Figure 2.
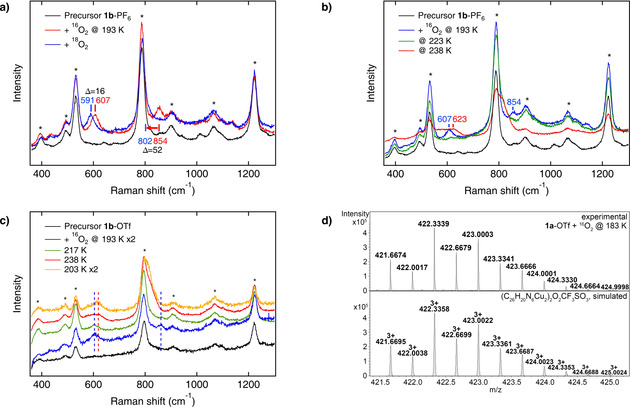
Mechanistic investigations: Breaking the O−O bond. a) Resonance Raman spectra of 1 b‐PF6 before (black) and after the reaction with 16O2 (red) and 18O2 (blue) at 193 K. b) Resonance Raman spectra of 1 b‐PF6 before (black) and upon reaction with dioxygen at three different temperatures (blue: 193 K; green: 223 K; red: 238 K). c) O−O bond homolysis of the Cu4O2 intermediate is irreversible; i.e., once the Cu2O complex of 1 b‐OTf is formed (red), the spectrum of the mono‐μ‐oxo species is retained after re‐cooling (orange). The spectra at 193 K and 203 K are rescaled by factor 2. d) Characteristic cutout of the UHR‐ESI mass spectrum obtained upon reaction of 1 a‐OTf with 16O2 at 183 K, confirming the mixed‐valent μ4‐peroxo complex. The corresponding species is also detected in the experiment with 18O2 (see Figure S36). General remarks: Raman: The asterisks mark solvent signals of acetone. The laser excitation wavelength was 393 nm.
