Scheme 1.
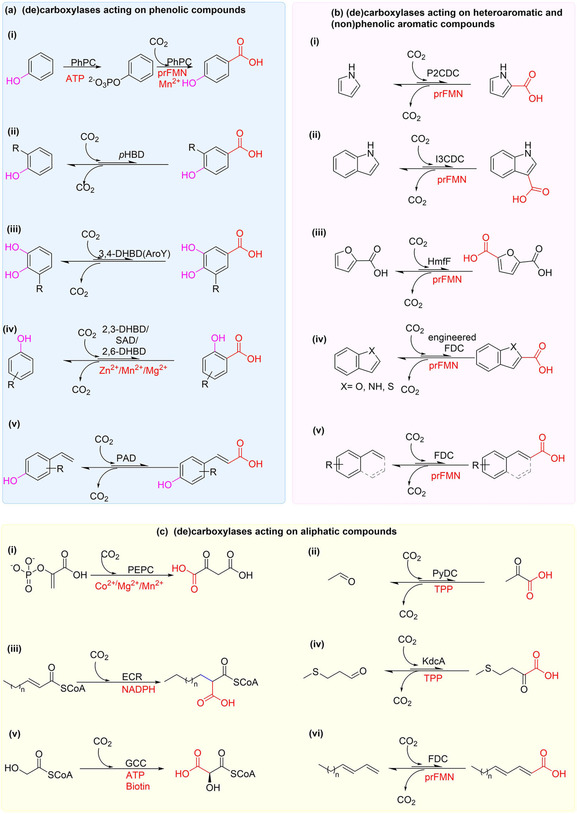
A selection of synthetically promising (de)carboxylases acting on distinct but diverse substrate groups and showing site of carboxylation: (a) acting on phenolic compounds; (b) acting on heteroaromatic and nonphenolic aromatic compounds; (c) acting on aliphatic compounds. Organic/divalent metal ions cofactors presented in red. Organic cofactors: ATP=adenosine triphosphate; prFMN=prenylated flavin; TPP=thiamine pyrophosphate; NADPH=nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide phosphate (reduced). Enzymes: PhPC=phenylphosphate carboxylase; pHBD=para‐hydroxybenzoic acid decarboxylase; DBHD=dihydroxybenzoate decarboxylase; PAD=phenolic acid decarboxylase; P2CDC=pyrrole‐2‐carboxylate decarboxylase; I3CDC=indole‐3‐carboxylate decarboxylase; HmfF=2,5‐furan dicarboxylic acid decarboxylase; FDC=(fungal) ferulic acid decarboxylases; PEPC=phosphoenolpyruvate carboxylase; pyruvate decarboxylases; KdcA=branched‐chain α‐ketoacid dehydrogenase; ECR=carboxylating enoyl‐thioester reductases; GCC=glycolyl‐CoA carboxylase.
