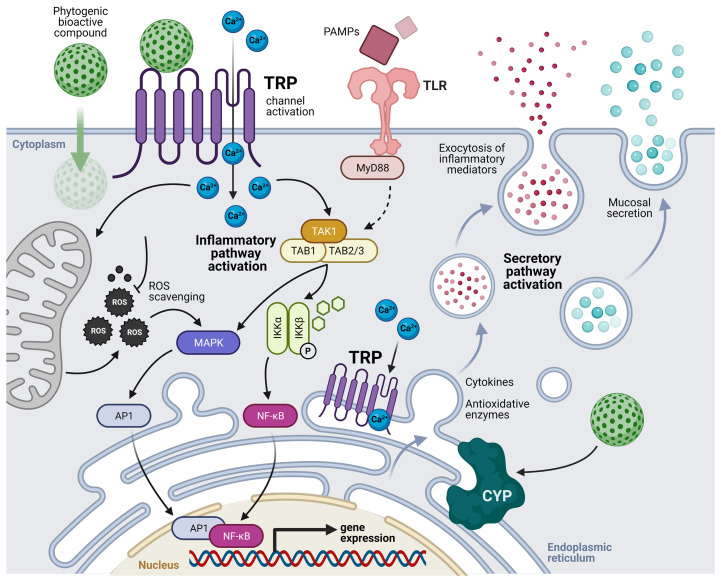
Figure 1.
Suggested mechanisms of cell activation by the transient receptor potential (TRP) cation channels mediated by phytogenics’ bioactive compounds in mucosal-associated lymphoid tissues (MALTs). Bioactive compounds activate TRP channels leading to intracellular Ca2+ increase and non-canonical activation of the TAK complex. In parallel, stimulation by pathogen-associated molecular patterns (PAMPs) may facilitate the activation of TLR and TRP signaling pathways. Modified from Galindo-Villegas, et al. (124). TLR, toll-like receptors; MyD88, myeloid differentiation primary response 88; TAK, transforming growth factor beta (TGFβ) activated kinase; TAB, TGFβ activated kinase binding protein; ROS, reactive oxygen species; NF-kB, nuclear factor kappa-B; IKK, inhibitor of NF-kB kinase; MAPK, mitogen-activated protein kinase; AP1, activator protein 1; CYP, cytochromes P450; P, phosphorylation.