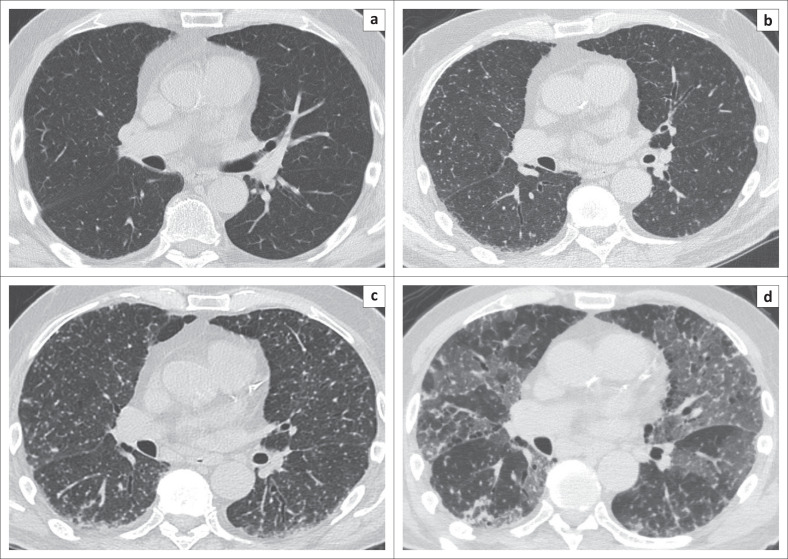
FIGURE 1.
A normal CT of the chest performed before the patient’s access to the Emergency Department (a). A CT scan of the same patient performed 10 days after the last Bacillus Calmette-Guérin instillation, showing 1 mm – 2 mm diameter nodules disseminated throughout the lung and distributed randomly with respect to the lobular structures in a miliary pattern (b). After two weeks of antibiotic therapy, CT imaging revealed a numerical and dimensional increase in the multiple micronodules (c). Despite the administration of anti-tubercular therapy, the patient’s clinical condition deteriorated again, requiring a new CT scan that revealed the presence of bilateral ground-glass opacities localised mainly in the middle and lower parts of the lungs, partially superimposed on the previously seen multiple lung micronodules, compatible with coronavirus disease 2019 superinfection (d).