Figure 4.
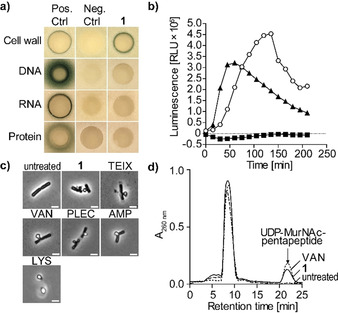
1 targets bacterial cell wall biosynthesis. a) B. subtilis bioreporter strains with selected promotor‐lacZ gene fusions were used to identify interference with major biosynthesis pathways including cell wall (PypuA), DNA (PyorB), RNA (PyvgS), and protein (Pyhel). A blue halo at the edge of the inhibition zone demonstrates induction of a specific stress response by β‐galactosidase expression. Antibiotics vancomycin (VAN), ciprofloxacin, rifampicin, and clindamycin were used as positive controls. b) Treatment with 1 (1×MIC, open circles) strongly induced Plial as observed by expression of the lux operon from Photorhabdus luminescens in B. subtilis PliaI‐lux. VAN (triangles) and clindamycin (CLI, squares) were used as control antibiotics. c) Phase‐contrast microscopy of B. subtilis confirmed impairment of cell wall integrity as severe cell‐shape deformations and characteristic blebbing were observed following 1 treatment. Cell wall active antibiotics teixobactin (TEIX), VAN, plectasin (PLEC), ampicillin (AMP), and lysozyme (LYS) were used as controls. Scale bar=2 μm. d) Intracellular accumulation of the cell wall precursor UDP‐MurNAc‐pentapeptide after treatment of S. aureus with 1 (5×MIC). Untreated and VAN‐treated (5×MIC) cells were used as controls. Experiments are representative of 3 independent experiments each.
