, Bish EK, Aprahamian H. Screening multi‐dimensional heterogeneous populations for infectious diseases under scarce testing resources, with application to COVID‐19. Naval Research Logistics. 2022;69:3–20. 10.1002/nav.21985
Funding information National Science Foundation, Division of Civil, Mechanical and Manufacturing Innovation, 1761842
HistoryAccepted by Sanjay Mehrotra, healthcare management
DATA AVAILABILITY STATEMENT
The data that support the findings of this study were derived from resources available in the public domain; and all data sources are provided in Section 5 and the References Section of the paper.
REFERENCES
- Abdalhamid, B. , Bilder, C. R. , McCutchen, E. L. , Hinrichs, S. H. , Koepsell, S. A. , & Iwen, P. C. (2020). Assessment of specimen pooling to conserve SARS CoV‐2 testing resources. American Journal of Clinical Pathology, 153(6), 715–718. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Alimohamadi, Y. , Taghdir, M. , & Sepandi, M. (2020). The estimate of the basic reproduction number for novel coronavirus disease (COVID‐19): A systematic review and meta‐analysis. Journal of Preventive Medicine and Public Health, 53, 151–157. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Allen, D. , Block, S. , Cohen, J. , Eckersley, P. , Eifler, M. , Gosti, L. , Goux, D. , Gruener, D. , Hart, V. , Hitzig, Z. , Krein, J. , Langford, O. , Nordhaus, T. , Rosentha, M. , Seth, R. , Siddarth, D. , Simons, O. , Sitaraman, G. , Slaughter, A.‐M. , … Weyl, E. G. (2020). Roadmap to pandemic resilience. Edmond J. Safra Center for Ethics, Harvard University. [Google Scholar]
- Aprahamian, H. , Bish, D. R. , & Bish, E. K. (2016). Residual risk and waste in donated blood with pooled nucleic acid testing. Statistics in Medicine, 35(28), 5283–5301. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Aprahamian, H. , Bish, D. R. , & Bish, E. K. (2019). Optimal risk‐based group testing. Management Science, 65(9), 4365–4384. [Google Scholar]
- Aprahamian, H. , Bish, D. R. , & Bish, E. K. (2020). Optimal group testing: Structural properties and robust solutions, with application to public health screening. INFORMS Journal on Computing, 32(4), 895–911. [Google Scholar]
- Aprahamian, H. , Bish, E. K. , & Bish, D. R. (2018). Adaptive risk‐based pooling in public health screening. IISE Transactions, 50(9), 753–766. [Google Scholar]
- Arevalo‐Rodriguez, I. , Buitrago‐Garcia, D. , Simancas‐Racines, D. , Zambrano‐Achig, P. , del Campo, R. , Ciapponi, A. , Sued, O. , Martinez‐Garcia, L. , Rutjes, A. , Low, N. , Bossuyt, P. M. , Perez‐Molina, J. A. , & Zamora, J. (2020). False‐negative results of initial RT‐PCR assays for COVID‐19. A systematic review. 15, e0242958. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Aviran, S. , & Onn, S. (2002). Momentopes, the complexity of vector partitioning, and Davenport–Schinzel sequences. Discrete & Computational Geometry, 27(3), 409–417. [Google Scholar]
- Bai, Y. , Yao, L. , Wei, T. , Tian, F. , Jin, D.‐Y. , Chen, L. , & Wang, M. (2020). Presumed asymptomatic carrier transmission of COVID‐19. JAMA, 323(14), 1406–1407. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ben‐Ami, R. , Klochendler, A. , Seidel, M. , Sido, T. , Gurel‐Gurevich, O. , Yassour, M. , Meshorer, E. , Benedek, G. , Fogel, I. , Oiknine‐Djian, E. , Gertler, A. , Rotstein, Z. , Lavi, B. , Dor, Y. , Wolf, D. G. , Salton, M. , Drier, Y. , Klochendler, A. , Eden, A. , … Daitch, Y. (2020). Large‐scale implementation of pooled RNA extraction and RT‐PCR for SARS‐CoV‐2 detection. Clinical Microbiology and Infection, 26(9), 1248–1253. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boyd, C. (2020). Coronavirus swabs should be analysed in batches to speed up government's lagging testing programme, experts say . https://www.dailymail.co.uk/news/article‐8843949/Corvnavirus‐swabs‐analysed‐using‐pooled‐testing‐experts‐say.html
- Burke, R. M. (2020). Active monitoring of persons exposed to patients with confirmed COVID‐19—United States, January–February 2020. MMWR. Morbidity and Mortality Weekly Report, 69, 245–246. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carter, L. J. , Garner, L. V. , Smoot, J. W. , Li, Y. , Zhou, Q. , Saveson, C. J. , Sasso, J. M. , Gregg, A. C. , Soares, D. J. , Beskid, T. R. , Jervey, S. R. , & Liu, C. (2020). Assay techniques and test development for COVID‐19 diagnosis. ACS Central Science, 6(5), 591–605. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention . (2020a). Interim guidance for use of pooling procedures in SARS‐ CoV‐2 diagnostic, screening, and surveillance testing , 2020. https://www.cdc.gov/coronavirus/2019‐ncov/lab/pooling‐procedures.html
