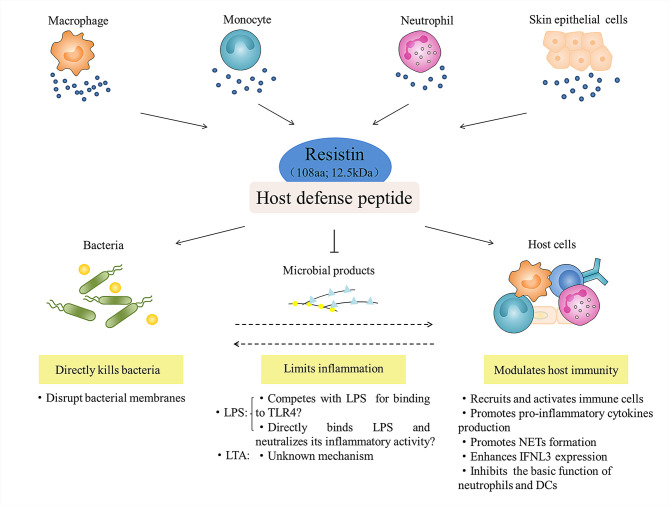
Figure 5.
Role of resistin in host defense. Leukocytes (i.e., macrophage, monocyte, and neutrophil) and skin epithelial cells-derived resistin act as host defense peptide, and participate in the innate anti-infection immunity of the host at least three ways: they directly kill bacteria; they regulate and balance the inflammatory response to microbial products (LPS and LTA); and they activate and amplify the host immune response to indirectly resist microbial infection.