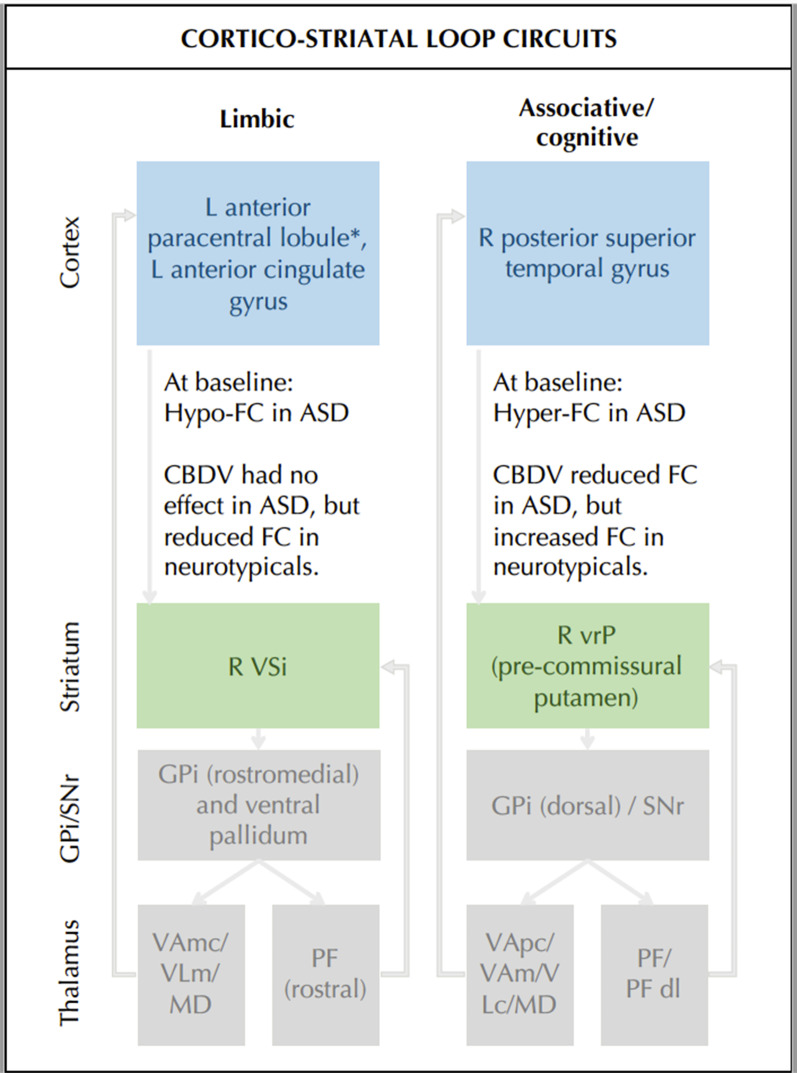
Fig. 4.
Reported findings in the context of cortico-striatal loop circuits. Baseline differences and group (ASD > neurotypicals) by drug (CBCV > PLC) interaction effects on cortico-striatal loop circuits, including the limbic and associative/cognitive loop, each of which are theorized to include different GPi/SNR and thalamic regions. Grey arrows indicate functional connections. ASD autism spectrum disorder, CBDV cannabidivarin, FC functional connectivity, GPi globus pallidus pars interna, L left, MD mediodorsal nucleus, PF parafascicular nucleus of the thalamus (dl: dorsolateral extension), R right, SNr substantia nigra pars reticulate, VA ventral anterior nucleus of the thalamus (mc: magnocellular part; pc: parvocellular part), VL ventrolateral nucleus of the thalamus (c: caudal part; m: medial part), vrP ventral-rostral putamen, VSi inferior ventral striatum. *The anterior paracentral lobule is associated with sensori-motor processing and may represent ectopic FC within the ‘limbic loop’ here