FIGURE 5.
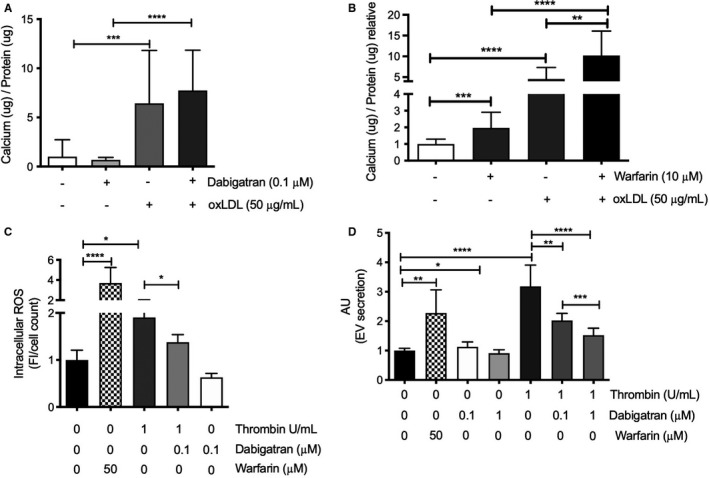
Interaction of warfarin and thrombin in vascular smooth muscle cells. Primary human vascular smooth muscle cells (VSMCs) were cultured in the presence of (A) warfarin, oxidized LDL (oxLDL), thrombin, dabigatran, or vehicle. oxLDL significantly increased calcification on VSMCs. Moreover, dabigatran did not influence oxLDL‐mediated calcification. (B) Both warfarin and oxLDL significantly increased calcification compared to control. Co‐stimulation of warfarin with oxLDL resulted in significantly more calcification compared with warfarin or oxLDL alone, indicating an additive effect. (C) Both warfarin and thrombin significantly increased intracellular ROS compared with control. Thrombin‐induced intracellular ROS was significantly attenuated when thrombin was combined with dabigatran, whereas dabigatran alone had no significant effect on ROS. (D) Extracellular vesicles, a hallmark of vascular calcification, were significantly increased after both warfarin and thrombin stimulation. In contrast, high dosage of dabigatran showed a significant reduction in extracellular vesicles. Elevated extracellular vesicles after thrombin stimulation were significantly and dose dependently reduced with dabigatran. ROS, reactive oxygen species
