Fig. 2.
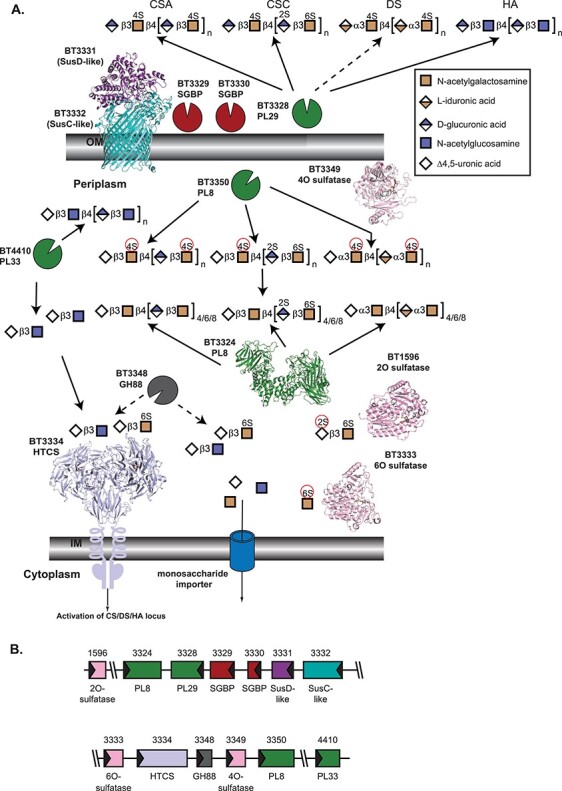
Architecture and activities within B. theta PULCS/DS/HA, as described by Ndeh et al. 2020. (A) Cartoon representation of extracellular and periplasmic components of PULCS/DS/HA. Carbohydrate at the cell surface undergoes some processing by BT3328-PL29, and the oligosaccharides are imported by the SusCD-like complex with help from two SGBP proteins, BT3329 and BT3330. Once imported, a suite of PL enzymes, a GH88, and three sulfatases depolymerize and desulfate all four carbohydrates shown. As in Figure 1A, the SusC-like protein is not the CS/DS/HA SusC-like protein but is the recently determined homolog BT2264 (Glenwright et al. 2017) (PDB 4FQ8). The SusD-like protein is that from PULHEP (PDB 3IHV). Unliganded BT3324-PL8 is PDB 2Q1F (Shaya et al. 2008). The 2O-sulfatase BT1596-S1_9 is complexed with Δ4,5UA2S-GlcNS6S (PDB 5G2T (Cartmell et al. 2017)). The 4O-sulfatase BT3349-S1_27 (PDB 6S21) is complexed with Δ4,5UA-GalNAc4S-GlcA, colored in gray (Ndeh et al. 2020). The 6O-sulfatase BT3333-S1_15 (PDB 6S20) is complexed with GalNAc6S, colored in gray (Ndeh et al. 2020). Instead of the cognate HTCS regulator, BT3334, the dimeric periplasmic domain of the PULHEP BT4663-HTCS is shown complexed with Δ4,5UA-GlcNAc6S (PDB 4A2M (Lowe et al. 2012)). (B) Architecture of the genetic loci. The gene representations are to scale and colored the same as their protein products.