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention . (2020b). Public health recommendations for community‐related exposure . https://www.cdc.gov/coronavirus/2019‐ncov/php/public‐health‐recommendations.html
- Chakravarty, A. , Orlin, J. , & Rothblum, U. (1982). A partitioning problem with additive objective with an application to optimal inventory groupings for joint replenishment. Operations Research, 30(5), 1018–1022. [Google Scholar]
- Chakravarty, A. K. , Orlin, J. B. , & Rothblum, U. G. (1985). Consecutive optimizers for a partitioning problem with applications to optimal inventory groupings for joint replenishment. Operations Research, 33(4), 820–834. [Google Scholar]
- Dorfman, R. (1943). The detection of defective members of large populations. The Annals of Mathematical Statistics, 14(4), 436–440. [Google Scholar]
- Eberhardt J. N., Breuckmann N. P., and Eberhardt C. S. (2020). Multi‐stage group testing improves efficiency of large‐scale COVID‐19 screening. Journal of Clinical Virology, 128, 104382. 10.1101/2020.04.10.20061176. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- EurekAlert . (2020). COVID‐19: Pooled testing among recommendations to fix test, trace and isolate system . https://www.eurekalert.org/pub‐releases/2020‐10/s‐cpt101620.php
- Gal, S. , & Klots, B. (1995). Optimal partitioning which maximizes the sum of the weighted averages. Operations Research, 43(3), 500–508. [Google Scholar]
- Gandhi, M. , Yokoe, D. S. , & Havlir, D. V. (2020). Asymptomatic transmission, the achilles' heel of current strategies to control COVID‐19. New England Journal of Medicine, 382, 2158–2160. 10.1056/NEJMe2009758 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gollier, C. , & Gossner, O. (2020). Group testing against COVID‐19. Covid Economics, 1, 32–42. [Google Scholar]
- Gupta, D. , & Malina, R. (1999). Group testing in presence of classification error. Statistics in Medicine, 18, 1049–1068. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hwang, F. K. (1975). A generalized binomial group testing problem. Journal of the American Statistical Association, 70(352), 923–926. [Google Scholar]
- Hwang, F. K. , Onn, S. , & Rothblum, U. G. (1999). A polynomial time algorithm for shaped partition problems. SIAM Journal on Optimization, 10(1), 70–81. [Google Scholar]
- Hwang, F. K. , Onn, S. , & Rothblum, U. G. (2000). Linear‐shaped partition problems. Operations Research Letters, 26(4), 159–163. [Google Scholar]
- Joseph, A. (2020). Safer reopening will require millions more COVID‐19 tests per day. One solution: ‘Pool testing’ . https://www.statnews.com/2020/06/26/pool‐testing‐covid‐19/
- Kim, H. Y. , Hudgens, M. G. , Dreyfuss, J. M. , Westreich, D. J. , & Pilcher, C. D. (2007). Comparison of group testing algorithms for case identification in the presence of test error. Biometrics, 63(4), 1152–1163. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kim, S. Y. , Lee, J. , Sung, H. , Lee, H. , Han, M. G. , Yoo, C. K. , Lee, S. W. , & Hong, K. H. (2020). Pooling upper respiratory specimens for rapid mass screening of COVID‐19 by real‐time RT‐PCR. Emerging Infectious Diseases, 26(10), 2469–2472. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Korea Centers for Disease Control and Prevention . (2020). Coronavirus disease‐19: Summary of 2,370 contact investigations of the first 30 cases in the Republic of Korea. Osong Public Health and Research Perspectives, 11(2), 81–84. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lohse, S. , Pfuhl, T. , Berkó‐Göttel, B. , Rissland, J. , Geißler, T. , Gärtner, B. , Becker, S. L. , Schneitler, S. , & Smola, S. (2020). Pooling of samples for testing for SARS‐CoV‐2 in asymptomatic people. The Lancet Infectious Diseases, 20, 1231–1232. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lu, J. , Peng, J. , Xiong, Q. , Liu, Z. , Lin, H. , Tan, X. , Kang, M. , Yuan, R. , Zeng, L. , Zhou, P. , Liang, C. , Yi, L. , du Plessis, L. , Song, T. , Ma, W. , Sun, J. , Pybus, O. G. , & Ke, C. (2020). Clinical, immunological and virological characterization of COVID‐19 patients that test re‐positive for SARS‐CoV‐2 by RT‐PCR. eBioMedicine, 59, 102960. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mallapaty, S. (2020). The mathematical strategy that could transform coronavirus testing. Nature, 583(7817), 504–505. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McMahan, C. S. , Tebbs, J. M. , & Bilder, C. R. (2012). Informative Dorfman screening. Biometrics, 68(1), 287–296. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- News Medical . (2020). Pooled testing for COVID‐19 could significantly increase testing capacity . https://www.newis‐medical.net/newis/20201016/Pooled‐testing‐for‐Covid‐19‐could‐significantly‐increase‐testing‐capacity.aspx
