FIGURE 6.
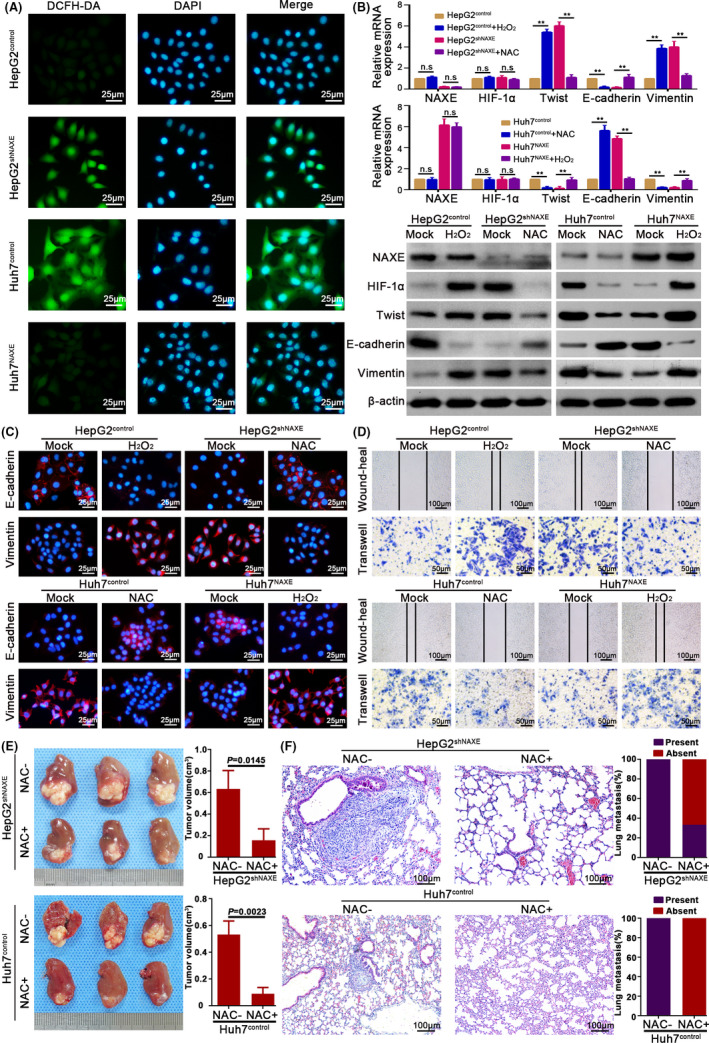
NAXE inhibits HIF‐1α signaling by eliminating ROS in HCC. A, Representative images show ROS level in indicated cells. DCFH‐DA is used as a probe to detect ROS level. The nuclei are stained by DAPI. B, mRNA and protein expression of indicated molecules in HepG2shNAXE, Huh7NAXE, and their control cells with either presence or absence of NAC (10 mmol/L) or H2O2 (5 μmol/L) treatment. **P < .01. C, IF analysis shows expression of E‐cadherin and vimentin in NAXE‐interfered cells and their control cells after treated with H2O2 (5 μmol/L) or NAC (10 mmol/L) or mock treatment. D, Wound‐heal and transwell assays respectively show the influence of H2O2 (5 μmol/L) or NAC (10 mmol/L) on migration and invasion capacity of HepG2shNAXE, Huh7NAXE, and their control cells. The data are quantified in Figure S8C,D. E, Mice bearing orthotopic tumors derived from HepG2shNAXE and Huh7control cells are treated with NAC by adding into drinking water (supplement with 40 mmol/L NAC for the entire duration of experiment), which could reverse HCC growth and metastasis caused by NAXE downregulation. F, Representative mice lung tissue sections from HepG2shNAXE and Huh7control cells treated with or without NAC. The incidence rate of lung metastasis is shown in right bar graphs
