FIGURE 2.
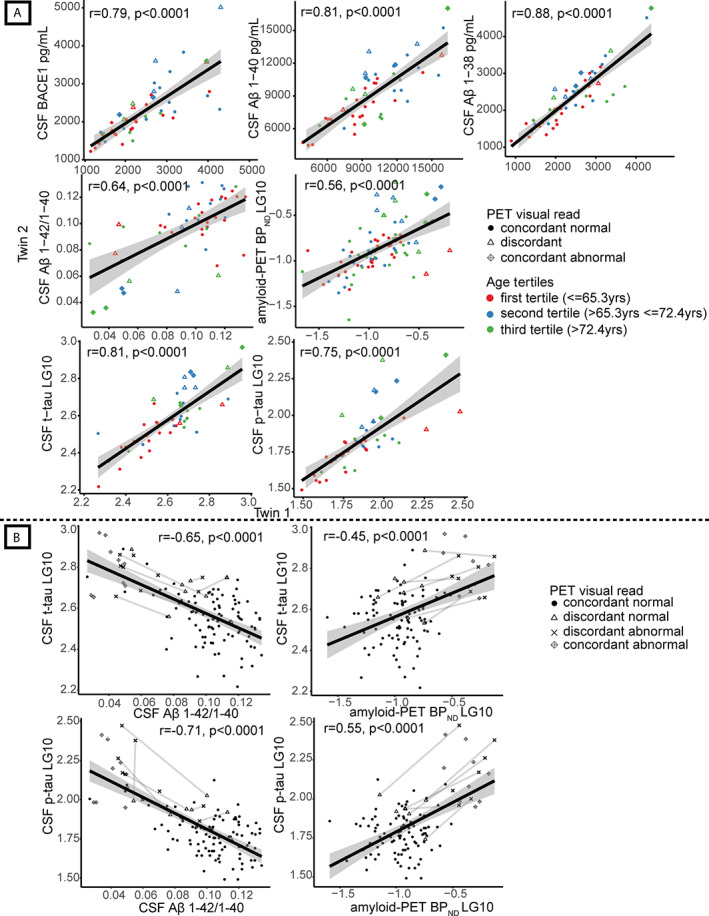
Monozygotic twin‐pair correlations and correlations in amyloid‐beta (Aβ) and tau levels, with discordant pairs connected. (A) Pearson correlation values for association of amyloid markers between one twin and their cotwin (Model 1); all p < 0.0001. Absolute values are shown for cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) beta‐secretase 1 (BACE1), Aβ1–40, Aβ1–38, Aβ1–42/1–40 ratio, and log‐transformed data (LG10) for global cortical positron emission tomography (PET) binding (nondisplaceable binding potential [BPND]) and CSF total‐tau (t‐tau) and 181‐phosphorylated‐tau (p‐tau). Each dot represents one twin‐pair; twin‐pairs who are concordant normal on amyloid PET visual read are shown as dots, and twin‐pairs who are concordant abnormal on amyloid PET visual read are shown as diamonds with a cross inside. Discordant pairs on amyloid PET visual read are shown as open triangles. Age‐groups based on tertiles (60–65.3, 65.3–72.4, >72.4 years) are represented in colors. From left to right: CSF BACE1, CSF Aβ1–40, CSF Aβ1–38, CSF Aβ1–42/1–40 ratio, global cortical PET binding (BPND), CSF t‐tau, CSF p‐tau. (B) Correlations of CSF Aβ1–42/1–40 ratio and CSF t‐tau; global cortical amyloid PET binding (BPND) and CSF t‐tau; CSF Aβ1–42/1–40 ratio and CSF p‐tau; and global cortical amyloid PET binding (BPND) and CSF p‐tau for twins who both have a normal amyloid PET visual read (concordant normal, shown as dots), twins from a discordant pair with a normal amyloid PET visual read (discordant normal, shown as open triangles), twins from a discordant pair with abnormal amyloid PET visual read (discordant abnormal, shown as crosses), and twin‐pairs who both have an abnormal amyloid PET visual read (concordant abnormal, shown as diamonds with a cross inside). Discordant twin‐pairs are connected with lines. LG10 = log‐transformed data.
