Figure 1.
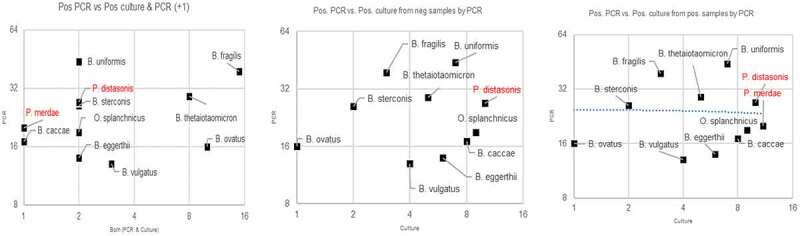
Correlation of PCR identification vs culture isolation from samples that were detected or undetected via qRT-PCR. Eleven Bacteroides and Parabacteroides species detected via qRT-PCR in 400 human surgical wound infection samples or closed abscesses. Target bacteria were detected from 31 samples (8%) via culture vs. 132 samples (33%) via qRT-PCR (p-value < 0.001). For each species, qRT-PCR detected higher counts than culture; this may reflect the detection of DNA of dead organisms by qRT-PCR. Plot created for this manuscript to illustrate the correlation between qRT-PCR and anerobic culture results for Bacteroides species isolated from wound samples using 132 isolates.33 a) y-axis corresponds to number of isolates detected by qRT-PCR; x-axis corresponds to number of isolates detected by both qRT-PCR and culture. b) y-axis corresponds to number of isolates detected by qRT-PCR; x-axis corresponds to number of isolates detected by culture. c) y-axis corresponds to number of isolates detected by qRT-PCR. Adapted from using data from Tong et al.33 with permission. Available from Anaerobe and used with permission from Elsevier
