FIGURE 1.
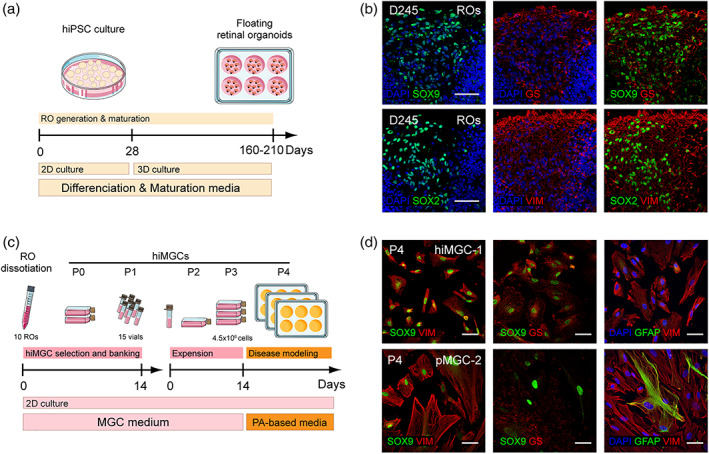
Generation and characterization of hiMGCs. (a) Schematic representation of RO generation and maturation. (b) Representative micrographs of the immunohistochemical detection of the following MGC makers: GS, SOX9 SOX2, and VIM in cryostated ROs at D245 (hiPSC clone AHF1pi2) showing the presence of MGCs in ROs. (c) Schematic representation of hiMGC selection, banking, and amplification. hiMGCs at P4 were used for palmitate‐based assays. (d) Representative micrographs of the immunohistochemical detection of the following MGC markers: SOX9 and VIM (left), SOX9 and GS (middle), and GFAP and VIM (right) P4 hiMGCs (top panels) and pMGCs (bottom panels) showing that the immunohistochemical labeling of MGC markers was similar between hiMGCs at P4 and pMGCs. Nuclei were stained with DAPI. GS, glutamine synthetase; hiMGCs, human iPSC‐derived MGCs; hiPSC, human induced‐pluripotent stem cell; MGC, Muller glial cell; pMGCs, primary MGCs; P, passage; PA, palmitate; RO, retinal organoid; VIM, vimentin. Scale bar = 50 μm [Color figure can be viewed at wileyonlinelibrary.com]
