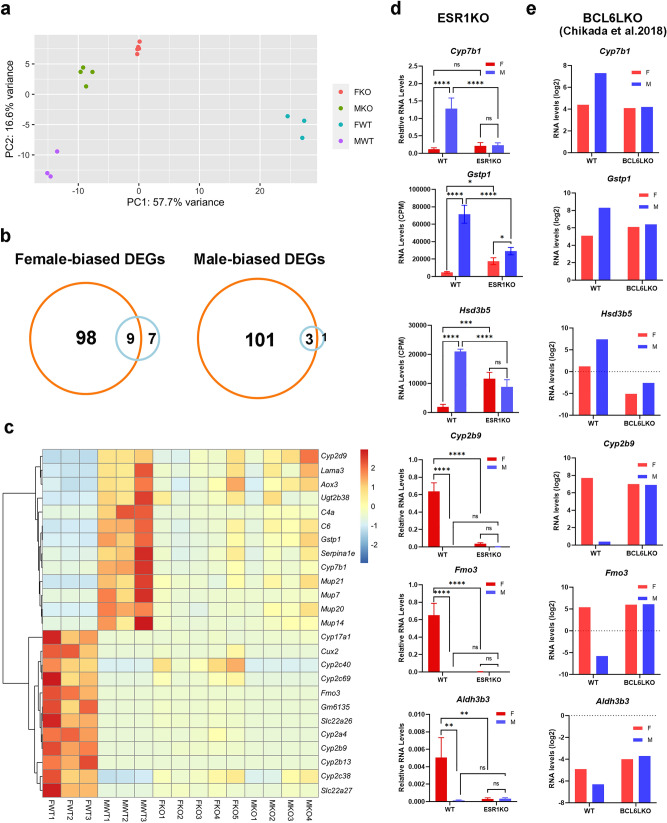
Figure 6.
Ablation of ESR1 is associated with loss of sex bias in gene expression. (a) Principal component analysis (PCA) for RNA-seq data from ESR1KO and control mouse livers shows that samples cluster by genotype and sex, when comparing the first two principal components. (b) Overlapping DEGs between WT (orange) compared to the ESR1KO (blue): female-biased DEGs (left panel) and male-biased DEGs (right panel) are shown separately. (c) Heatmap shows the top 22 significant sDEGs as well as Cyp2b9, Cyp2b13, and Fmo3 in WT and ESR1KO mice. (d) Relative expression levels of sDEGs in ESR1KO mice determined by RT-qPCR and normalized to Rpl19 (WT: 3 females and 3 males, ESR1KO: 4 females and 4 males) or retrieved from RNA-seq data (Gstp1, Hsd3b5). Error bars show standard deviation. Statistically significant differences between sexes are shown with asterisks *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001, ****P < 0.0001, ns: non-significant (two-way ANOVA followed by multiple testing with Sidak’s correction). (e) Expression levels of sDEGs in Bcl6-LKO mice (data from GSE89091 and GSE107435 displayed as log2 of normalized signal intensity).