- Nguyen, N. T. , Aprahamian, H. , Bish, E. K. , & Bish, D. R. (2019). A methodology for deriving the sensitivity of pooled testing, based on viral load progression and pooling dilution. Journal of Translational Medicine, 17(1), 252. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Onn, S. , & Schulman, L. J. (2001). The vector partition problem for convex objective functions. Mathematics of Operations Research, 26(3), 583–590. [Google Scholar]
- Park, A. (2020). How pooled testing for coronavirus could help test more people in less time . https://time.com/5867102/pooled‐testing‐coronavirus/
- Pilcher, C. D. , Westreich, D. , & Hudgens, M. G. (2020). Group testing for SARS‐CoV‐2 to enable rapid scale‐up of testing and real‐time surveillance of incidence. The Journal of Infectious Diseases, 222, 903–909. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rothe, C. , Schunk, M. , Sothmann, P. , Bretzel, G. , Froeschl, G. , Wallrauch, C. , Zimmer, T. , Thiel, V. , Janke, C. , Guggemos, W. , Seilmaier, M. , Drosten, C. , Vollmar, P. , Zwirglmaier, K. , Zange, S. , Wölfel, R. , & Hoelscher, M. (2020). Transmission of 2019‐nCoV infection from an asymptomatic contact in Germany. New England Journal of Medicine, 382(10), 970–971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Surkova, E. , Nikolayevskyy, V. , & Drobniewski, F. (2020). False‐positive COVID‐19 results: Hidden problems and costs. The Lancet Respiratory Medicine, 8, 1167–1168. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wacharapluesadee, S. , Kaewpom, T. , Ampoot, W. , Ghai, S. , Khamhang, W. , Worachotsueptrakun, K. , Wanthong, P. , Nopvichai, C. , Supharatpariyakorn, T. , Putcharoen, O. , Paitoonpong, L. , Suwanpimolkul, G. , Jantarabenjakul, W. , Hemachudha, P. , Krichphiphat, A. , Buathong, R. , Plipat, T. , & Hemachudha, T. (2020). Evaluating the efficiency of specimen pooling for PCR‐based detection of COVID‐19. Journal of Medical Virology, 92, 2193–2199. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Y. , Tian, H. , Zhang, L. , Zhang, M. , Guo, D. , Wu, W. , Zhang, X. , Kan, G. L. , Jia, L. , Huo, D. , Liu, B. , Wang, X. , Sun, Y. , Wang, Q. , Yang, P. , & MacIntyre, C. R. (2020). Reduction of secondary transmission of SARS‐CoV‐2 in households by face mask use, disinfection and social distancing: A cohort study in Beijing, China. BMJ Global Health, 5(5), e002794. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Watson, J. , Whiting, P. F. , & Brush, J. E. (2020). Interpreting a COVID‐19 test result. BMJ, 369, m1808. 10.1136/bmj.m1808 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wiesbauer, F. (2020). How is RT‐PCR used to test for COVID‐19?. MedMastery. https://www.medmastery.com/guide/covid‐19‐clinical‐guide/how‐real‐time‐reverse‐transcription‐polymerase‐chain‐reaction‐rt‐pcr [Google Scholar]
- World Health Organization . (2020). WHO Director‐General's opening remarks at the media briefing on COVID‐19 2020. https://www.who.int/dg/speeches/detail/who‐director‐general‐s‐opening‐remarks‐at‐the‐media‐briefing‐on‐covid‐19‐16‐march‐2020
- Yelin, I. , Aharony, N. , Shaer Tamar, E. , Argoetti, A. , Messer, E. , Berenbaum, D. , Shafran, E. , Ku‐zli, A. , Gandali, N. , Shkedi, O. , Hashimshony, T. , Mandel‐Gutfreund, Y. , Halberthal, M. , Geffen, Y. , Szwarcwort‐Cohen, M. , & Kishony, R. (2020). Evaluation of COVID‐19 RT‐qPCR test in multi‐sample pools. Clinical Infectious Diseases, 71, 2073–2078. 10.1093/cid/ciaa531 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zenios, S. A. , & Wein, L. M. (1998). Pooled testing for HIV prevalence estimation: Exploiting the dilution effect. Statistics in Medicine, 17(13), 1447–1467. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, J. , Tian, S. , Lou, J. , & Chen, Y. (2020). Familial cluster of COVID‐19 infection from an asymptomatic. Critical Care, 24(1), 1–3. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Data Availability Statement
The data that support the findings of this study were derived from resources available in the public domain; and all data sources are provided in Section 5 and the References Section of the paper.


